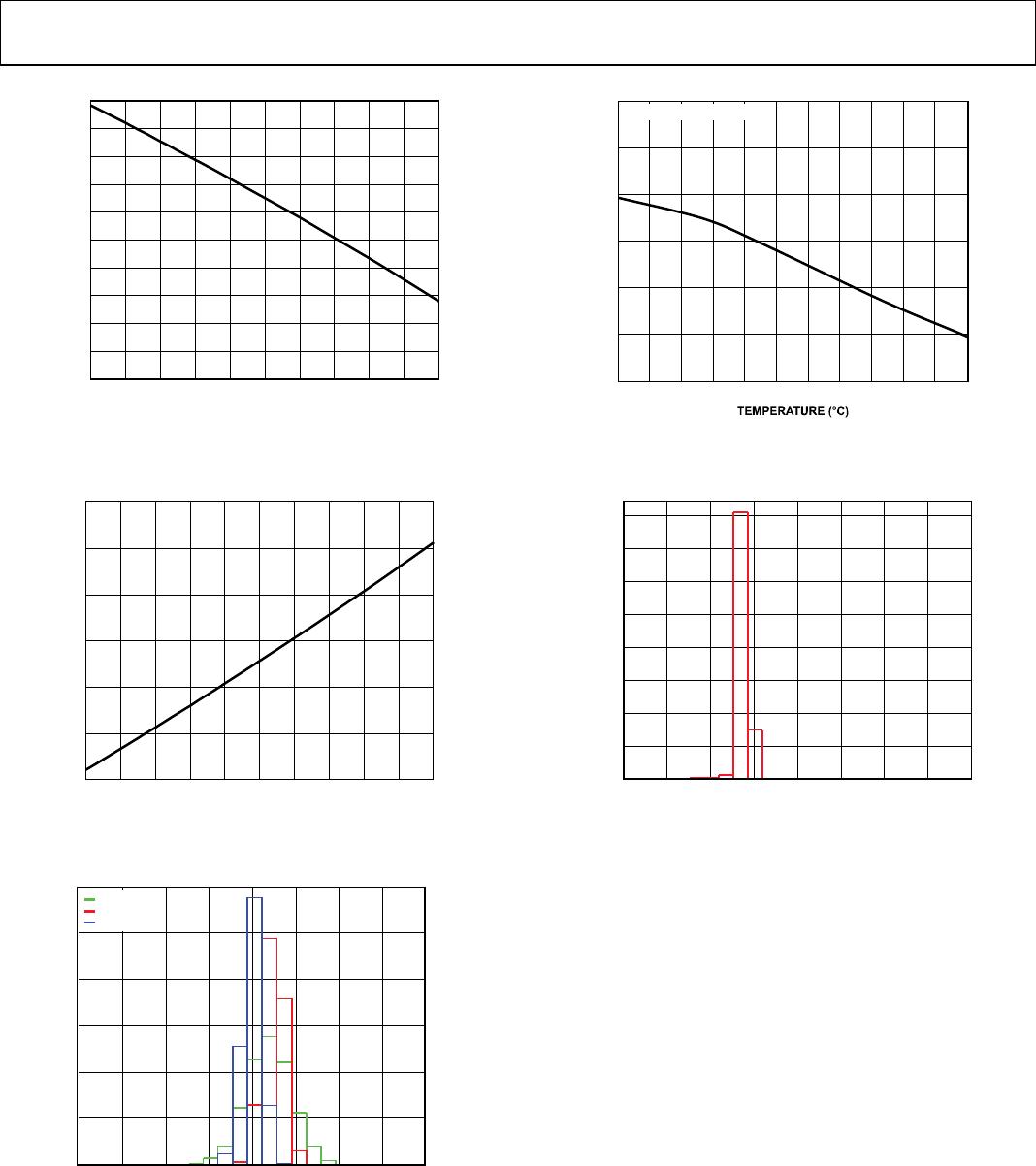
Data Sheet AD8417
OUTPUT OFFSET ADJUSTMENT
The output of the AD8417 can be adjusted for unidirectional or
bidirectional operation.
UNIDIRECTIONAL OPERATION
Unidirectional operation allows the AD8417 to measure currents
through a resistive shunt in one direction. The basic modes for
unidirectional operation are ground referenced output mode
and V
S
referenced output mode.
For unidirectional operation, the output can be set at the negative
rail (near ground) or at the positive rail (near V
S
) when the
differential input is 0 V. The output moves to the opposite rail
when a correct polarity differential input voltage is applied. The
required polarity of the differential input depends on the output
voltage setting. If the output is set at the positive rail, the input
polarity must be negative to decrease the output. If the output is
set at ground, the polarity must be positive to increase the output.
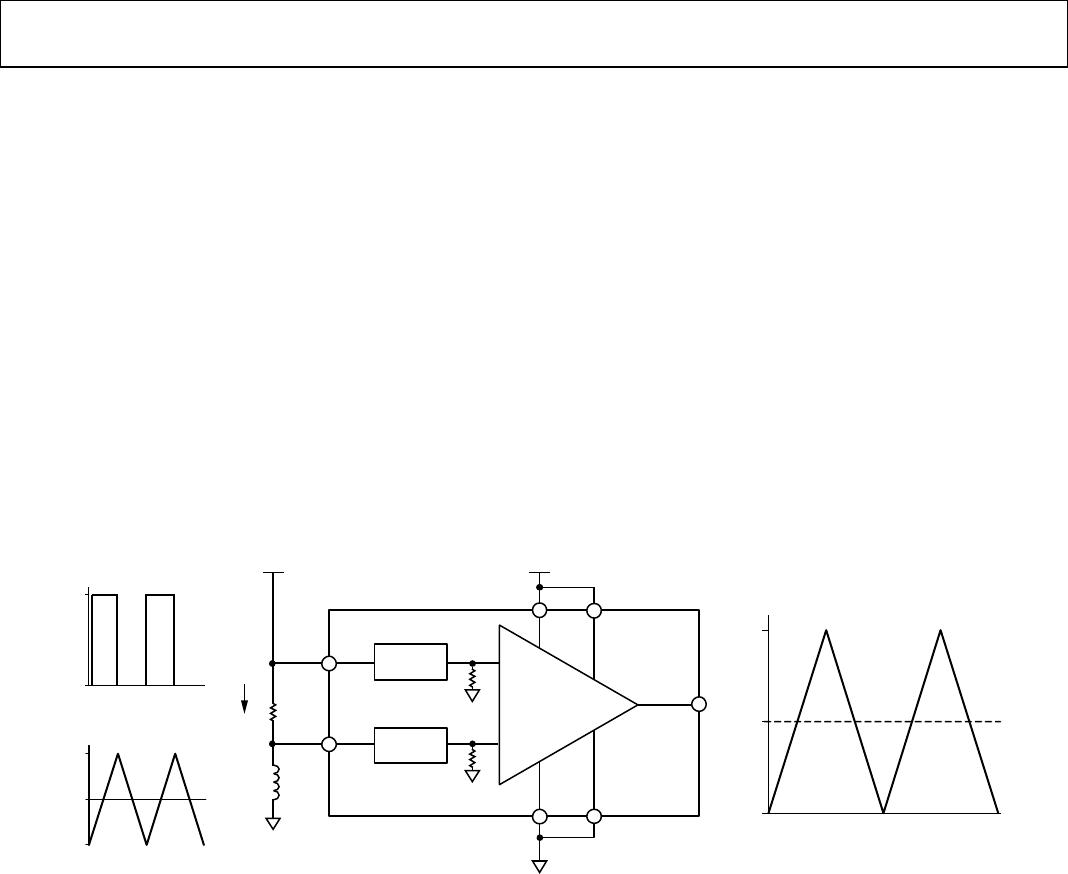
Ground Referenced Output Mode
When using the AD8417 in ground referenced output mode, both
referenced inputs are tied to ground, which causes the output to sit
at the negative rail when there are zero differential volts at the input
(see Figure 27).
–
+
R1
OUT
GND
V
S
V
REF
1
V
REF
2
AD8417
R2
R3
R4
–IN
+IN
11882-025
Figure 27. Ground Referenced Output
V
S
Referenced Output Mode
V
S
referenced output mode is set when both reference pins are tied
to the positive supply. It is typically used when the diagnostic
scheme requires detection of the amplifier and the wiring before
power is applied to the load (see Figure 28).
–
+
R1
OUT
GND
V
S
V
REF
1
V
REF
2
AD8417
R2
R3
R4
–IN
+IN
11882-026
Figure 28. V
S
Referenced Output
BIDIRECTIONAL OPERATION
Bidirectional operation allows the AD8417 to measure currents
through a resistive shunt in two directions.
In this case, the output is set anywhere within the output range.
Typically, it is set at half-scale for equal range in both directions.
In some cases, however, it is set at a voltage other than half scale
when the bidirectional current is nonsymmetrical.
Adjusting the output is accomplished by applying voltage(s) to
the referenced inputs. V
REF
1 and V
REF
2 are tied to internal
resistors that connect to an internal offset node. There is no
operational difference between the pins.
Rev. B | Page 11 of 16