MAX66140
ISO 15693-Compliant Secure Memory
12 ______________________________________________________________________________________
ABRIDGED DATA SHEET
ISO 15693 Slave States and
Address Modes
Initially, the master has no information whether there are
any RF devices in the field of its antenna. The master
learns the UIDs of the slaves in its field from the
responses to the Inventory command, which does not
use the Address_flag and the Select_flag bits. The state
transitions are controlled by network function com-
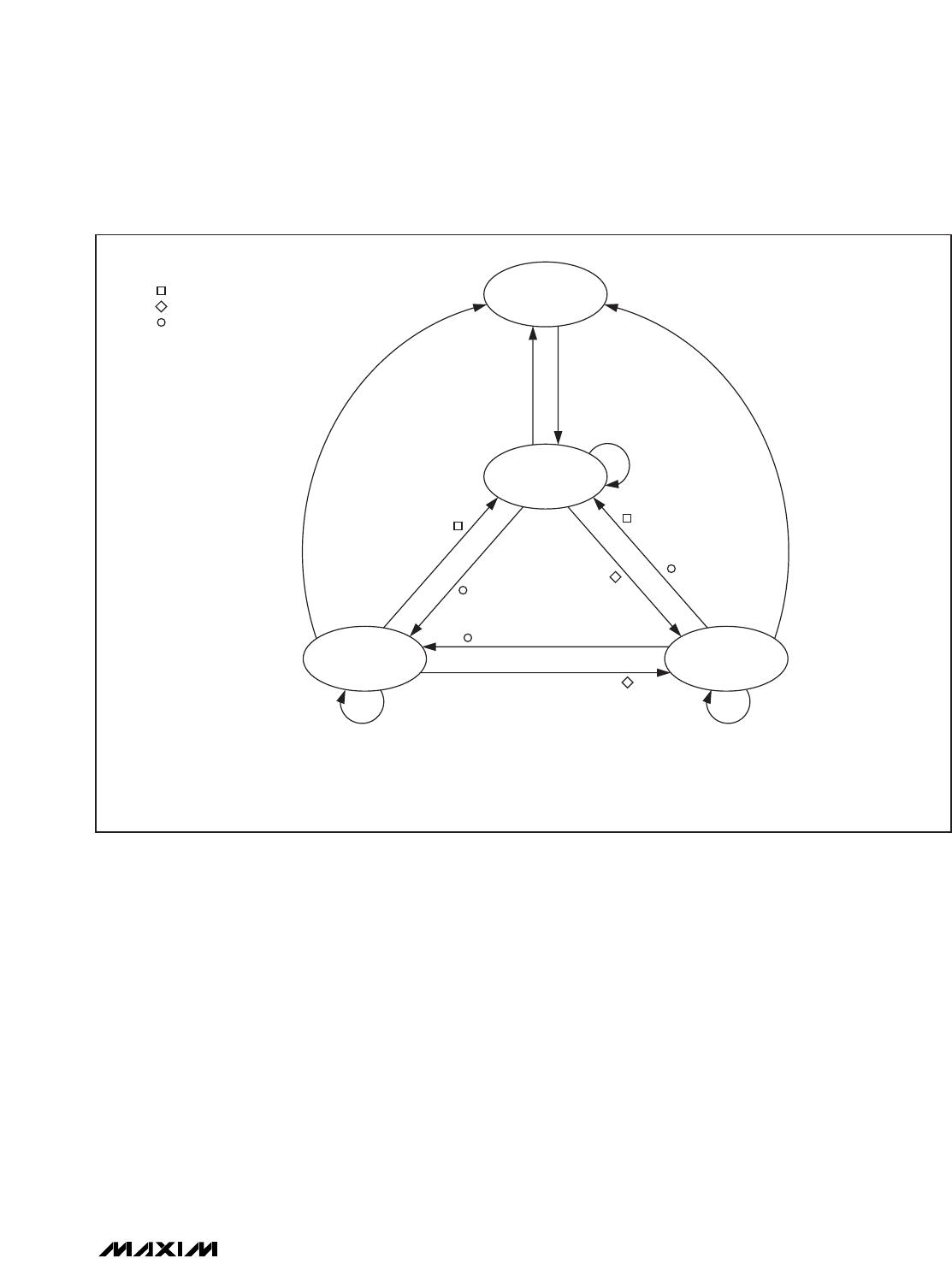
mands. Figure 16 shows details.
ISO 15693 defines four states in which a slave can be
plus three address modes. The states are power-off,
ready, quiet, and selected. The address modes are
nonaddressed, addressed, and selected. The
addressed mode requires that the master include the
slave’s UID in the request, which increases the size of
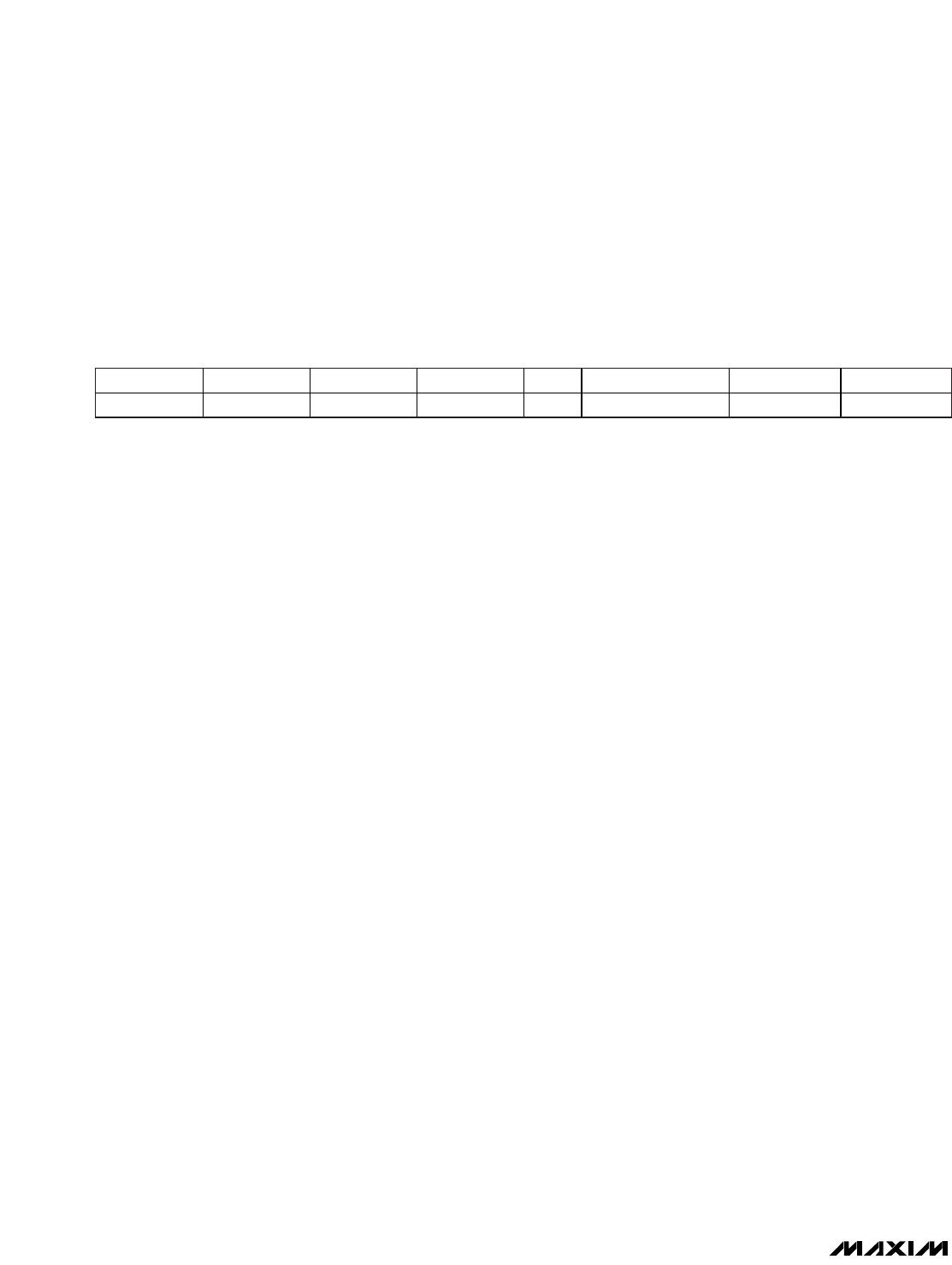
the requests by 8 bytes. Table 5 shows which address
mode is applicable depending on the slave’s state and
how to set the Address_flag and the Select_flag bits for
each address mode.
ISO 15693 States and Transitions
Power-Off State
This state applies if the slave is outside the master’s RF
field. A slave transitions to the power-off state when
leaving the power-delivering RF field. When entering
the RF field, the slave automatically transitions to the
ready state.
Ready State
In this state, a slave has enough power to perform any
of its functions. The purpose of the ready state is to
have the slave population ready to process the invento-
ry command as well as other commands sent in the
addressed or nonaddressed mode. A slave can exit the
ready state and transition to the quiet or the selected
state upon receiving the Stay Quiet or Select command
sent in the addressed mode.
Quiet State
In this state, a slave has enough power to perform any
of its functions. The purpose of the quiet state is to
silence slaves that the master does not want to commu-
nicate with. Only commands sent with the addressed
mode are accepted and processed. This way the mas-
ter can use the nonaddressed mode for communication
with remaining slaves in the ready state, which mini-
mizes the size of the request data packets. As long as
no additional slaves arrive in the RF field, it is safe for
the master to continue communicating in the nonad-
dressed mode. A slave can exit the quiet state and
transition to the ready or the selected state upon receiv-
ing the Reset to Ready or Select command sent in the
addressed mode.
Selected State
In this state, a slave has enough power to perform any
of its functions. The purpose of the selected state is to
isolate the slave that the master wants to communicate
with. Commands are accepted and processed regard-
less of the address mode in which they are sent, includ-
ing the Inventory command. With multiple slaves in the
RF field, the master can put one slave in the selected
state and leave all the others in the ready state. This
method requires less communication than using the
quiet state to single out the slave for communication.
For a slave in the selected state, the master can use the
selected mode, which keeps the request data packets
as short as with the nonaddressed mode. A new slave
entering the RF field cannot disturb the communication,
since it stays in the ready state. A slave can exit the