General Description
DDR3 SDRAM modules are high-speed, CMOS dynamic random access memory mod-
ules that use internally configured 8-bank DDR3 SDRAM devices. DDR3 SDRAM mod-
ules use DDR architecture to achieve high-speed operation. DDR3 architecture is essen-
tially an 8n-prefetch architecture with an interface designed to transfer two data words
per clock cycle at the I/O pins. A single read or write access for the DDR3 SDRAM mod-
ule effectively consists of a single 8n-bit-wide, one-clock-cycle data transfer at the inter-
nal DRAM core and eight corresponding n-bit-wide, one-half-clock-cycle data transfers
at the I/O pins.
DDR3 modules use two sets of differential signals: DQS, DQS# to capture data and CK
and CK# to capture commands, addresses, and control signals. Differential clocks and
data strobes ensure exceptional noise immunity for these signals and provide precise
crossing points to capture input signals.
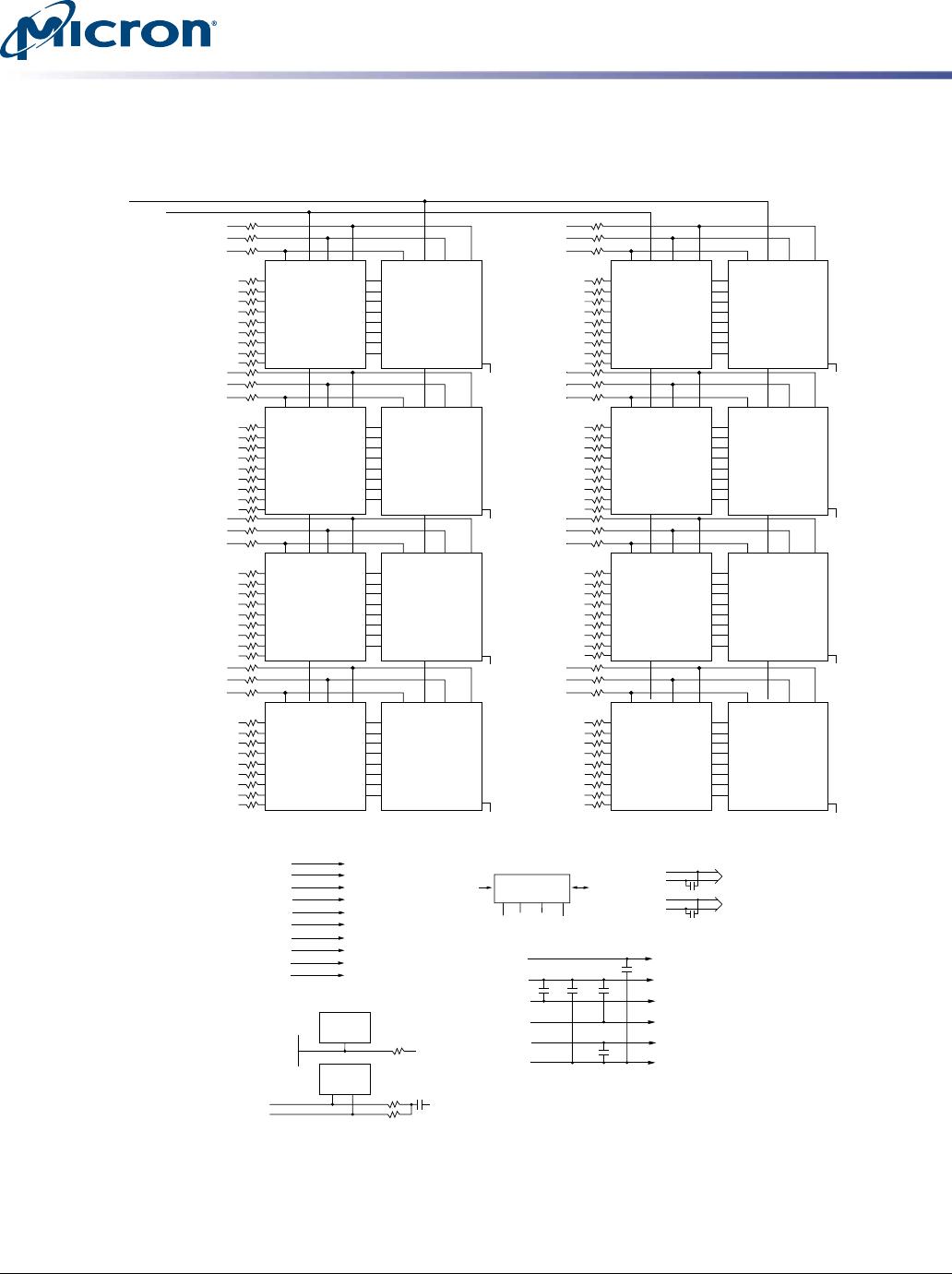
Fly-By Topology
DDR3 modules use faster clock speeds than earlier DDR technologies, making signal
quality more important than ever. For improved signal quality, the clock, control, com-
mand, and address buses have been routed in a fly-by topology, where each clock, con-
trol, command, and address pin on each DRAM is connected to a single trace and ter-
minated (rather than a tree structure, where the termination is off the module near the
connector). Inherent to fly-by topology, the timing skew between the clock and DQS sig-
nals can be easily accounted for by using the write-leveling feature of DDR3.
Serial Presence-Detect EEPROM Operation
DDR3 SDRAM modules incorporate serial presence-detect. The SPD data is stored in a
256-byte EEPROM. The first 128 bytes are programmed by Micron to comply with
JEDEC standard JC-45, "Appendix X: Serial Presence Detect (SPD) for DDR3 SDRAM
Modules." These bytes identify module-specific timing parameters, configuration infor-
mation, and physical attributes. The remaining 128 bytes of storage are available for use
by the customer. System READ/WRITE operations between the master (system logic)
and the slave EEPROM device occur via a standard I
2
C bus using the DIMM’s SCL
(clock) SDA (data), and SA (address) pins. Write protect (WP) is connected to V
SS
, per-
manently disabling hardware write protection. For further information refer to Micron
technical note TN-04-42, "Memory Module Serial Presence-Detect."
4GB, 8GB (x64, DR) 204-Pin 1.35V DDR3L SODIMM
General Description
PDF: 09005aef846206a0
ktf16c512_1gx64hz.pdf - Rev. K 7/15 EN
12
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2011 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.