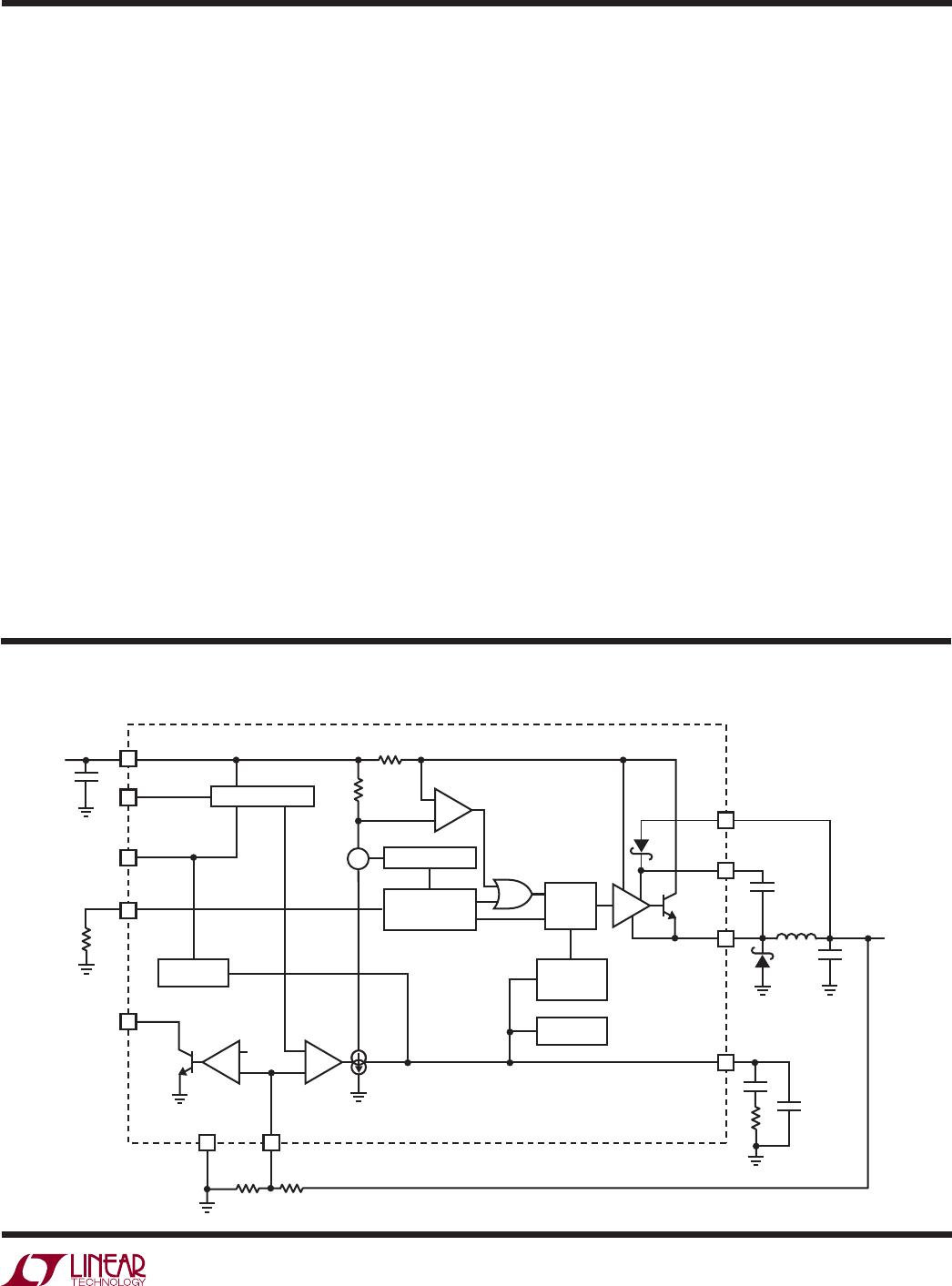
LT3481
9
3481fc
FB Resistor Network
The output voltage is programmed with a resistor divider
between the output and the FB pin. Choose the 1% resis-
tors according to:
RR
V
OUT
12
1 265
1=
⎛
⎝
⎜
⎞
⎠
⎟
.
–
Reference designators refer to the Block Diagram.
Setting the Switching Frequency
The LT3481 uses a constant frequency PWM architecture
that can be programmed to switch from 300kHz to 2.8MHz
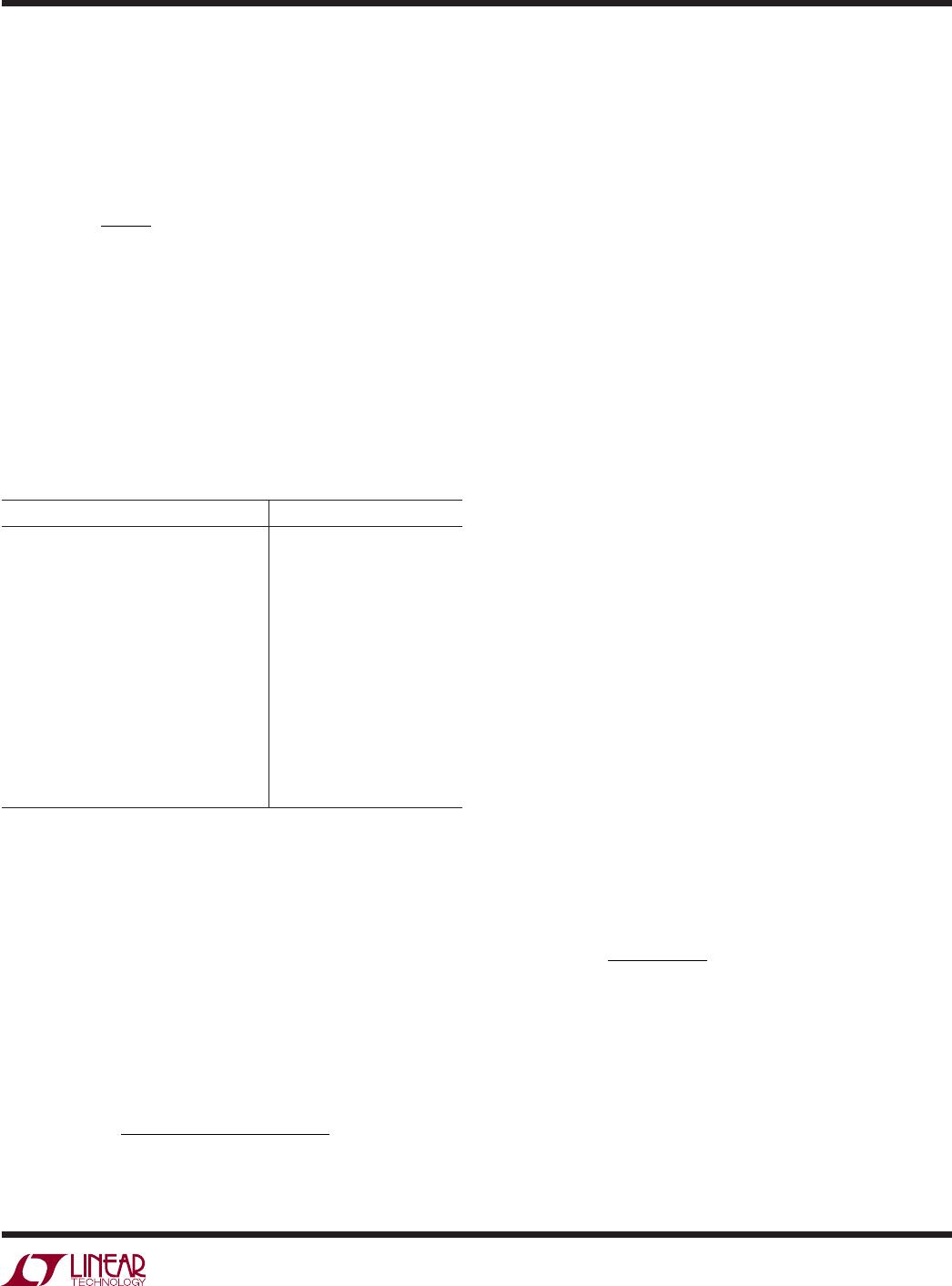
by using a resistor tied from the RT pin to ground. A table
showing the necessary R
T
value for a desired switching
frequency is in Figure 1.
SWITCHING FREQUENCY (MHz) R
T
VALUE (kΩ)
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.0
2.2
2.4
2.6
2.8
267
187
133
84.5
60.4
45.3
36.5
29.4
23.7
20.5
16.9
14.3
12.1
10.2
8.66
Operating Frequency Trade-Offs
Selection of the operating frequency is a trade-off between
effi ciency, component size, minimum dropout voltage, and
maximum input voltage. The advantage of high frequency
operation is that smaller inductor and capacitor values may
be used. The disadvantages are lower effi ciency, lower
maximum input voltage, and higher dropout voltage. The
highest acceptable switching frequency (f
SW(MAX)
) for a
given application can be calculated as follows:
f
VV
tVVV
SW MAX
D OUT
ON MIN
DINSW
()
()
=
+
+
()
–
where V
IN
is the typical input voltage, V
OUT
is the output
voltage, is the catch diode drop (~0.5V), V
SW
is the internal
switch drop (~0.5V at max load). This equation shows
that slower switching frequency is necessary to safely
accommodate high V
IN
/V
OUT
ratio. Also, as shown in
the next section, lower frequency allows a lower dropout
voltage. The reason input voltage range depends on the
switching frequency is because the LT3481 switch has
fi nite minimum on and off times. The switch can turn on
for a minimum of ~150ns and turn off for a minimum of
~150ns. This means that the minimum and maximum
duty cycles are:
DC f t
DC f t
MIN SW
ON MIN
MAX SW
OFF MIN
=
=
()
()
1–
where f
SW
is the switching frequency, the t
ON(MIN)
is the
minimum switch on-time (~150ns), and the t
OFF(MIN)
is
the minimum switch off-time (~150ns). These equations
show that duty cycle range increases when switching
frequency is decreased.
A good choice of switching frequency should allow ad-
equate input voltage range (see next section) and keep
the inductor and capacitor values small.
Input Voltage Range
The maximum input voltage for LT3481 applications
depends on switching frequency, the absolute maximum
ratings on V
IN
and BOOST pins, and on operating mode.
If the output is in start-up or short-circuit operating modes,
then V
IN
must be below 34V and below the result of the
following equation:
V
VV
ft
VV
IN MAX
OUT D
SW
ON MIN
DSW
()
()
=
+
+–
where V
IN(MAX)
is the maximum operating input voltage,
V
OUT
is the output voltage, V
D
is the catch diode drop
(~0.5V), V
SW
is the internal switch drop (~0.5V at max
load), f
SW
is the switching frequency (set by R
T
), and
t
ON(MIN)
is the minimum switch on-time (~150ns). Note that
a higher switching frequency will depress the maximum
operating input voltage. Conversely, a lower switching
Figure 1. Switching Frequency vs R
T
Value
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION