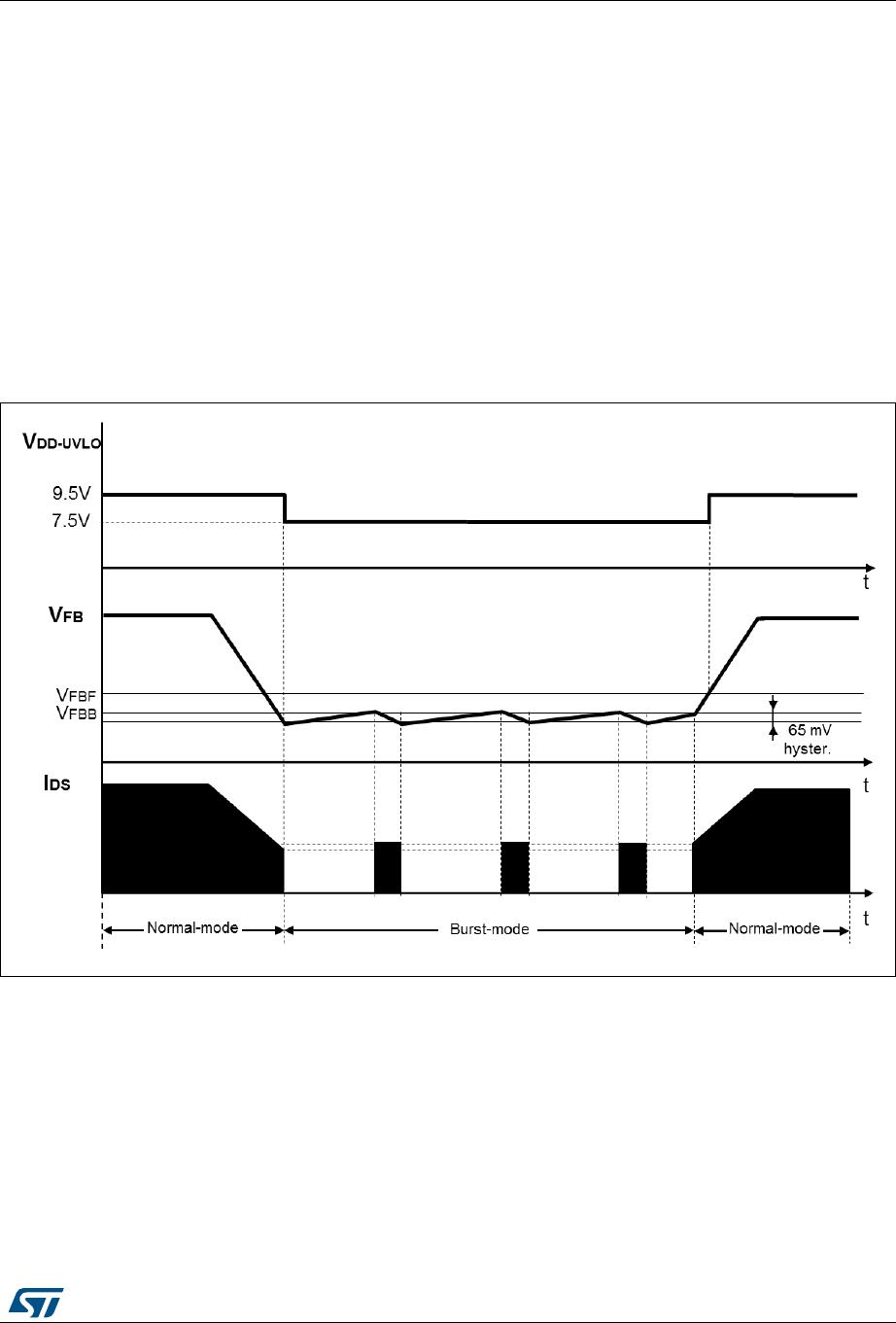
DocID031526 Rev 1 13/25
STCH03 Application information
25
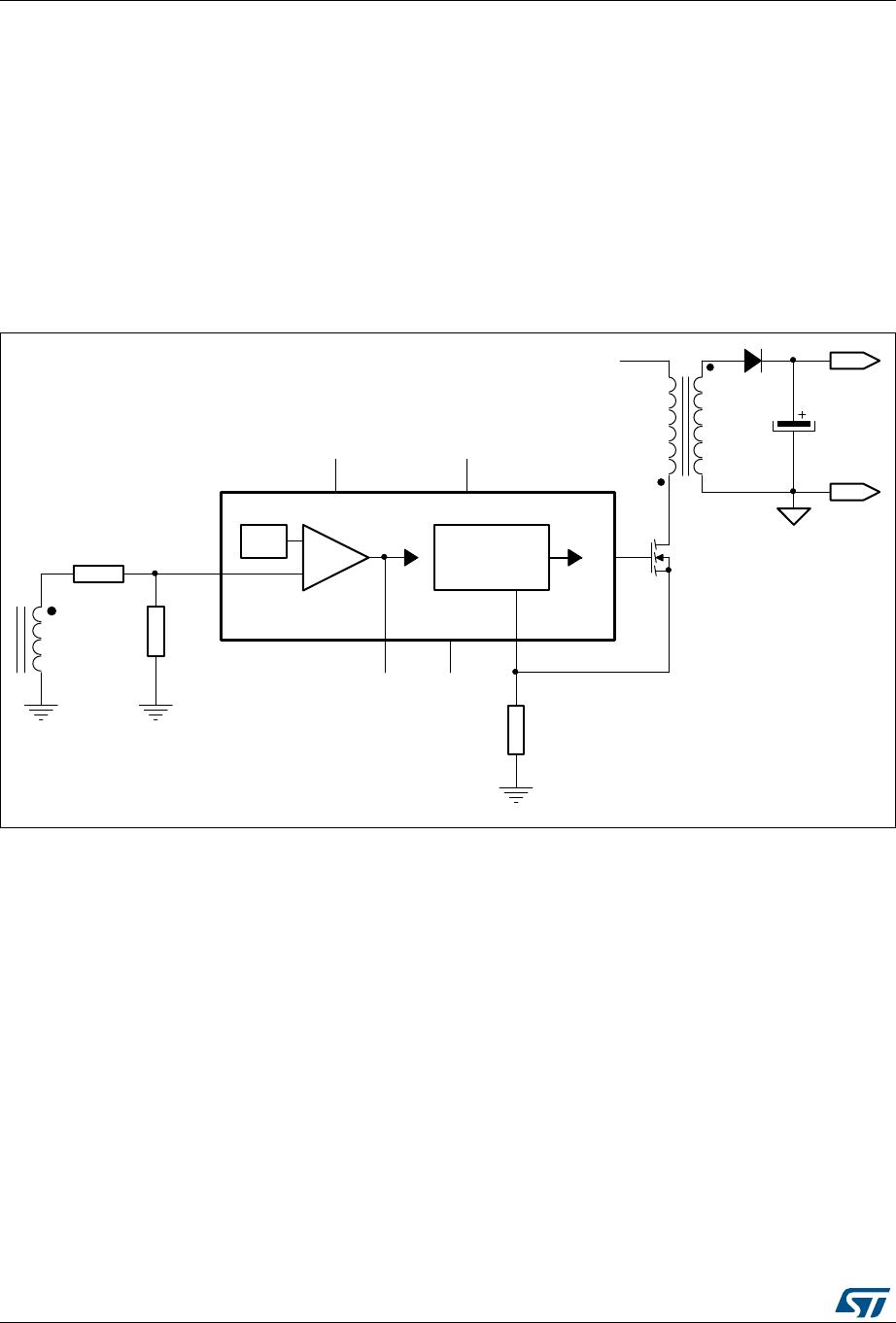
6.5 Constant voltage operation
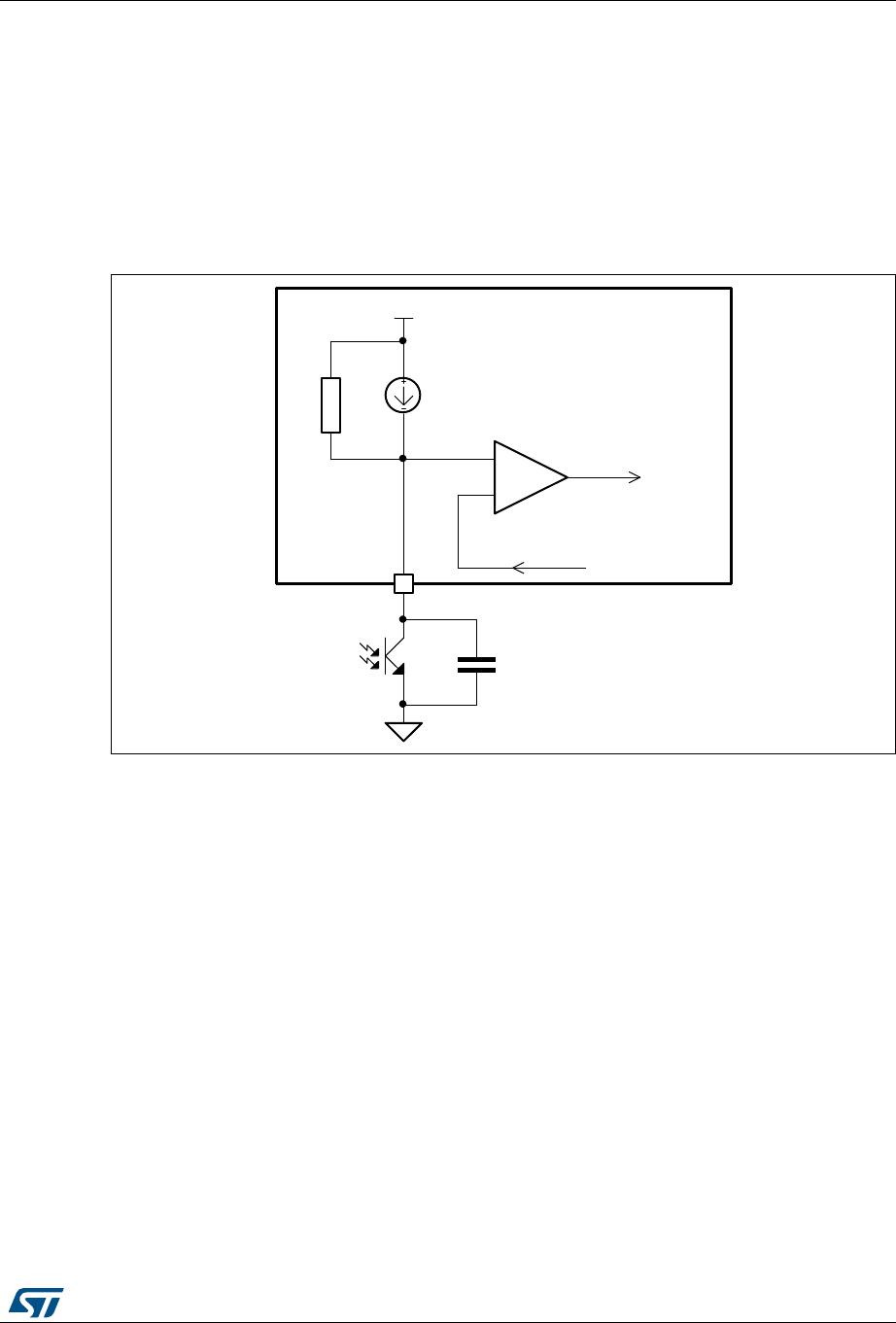
The device is specific for the secondary feedback. The FB pin is connected to an
optocoupler which transmits the error signal from the regulation loop located on the
secondary side of the converter. Typically, a TS431 is used as a voltage reference.
The FB pin is driven directly by the phototransistor's collector to modulate the duty cycle.
The voltage coming from the FB pin is compared with the voltage across the sense resistor,
controlling the peak drain current cycle-by-cycle.
Figure 5. Voltage control principle: internal schematic
6.6 Constant current operation
The voltage of the auxiliary winding is fed into the internal CC block trough the ZCD pin to
achieve an output constant current regulation.
Equation 1 can be used to define the output current in the CC-mode.
Equation 1
This formula shows that the average output current does not depend anymore on the input
or the output voltage, neither on transformer inductance values. The external parameters
defining the output current are the transformer ratio and the sense resistor R
SENSE
. The
current loop gain K
I
is internally defined.
3GC
'SPN3TFOTF
'#
7GC
5P18.-PHJD
$7
*GC
$GC
".
I
OUT
N
PRI
N
SEC
--------------
K
I
2R
SENSE
-----------------------------=