15
LTC1197/LTC1197L
LTC1199/LTC1199L
Lower Supply Voltage
For lower supply voltages, LTC offers the LTC1197L/
LTC1199L. These pin compatible devices offer specified
performance to 2.7V supplies.
OPERATING ON OTHER THAN 5V SUPPLIES
The LTC1197 operates from 4V to 9V supplies and the
LTC1199 operates from 4V to 6V supplies. The LTC1197L/
LTC1199L operate from 2.7V to 4V supplies. To use these
parts at other than 5V supplies a few things must be kept
in mind.
Bypassing
At higher supply voltages, bypass capacitors on V
CC
and
V
REF
if applicable, need to be increased beyond what is
necessary for 5V. For a 9V supply a 10µF tantalum in
parallel with a 0.1µF ceramic is recommended.
Input Logic Levels
The input logic levels of CS, CLK and D
IN
are made to meet
TTL threshold levels on a 5V supply. When the supply
voltage varies, the input logic levels also change. For the
ADC to sample and convert correctly, the digital inputs
have to meet logic low and high levels relative to the
operating supply voltage (see typical curve of Digital Input
Logic Threshold vs Supply Voltage). If achieving mi-
cropower consumption is desirable, the digital inputs
must go rail-to-rail between V
CC
and ground (see ACHIEV-
ING MICROPOWER PERFORMANCE section).
Clock Frequency
The maximum recommended clock frequency is 7.2MHz
for the LTC1197/LTC1199 running off a 5V supply and
3.5MHz for the LTC1197L/LTC1199L running off a 2.7V
supply. With the supply voltage changing, the maximum
clock frequency for the devices also changes (see the
typical curve of Maximum Clock Rate vs Supply Voltage).
If the maximum clock frequency is used, care must be
taken to ensure that the device converts correctly.
that convert continuously, the LTC1197/LTC1197L/
LTC1199/LTC1199L will draw their normal operating power
continuously. Several things must be taken into account
to achieve micropower operation.
Shutdown
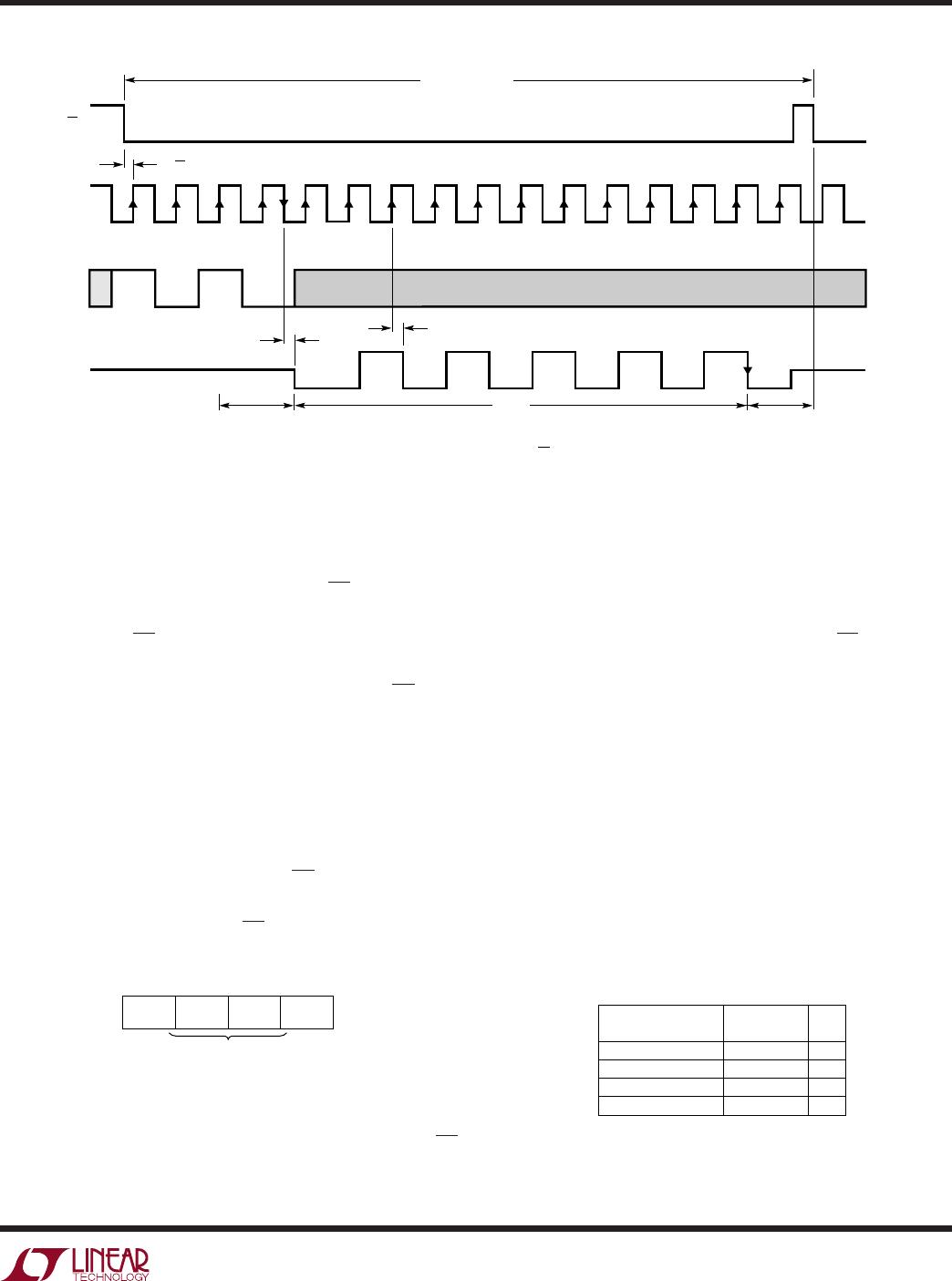
Figures 1 and 2 show the operating sequence of the
LTC1197/LTC1197L/LTC1199/LTC1199L. The converter
draws power when the CS pin is low and powers itself
down when that pin is high. If the CS pin is not taken all the
way to ground when it is low and not taken to V
CC
when it
is high, the input buffers of the converter will draw current.
This current may be tens of microamps. It is worthwhile to
bring the CS pin all the way to ground when it is low and
all the way to V
CC
when it is high to obtain the lowest
supply current.
When the CS pin is high (= supply voltage), the converter
is in shutdown mode and draws only leakage current. The
status of the D
IN
and CLK inputs have no effect on supply
current during this time. There is no need to stop D
IN
and
CLK with CS = high, except the MPU may benefit.
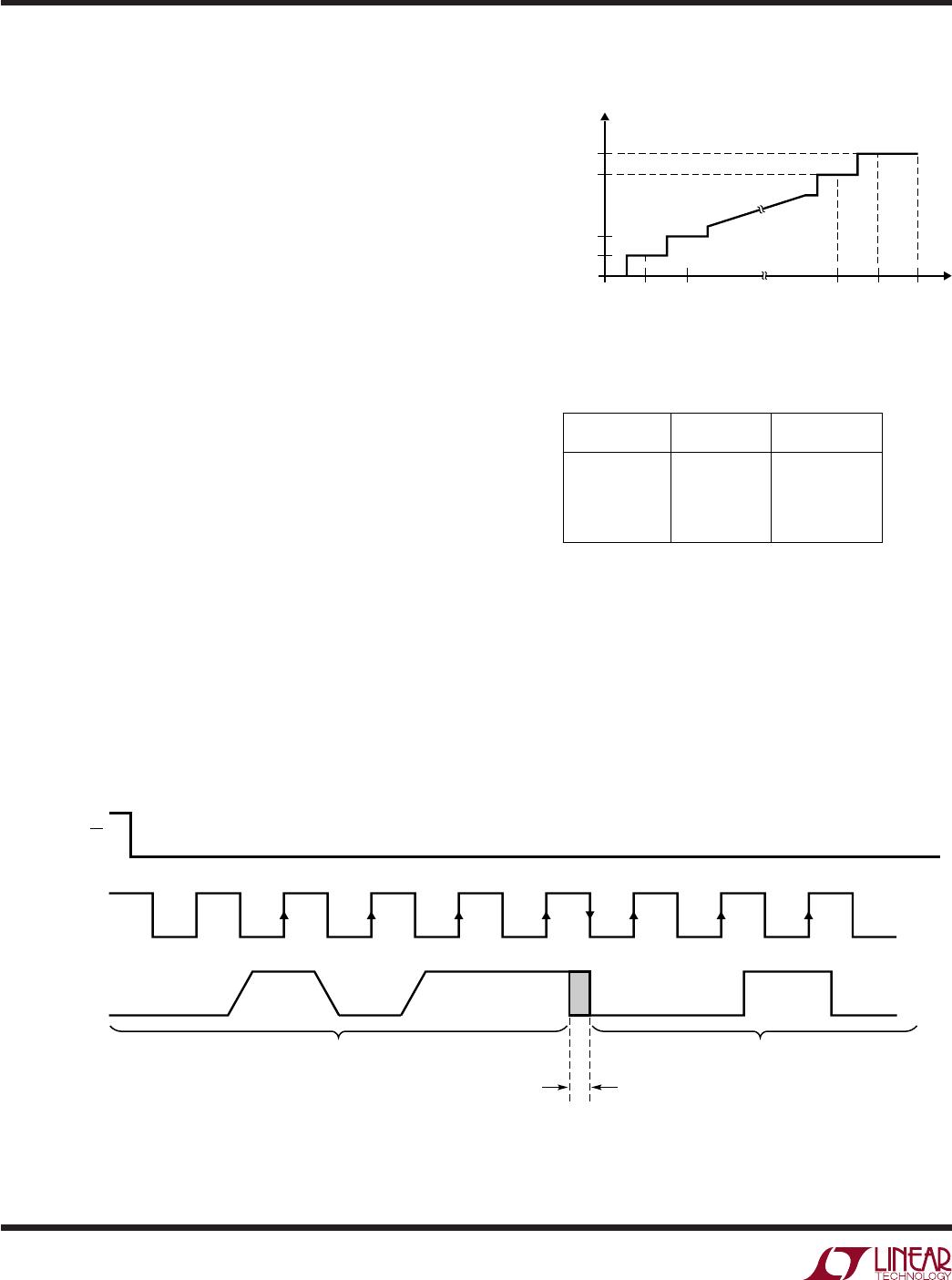
Minimize CS Low Time
In systems that have significant time between conver-
sions, lowest power drain will occur with the minimum CS
low time. Bringing CS low, transferring data as quickly as
possible, and then returning CS high will result in the
lowest possible current drain. This minimizes the amount
of time the device draws power. Even though the device
draws more power at high clock rates, the net power is less
because the device is on for a shorter time.
D
OUT
Loading
Capacitive loading on the digital output can increase
power consumption. A 100pF capacitor on the D
OUT
pin
can add 200µA to the supply current at a 7.2MHz clock
frequency. The extra 200µA goes into charging and dis-
charging the load capacitor. The same goes for digital lines
driven at a high frequency by any logic. The C • V • f currents
must be evaluated and the troublesome ones minimized.
APPLICATIO S I FOR ATIO
WUUU