Performance
Measured performance can vary for a number of reasons. The major factors affecting
drive performance are the capacity of the drive and the interface of the host. Addition-
ally, overall system performance can affect the measured drive performance. When
comparing drives, it is recommended that all system variables are the same, and only
the drive being tested varies.
Performance numbers will vary depending on the host system configuration.
For SSDs designed for the client computing market, Micron specifies performance in
fresh-out-of-box (FOB) state. Data throughput measured in "steady state" may be lower
than FOB state, depending on the nature of the data workload.
For a description of these performance states and of Micron's best practices for per-
formance measurement, refer to Micron's technical marketing brief Best Practices for
SSD Performance Measurement.
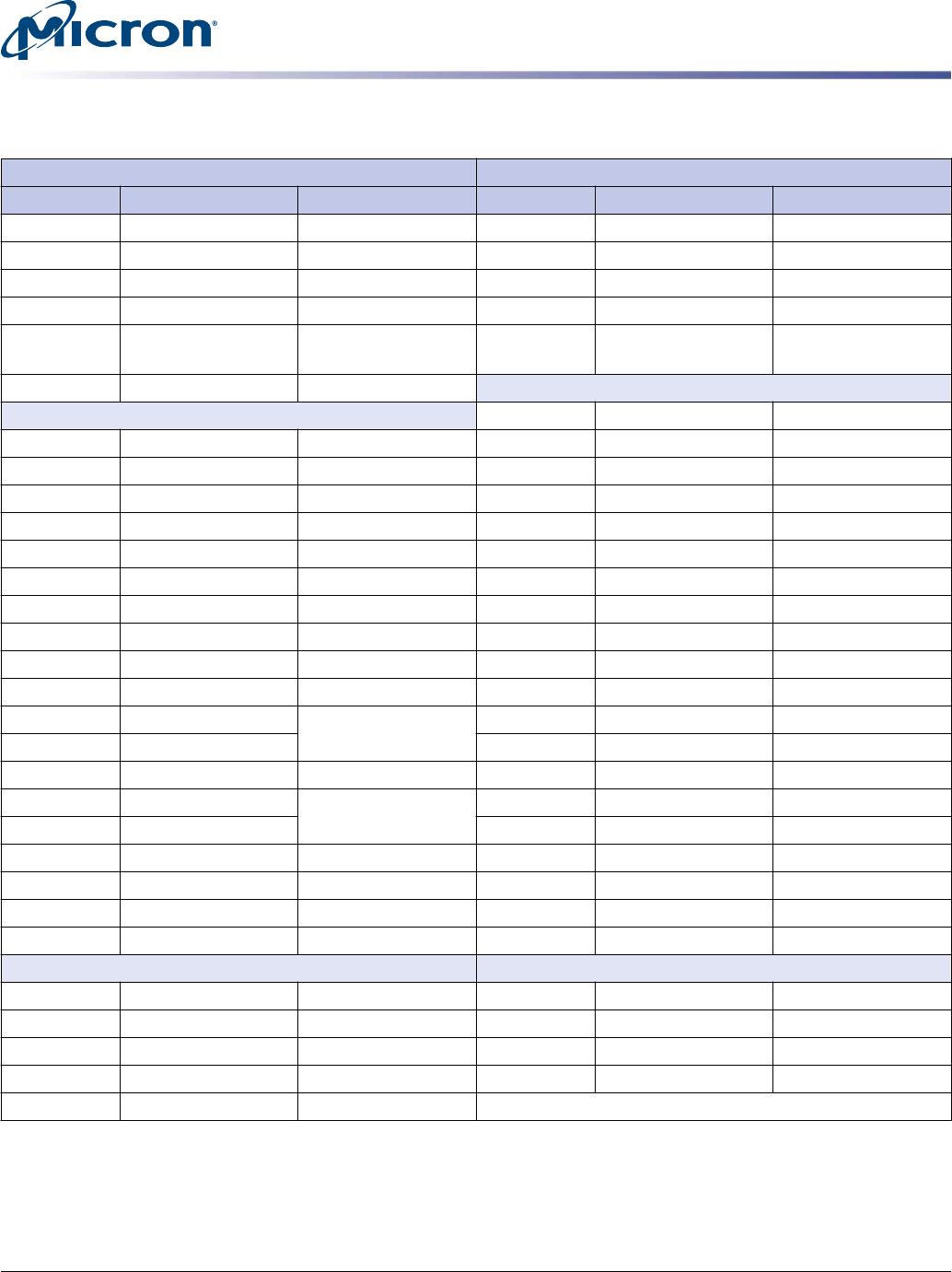
Table 5: Drive Performance
Capacity 128GB 256GB 512GB
UnitInterface Speed 6 Gb/s 6 Gb/s 6 Gb/s
PCMark Vantage 87,000 87,000 87,000 HDD score
Sequential read (128KB transfer) 560 560 560 MB/s
Sequential write (128KB transfer) 400 510 510 MB/s
Random read (4KB transfer) 90,000 100,000 100,000 IOPS
Random write (4KB transfer) 88,000 88,000 88,000 IOPS
READ latency (TYP) 120 120 120 µs
WRITE latency (TYP) 30 30 30 µs
Notes:
1. Performance numbers are maximum values, except as noted.
2. Typical I/O performance numbers as measured using Iometer with a queue depth of 32
and write cache enabled. Fresh-out-of-box (FOB) state is assumed. For performance
measurement purposes, the SSD may be restored to FOB state using the secure erase
command.
3. Iometer measurements are performed on an 20GB span of logical block addresses
(LBAs).
4. 4KB transfers with a queue depth of 1 are used to measure READ/WRITE latency values
with write cache enabled.
5. System variations will affect measured results. For comparison, PCMark scores are meas-
ured with the SSD as a secondary drive in a two-drive system. When measured as an OS
drive, system overhead can cause lower scores.
M600 M.2 Type 2260/2280 NAND Flash SSD
Performance
PDF: 09005aef859ad464
m600_m2_2260_2280_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 3/15 EN
8
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2014 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.