LTC4370
8
4370f
operaTion
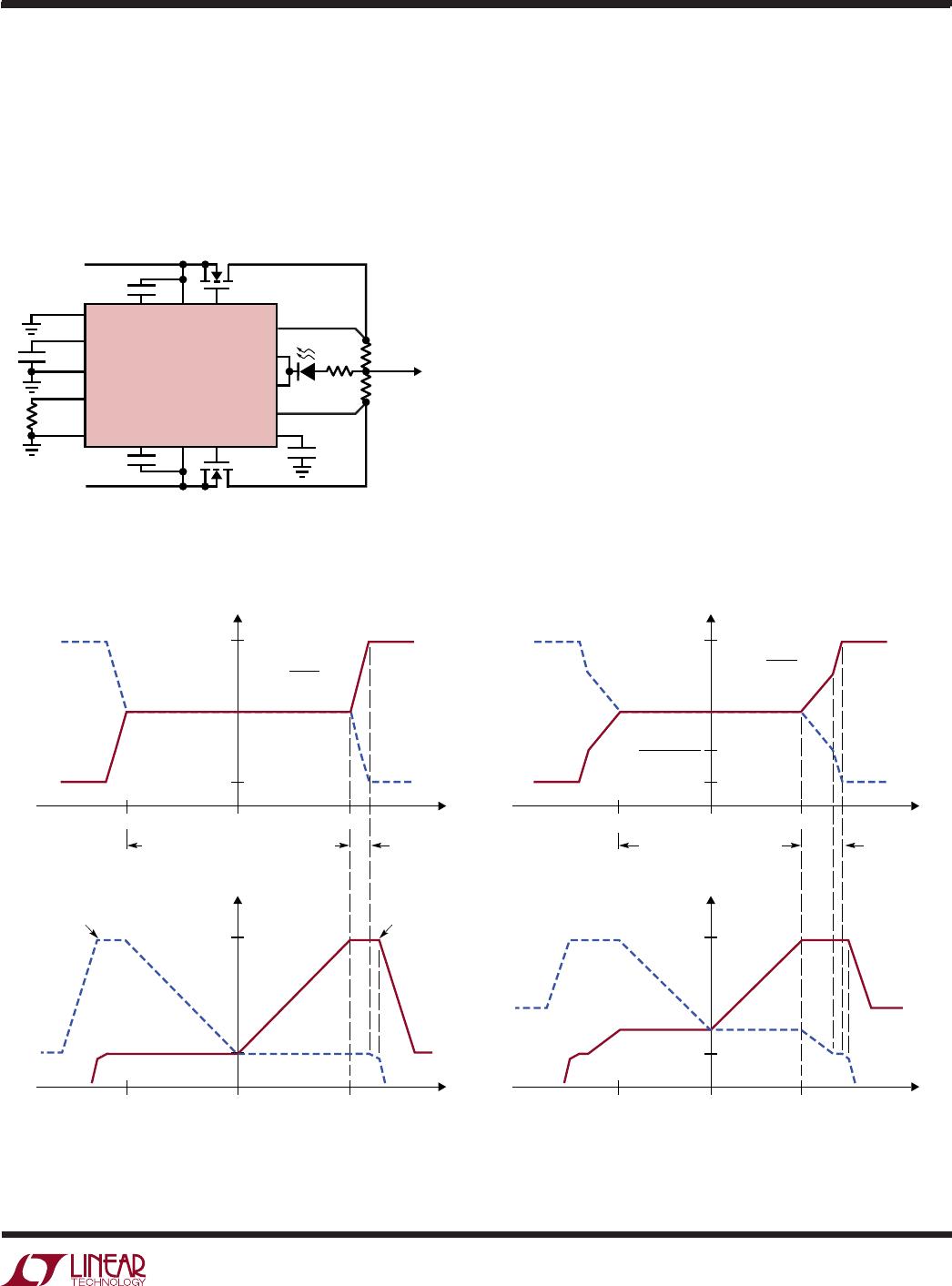
The LTC4370 controls N-channel MOSFETs, M1 and M2,
to share the load between two supplies. Error amplifier
EA compares OUT1 to OUT2 and sets the servo com-
mand voltages, V
FR1
and V
FR2
, for servo amplifiers, SA1
and SA2. When enabled, each servo amplifier controls
the gate of the external MOSFET to regulate its forward
voltage drop (V
FWD
= V
IN
– OUT) to V
FR
. The combined
action of EA and SA forces OUT1 to equal OUT2. Having
the power path resistance from OUT1 to the load (R1)
equal that from OUT2 to the load (R2) forces each supply
to source half of the load current.
The lower limit of V
FR
adjustment is 25mV at higher supply
voltages (reducing to 12mV at lower voltages to conserve
power and voltage drop). The upper limit is V
RANGE
+ 25mV
(or V
RANGE
+ 12mV). V
RANGE
itself is set by the 10µA pull-
up current source into resistor R3. The servo adjust block
ensures that only the higher supply’s V
FR
is adjusted up
while the other is pinned to the minimum. Tying RANGE to
V
CC
(CP5) forces both V
FR
to the minimum, transforming
the device into a dual ideal diode controller.
The
servo amplifier raises the gate voltage to enhance
the MOSFET whenever the load current causes the drop
to exceed V
FR
. For large output currents the MOSFET
gate is driven fully on and the voltage drop is equal to
I
FET
• R
DS(ON)
.
In the case of an input supply short-circuit, when the
MOSFET is conducting, a large reverse current starts
flowing from the load towards the input. SA detects this
failure condition as soon as it appears and turns off the
MOSFET by rapidly pulling down its gate.
SA quickly pulls up the gate whenever it senses a large
forward voltage drop. An external capacitor (C1, C2)
between the CPO and V
IN
pins is needed for fast gate
pull-up. This capacitor is charged up, at device power-up,
by the internal charge-pump. The stored charge is used
for the fast gate pull-up.
The GATE pin sources current from the CPO pin and sinks
current to the V
IN
and GND pins. Clamps limit the GATE
and CPO voltages to 12V above and a diode below V
IN
.
Internal switches pull the FETON pins low when the GATE
to V
IN
voltage is below 0.7V to indicate that the external
MOSFET is off (body diode could still conduct).
LDO is a low dropout regulator that generates a 5V supply
at the V
CC
pin from the highest V
IN
input. When supplies
below 2.9V are being shared, an external supply in the
2.9V to 6V range is required at the V
CC
pin.
V
CC
and EN pin comparators, CP1 to CP3, control power
passage. The MOSFET is held off whenever the EN pin is
above 0.6V, or the V
CC
pin is below 2.55V. A high on both
EN pins lowers the current consumption of the device.