MAX9730
2.4W, Single-Supply, Class G Power Amplifier
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 9
In differential input configurations, the common-mode
rejection ratio (CMRR) is primarily limited by the exter-
nal resistor and capacitor matching. Ideally, to achieve
the highest possible CMRR, the following external com-
ponents should be selected where:
and
Component Selection
Input-Coupling Capacitor
The AC-coupling capacitors (C
IN_
) and input resistors
(R
IN_
) form highpass filters that remove any DC bias from
an input signal (see the
Typical Application
Circuit/Functional Diagram
). C
IN_
blocks DC voltages
from the amplifier. The -3dB point of the highpass filter,
assuming zero source impedance due to the input signal
source, is given by:
Choose C
IN
so that f
-3dB
is well below the lowest fre-
quency of interest. Setting f
-3dB
too high affects the
amplifier’s low frequency response. Use capacitors with
low-voltage coefficient dielectrics. Aluminum electrolytic,
tantalum, or film dielectric capacitors are good choices
for AC-coupling capacitors. Capacitors with high-voltage
coefficients, such as ceramics (non-C0G dielectrics),
can result in increased distortion at low frequencies.
Charge-Pump Capacitor Selection
Use capacitors with an ESR less than 50mΩ for opti-
mum performance. Low-ESR ceramic capacitors mini-
mize the output resistance of the charge pump. For
best performance over the extended temperature
range, select capacitors with an X7R dielectric.
Flying Capacitor (C1)
The value of the flying capacitor (C1) affects the load
regulation and output resistance of the charge pump. A
C1 value that is too small degrades the device’s ability
to provide sufficient current drive. Increasing the value
of C1 improves load regulation and reduces the charge-
pump output resistance to an extent. Above 1µF, the on-
resistance of the switches and the ESR of C1 and C2
dominate. A 4.7µF capacitor is recommended.
Hold Capacitor (C2)
The output capacitor value and ESR directly affect the
ripple at PV
SS
. Increasing C2 reduces output ripple.
Likewise, decreasing the ESR of C2 reduces both rip-
ple and output resistance. A 10µF capacitor is recom-
mended.
Charge-Pump Frequency Set Resistor (R
FS
)
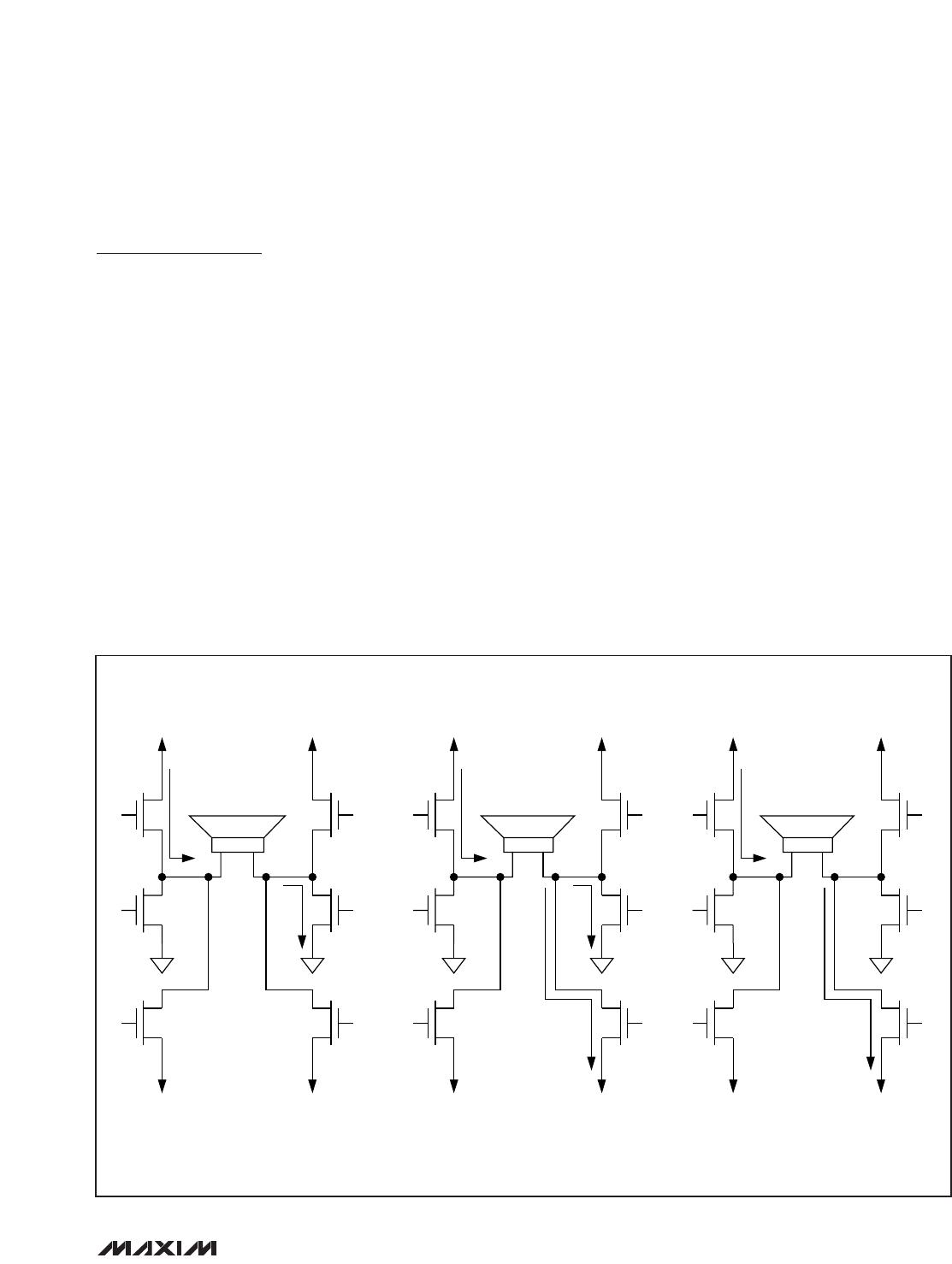
The charge pump operates in two modes. When the
charge pump is loaded below 100mA, it operates in a
slow mode where the oscillation frequency is reduced
to 1/4 of its normal operating frequency. Once loaded,
the charge-pump oscillation frequency returns to nor-
mal operation. In applications where the design may be
sensitive to the operating charge-pump oscillation fre-
quency, the value of the external resistor R
FS
can be
changed to adjust the charge-pump oscillation fre-
quency (see Figure 4).
FREQUENCY vs. R