As these threshold voltages are nominally set to V
THH
=
3V and V
THL
= 1V the equations can be simplified as
follows:
T
C
I
C
I
PWM
PWMC PWMD
=+
22
C
LCK
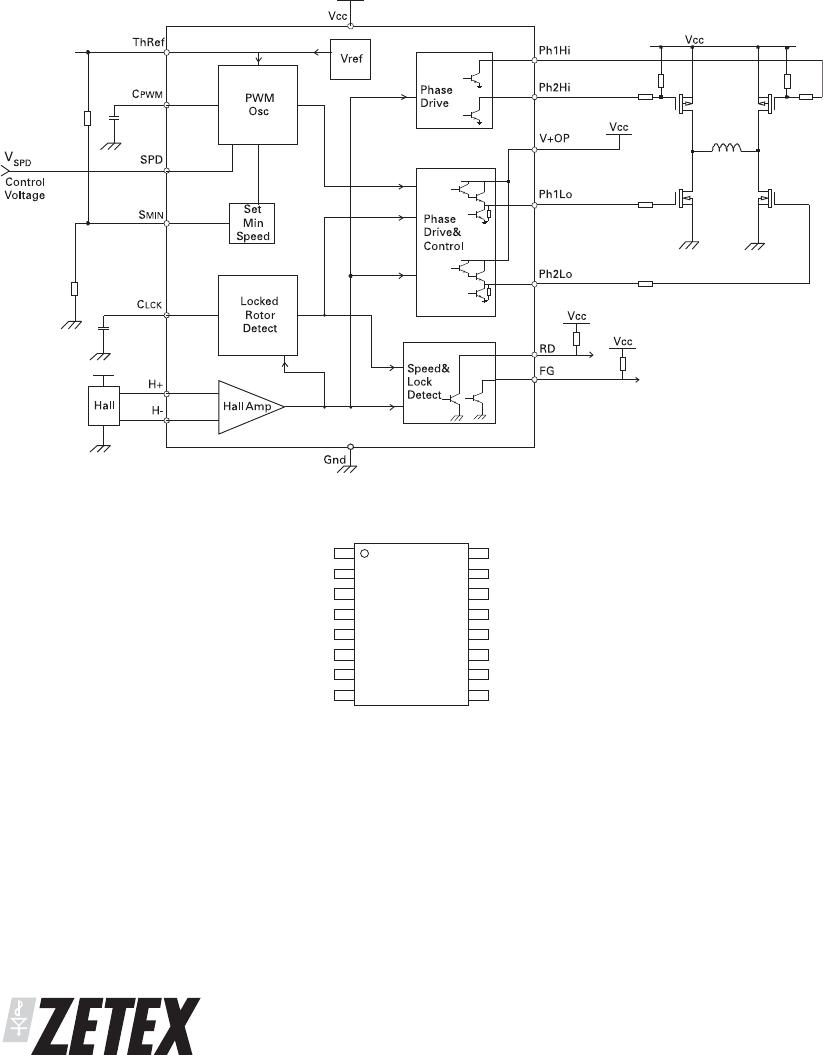
- Locked rotor timing capacitor
Should the fan stop rotating for any reason, i.e. an
obstruction in the fan blade or a seized bearing, then
the device will enter a Rotor Locked condition. In this
condition after a predetermined time (T
LOCK
) the RD pin
will go high and the Phase outputs will be disabled.
After a further delay (T
OFF
) the controller will re-enable
the Phase drive for a defined period (T
ON
) in an attempt
to re-start the fan. This cycle of (T
OFF
) and (T
ON
) will be
repeated indefinitely or until the fan re-starts.
GND - Ground
This is the device supply ground return pin and will
generally be the most negative supply pin to the fan.
RD - Locked Rotor error output
This pin is the Locked Rotor output as referred to in the
C
LCK
timing section above. It is high when the rotor is
stopped and low when it is running.
This is an open collector drive giving an active pull
down with the high level being provided by an external
pull up resistor.
FG - Frequency Generator (speed) output
This is the Frequency Generator output and is a
buffered signal from the Hall sensor.
This is an open collector drive giving an active pull
down with the high level being provided by an external
pull up resistor.
Ph1Lo & Ph2Lo - Low-side External
H-bridge Driver
This pair of outputs drive the Low side of the external
high power H-bridge devices which in turn drives the
single phase winding. These outputs provide both the
commutation and PWM waveforms. The outputs are of
the Darlington emitter follower type with an active
pull-down to help faster switch off when using bipolar
devices. When in the high state the outputs will provide
up to 80mA of drive into the base or gates of external
transistors as shown in the Typical Application circuit
following.
When in the low state the active Phase drive is capable
of sinking up to 16mA when driving low to aid turn off
times during PWM operation. When the Phase is
inactive the output is held low by an internal pull-down
resistor.
Ph1Hi & Ph2Hi - High-side External H-bridge
Driver
These are the High side outputs to the external
H-bridge and are open collector outputs capable of
sinking 100mA. This signal provides commutation only
to the H-bridge.
V+OP - Phase Outputs Supply Voltage
This pin is the supply to the Phase outputs and will be
connected differently dependant upon external
transistor type.
For bipolar devices this pin will be connected by a
resistor to the V
CC
pin. The resistor is used to control
the current into the transistor base so its value is
chosen accordingly.
For MOSFET devices the pin will connect directly to the
V
CC
pin.
ZXBM1004
ISSUE 6 - MAY 2007
6