PDF: 09005aef80a8e793/Source: 09005aef80a8e767 Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
dd5c16_32x72h.fm - Rev. F 2/07 EN
4 ©2004 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
128MB, 256MB: (x72, ECC, SR) 200-Pin DDR SODIMM
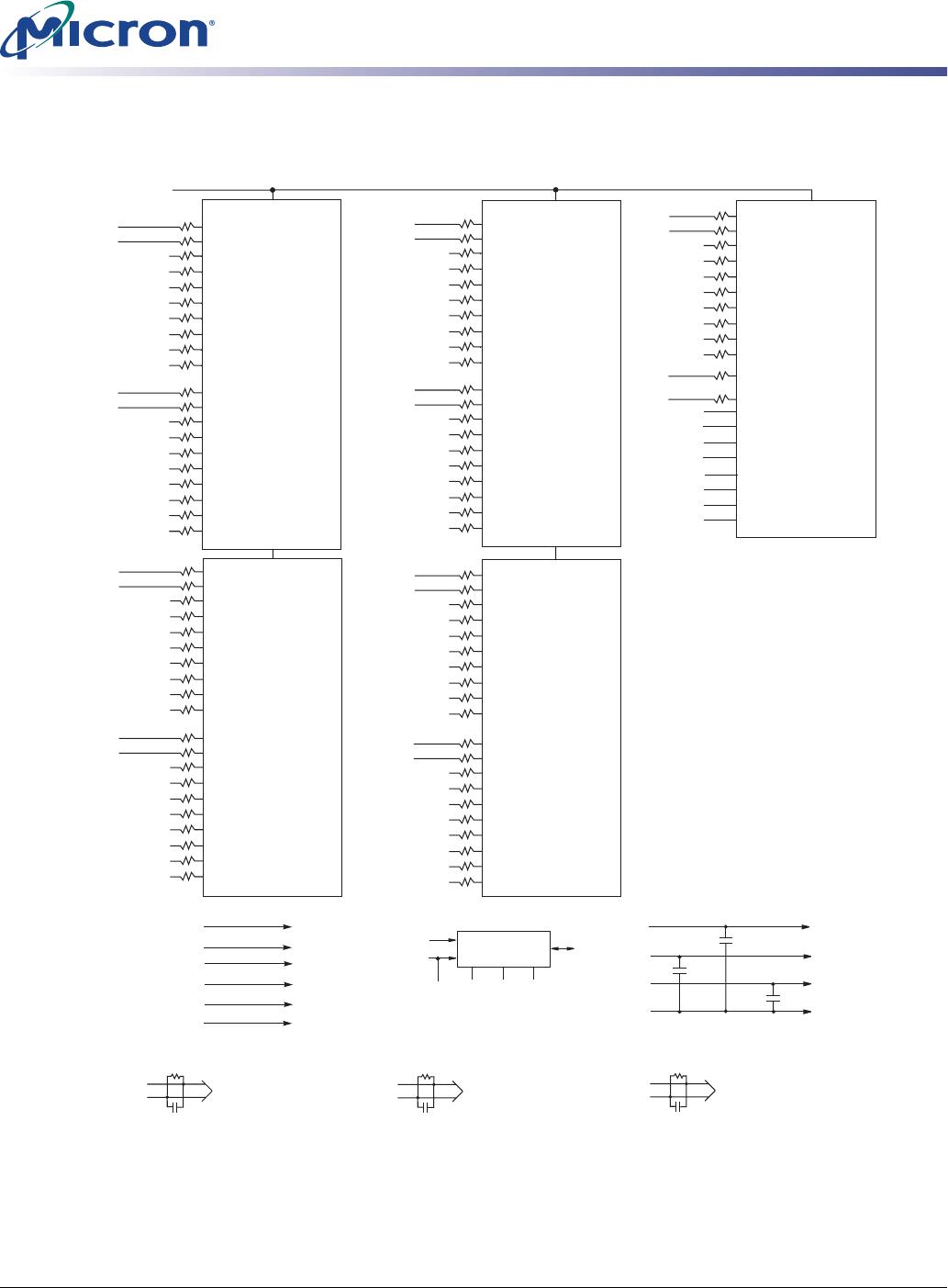
Pin Assignments and Descriptions
Table 6: Pin Descriptions
Symbol Type Description
WE#, CAS#,
RAS#
Input
Command inputs: RAS#, CAS#, and WE# (along with S#) define the command
being entered.
CK0, CK0#, CK1,
CK1#, CK2, CK2#
Input
Clocks: CK and CK# are differential clock inputs. All address and control input
signals are sampled on the crossing of the positive edge of CK and negative edge
of CK#. Output data (DQs and DQS) is referenced to the crossings of CK and CK#.
CKE0 Input
Clock enable: CKE HIGH activates and CKE LOW deactivates the internal clock,
input buffers and output drivers.
S0# Input
Chip select: S# enables (registered LOW) and disables (registered HIGH) the
command decoder. All commands are masked when S# is registered HIGH. S# is
considered part of the command code.
BA0, BA1 Input
Bank address: BA0 and BA1 define the device bank to which an ACTIVE, READ,
WRITE, or PRECHARGE command is being applied.
A0–A12 Input
Address inputs: Provide the row address for ACTIVE commands, and the column
address and auto precharge bit (A10) for READ/WRITE commands, to select one
location out of the memory array in the respective device bank. A10 sampled
during a PRECHARGE command determines whether the PRECHARGE applies to
one device bank (A10 LOW, device bank selected by BA0, BA1) or all device banks
(A10 HIGH). The address inputs also provide the op-code during a MODE
REGISTER SET command. BA0 and BA1 define which mode register (mode register
or extended mode register) is loaded during the LOAD MODE REGISTER
command.
DM0–DM8 Input
Data mask: DM is an input mask signal for write data. Input data is masked
when DM is sampled HIGH along with that input data during a WRITE access. DM
is sampled on both edges of DQS. Although DM pins are input-only, the DM
loading is designed to match that of DQ and DQS pins.
SDA Input/
Output
Serial presence-detect data: SDA is a bidirectional pin used to transfer
addresses and data into and out of the presence-detect portion of the module.
SCL Input
Serial clock for presence-detect: SCL is used to synchronize the presence-
detect data transfer to and from the module.
SA0–SA2 Input
Presence-detect address inputs: These pins are used to configure the
presence-detect device.
DQS0–DQS8 Input/
Output
Data strobe: Output with READ data, input with WRITE data. DQS is edge-
aligned with READ data, centered in WRITE data. Used to capture data.
CB0–CB7 Input/
Output
Check bits.
DQ0–DQ63 Input/
Output
Data input/output: Data bus.
V
REF Supply
SSTL_2 reference voltage.
V
DD Supply
Power supply: +2.5V ±0.2V. (-40B speed grade requires 2.6V ±0.1V)
V
SS Supply
Ground.
V
DDSPD Supply
Serial EEPROM positive power supply: +2.3V to +3.6V.
NC –
No connect: These pins should be left unconnected.