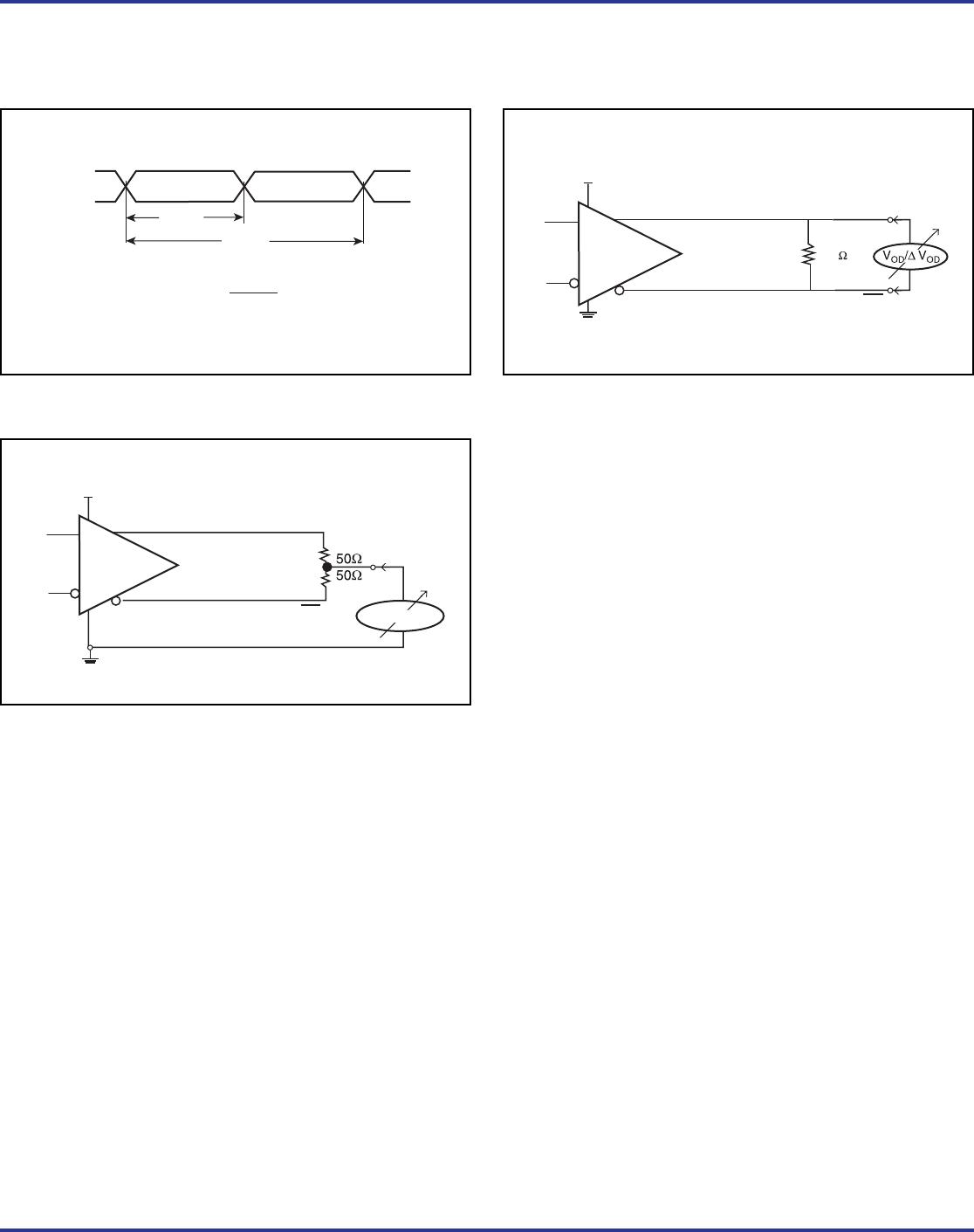
ICS854S01AKI REVISION A OCTOBER 29, 2012 9 ©2012 Integrated Device Technology, Inc.
ICS854S01I Data Sheet 2:1 DIFFERENTIAL-TO-LVDS MULTIPLEXER
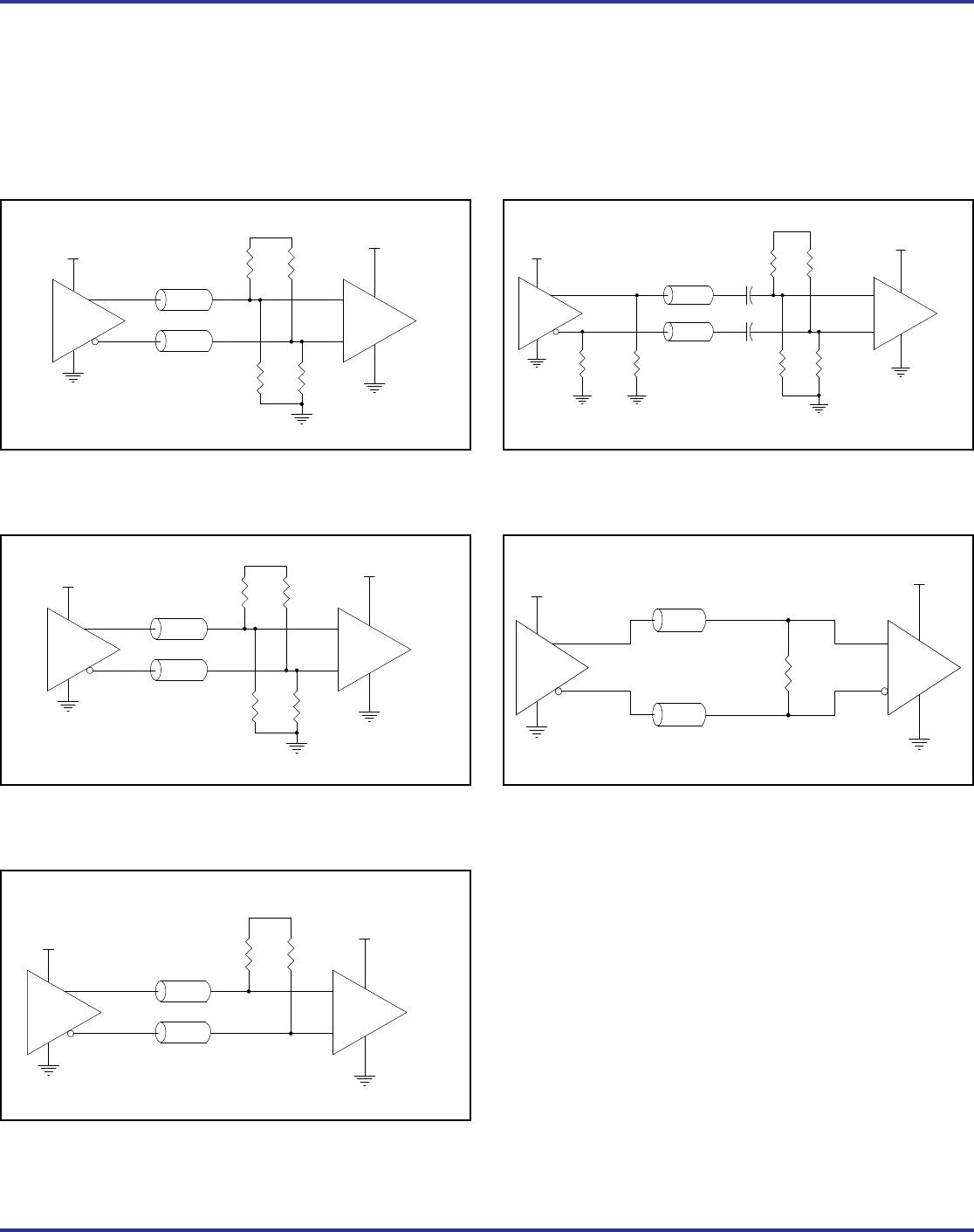
LVPECL Clock Input Interface
The PCLK /nPCLK accepts LVPECL, LVDS and other differential
signals. Both signals must meet the V
PP
and V
CMR
input
requirements. Figures 2A to 2C show interface examples for the
PCLK/ nPCLK input driven by the most common driver types. The
input interfaces suggested here are examples only. If the driver is
from another vendor, use their termination recommendation. Please
consult with the vendor of the driver component to confirm the driver
termination requirements.
Figure 2A. PCLK/nPCLK Input Driven by a
3.3V LVDS Driver
Figure 2C. PCLK/nPCLK Input Driven by a
3.3V LVPECL Driver
Figure 2E. PCLK/nPCLK Input Driven by a CML Driver
Figure 2B. PCLK/nPCLK Input Driven by a
3.3V LVPECL Driver with AC Couple
Figure 2D. PCLK/nPCLK Input Driven by a
Built-In Pullup CML Driver
R3
125Ω
R4
125Ω
R1
84Ω
R2
84Ω
3.3V
Zo = 50Ω
Zo = 50Ω
PCLK
nPCLK
3.3V
3.3V
LVPECL
LVPECL
Input
R3
125Ω
R4
125Ω
R1
84Ω
R2
84Ω
3.3V
Zo = 50Ω
Zo = 50Ω
PCLK
nPCLK
3.3V
3.3V
LVPECL
LVPECL
Input
PCLK
nPCLK
LVPECL
Input
CML
3.3V
Zo = 50Ω
Zo = 50Ω
3.3V
3.3V
R1
50Ω
R2
50Ω
R3
84
R4
84
R1
125
R2
125
R5
100 - 200
R6
100 - 200
PCLK
nPCLK
3.3V LVPECL
3.3V
Zo = 50Ω
Zo = 50Ω
3.3V
3.3V
LVPECL
Input
C1
C2
PCLK
nPCLK
3.3V
LVPECL
Input
3.3V
Zo = 50Ω
Zo = 50Ω
R1
100Ω
CML Built-In Pullup