NCP1082
http://onsemi.com
11
DESCRIPTION OF OPERATION
Powered Device Interface
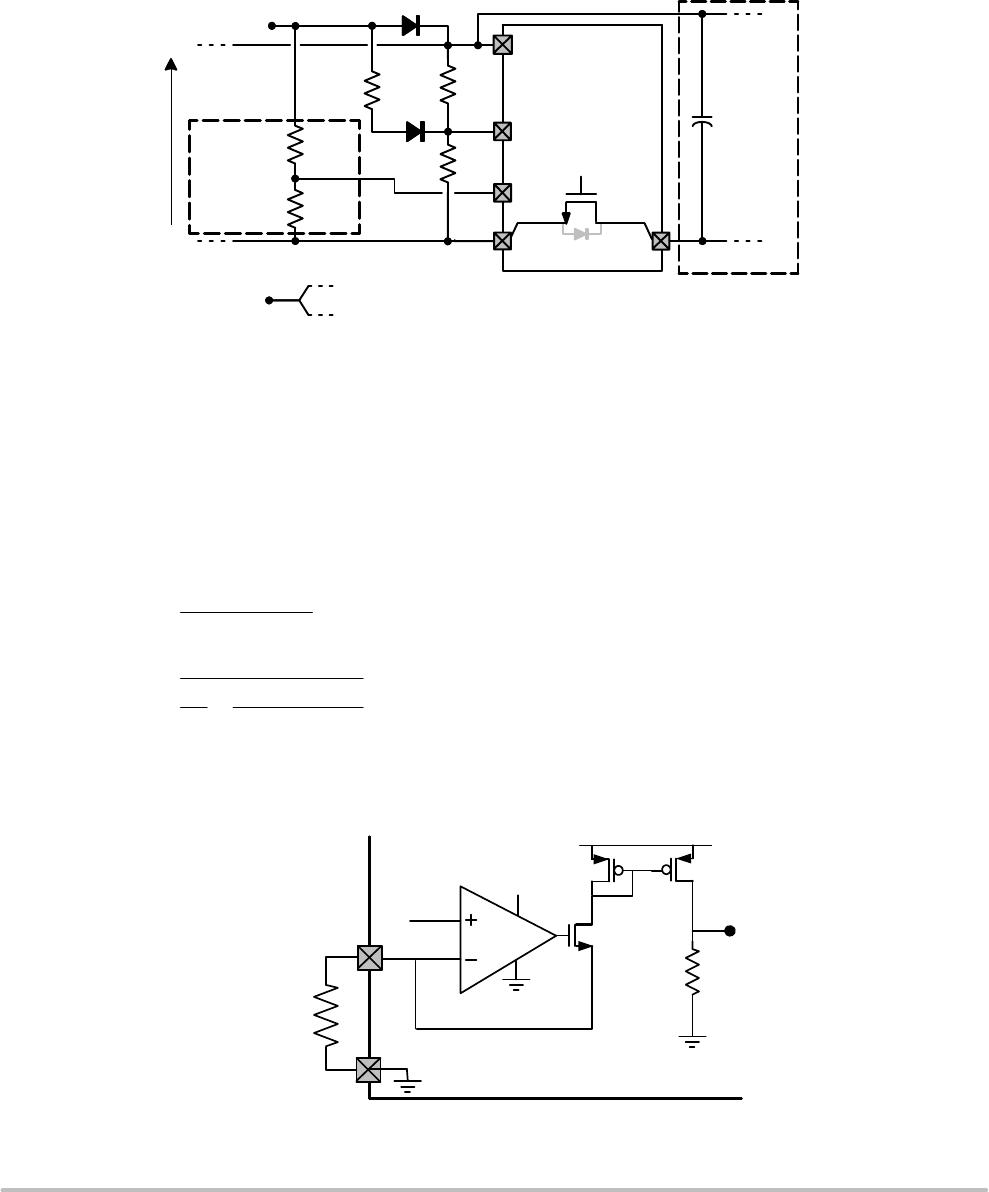
The PD interface portion of the NCP1082 supports the
IEEE 802.3af defined operating modes: detection signature,
current source classification, inrush and operating current
limits. In order to give more flexibility to the user and also
to keep control of the power dissipation in the NCP1082,
both current limits are configurable. The device enters
operation once its programmable Vuvlo_on threshold is
reached, and operation ceases when the supplied voltage
falls below the Vuvlo_off threshold. Sufficient hysteresis
and Uvlo filter time are provided to avoid false power on/off
cycles due to transient voltage drops on the cable.
Detection
During the detection phase, the incremental equivalent
resistance seen by the PSE through the cable must be in the
IEEE 802.3af standard specification range (23.75 kW to
26.25 kW) for a PSE voltage from 2.7 V to 10.1 V. In order
to compensate for the non−linear effect of the diode bridge
and satisfy the specification at low PSE voltage, the
NCP1082 presents a suitable impedance in parallel with the
25.5 kW R
det
external resistor connected between VPORTP
and VPORTN. For some types of diodes (especially Schottky
diodes), it may be necessary to adjust this external resistor.
When the Detection_Off level is detected (typically
11.5 V) on VPORTP, the NCP1082 turns on its internal
3.3 V regulator and biasing circuitry in anticipation of the
classification phase as the next step.
Classification
Once the PSE device has detected the PD device, the
classification process begins. In classification, the PD
regulates a constant current source that is set by the external
resistor RCLASS value on the CLASS pin. Figure 8 shows
the schematic overview of the classification block. The
current source is defined as:
I
class
+
V
bg
R
class
, (where V
bg
is 1.2 V)
CLASS
VDDA1
1.2 V
VPORTP
VPORTN1,2
NCP1082
Rclass
Figure 8. Classification Block Diagram
Power Mode
When the classification hand−shake is completed, the
PSE and PD devices move into the operating mode.
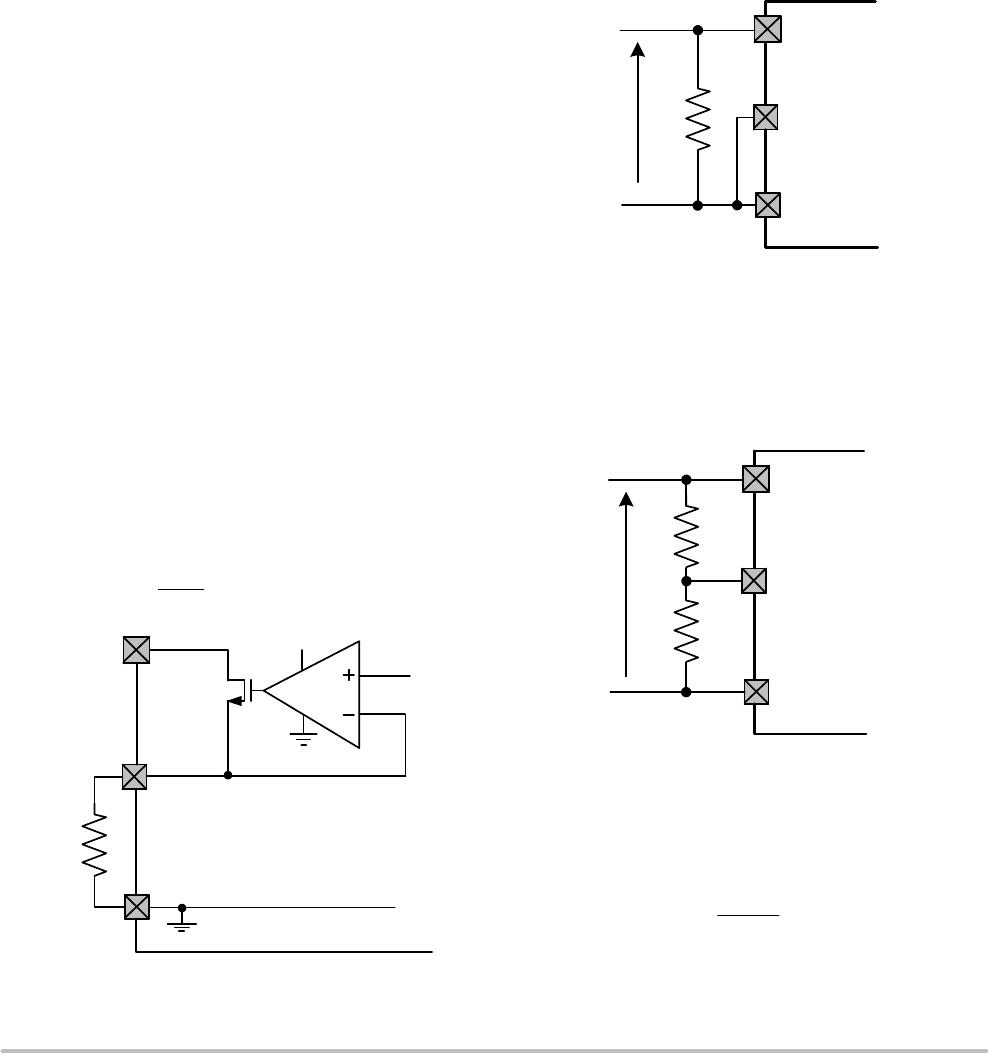
Under Voltage Lock Out (UVLO)
The NCP1082 incorporates an under voltage lock out
(UVLO) circuit which monitors the input voltage and
determines when to apply power to the DC−DC controller.
To use the default settings for UVLO (see Table 3), the pin
UVLO must be connected to VPORTN
1,2
. In this case the
signature resistor has to be placed directly between
VPORTP and VPORTN
1,2
, as shown in Figure 9.
Figure 9. Default UVLO Settings
UVLO
VPORTP
VPORTN1,2
NCP1082
VPORT
Rdet
To define the UVLO threshold externally, the UVLO pin
must be connected to the center of an external resistor
divider between VPORTP and VPORTN
1,2
as shown in
Figure 10. The series resistance value of the external
resistors must add to 25.5 kW and replaces the internal
signature resistor.
Figure 10. External UVLO Configuration
UVLO
VPORTN1,2
NCP1082
VPORT
R2
R1
VPORTP
For a Vuvlo_on desired turn−on voltage threshold, R1 and
R2 can be calculated using the following equations:
R1 ) R2 + R
det
R2 +
1.2
V
ulvo_on
R
det
When using the external resistor divider, the NCP1082 has
an external reference voltage hysteresis of 15 percent typical.