M41ST85W Clock operation
Doc ID 7531 Rev 11 23/43
3.4 Setting alarm clock registers
Address locations 0Ah-0Eh contain the alarm settings. The alarm can be configured to go
off at a prescribed time on a specific month, date, hour, minute, or second, or repeat every
year, month, day, hour, minute, or second. It can also be programmed to go off while the
M41ST85W is in the battery backup to serve as a system wake-up call.
Bits RPT5–RPT1 put the alarm in the repeat mode of operation. Tabl e 3 shows the possible
configurations. Codes not listed in the table default to the once per second mode to quickly
alert the user of an incorrect alarm setting.
When the clock information matches the alarm clock settings based on the match criteria
defined by RPT5–RPT1, the AF (alarm flag) is set. If AFE (alarm flag enable) is also set, the
alarm condition activates the IRQ
/FT/OUT pin as shown in Figure 15. To disable alarm,
write '0' to the alarm date register and to RPT5–RPT1.
Note: If the address pointer is allowed to increment to the flag register address, an alarm condition
will not cause the interrupt/flag to occur until the address pointer is moved to a different
address. It should also be noted that if the last address written is the “Alarm Seconds,” the
address pointer will increment to the flag address, causing this situation to occur.
The IRQ
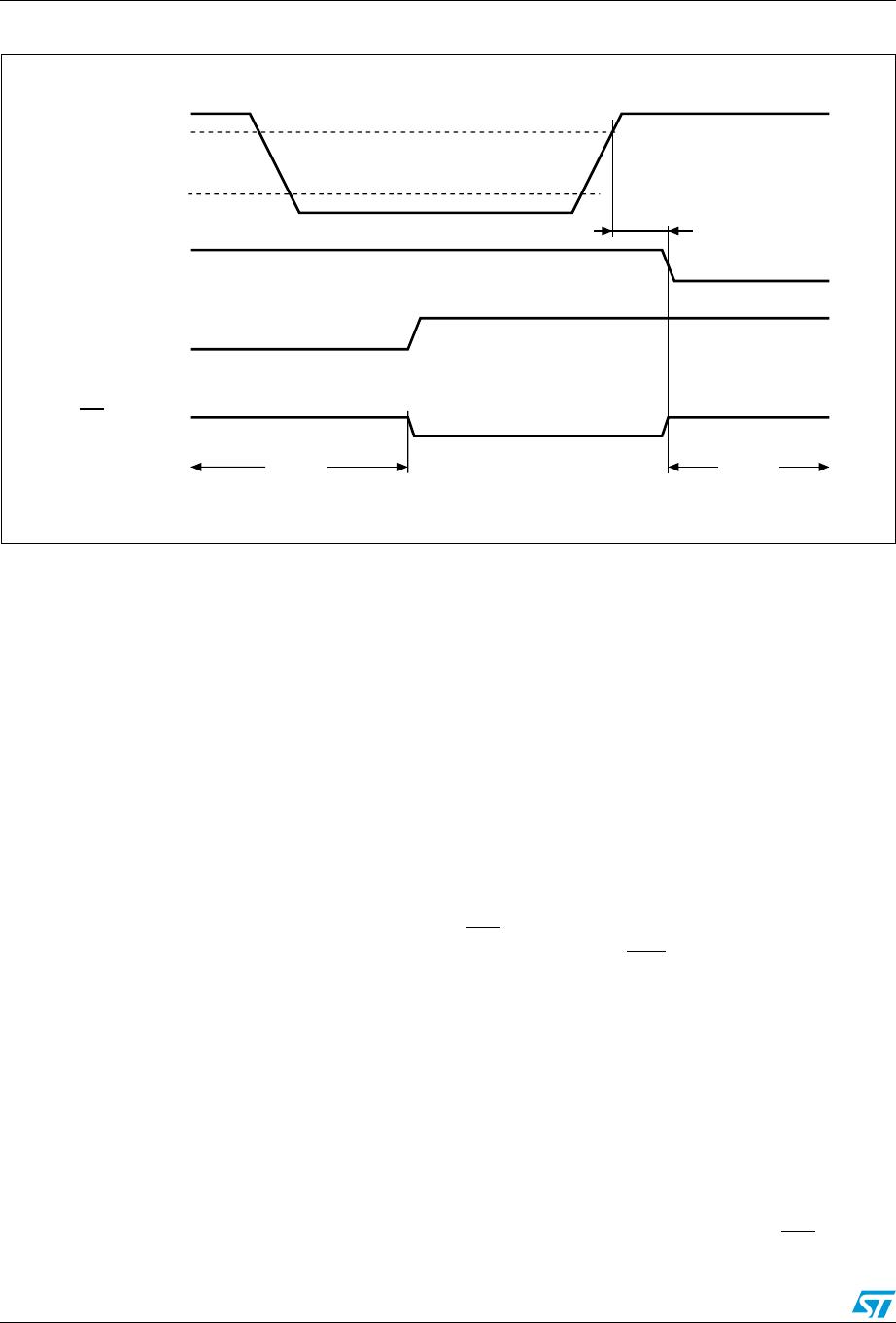
/FT/OUT output is cleared by a READ to the flags register. A subsequent READ of
the flags register is necessary to see that the value of the alarm flag has been reset to '0.'
The IRQ
/FT/OUT pin can also be activated in the battery backup mode. The IRQ/FT/OUT
will go low if an alarm occurs and both ABE (alarm in battery backup mode enable) and AFE
are set. The ABE and AFE bits are reset during power-up, therefore an alarm generated
during power-up will only set AF. The user can read the flag register at system boot-up to
determine if an alarm was generated while the M41ST85W was in the deselect mode during
power-up. Figure 16 on page 24 illustrates the backup mode alarm timing.
Figure 15. Alarm interrupt reset waveform
Table 3. Alarm repeat modes
RPT5 RPT4 RPT3 RPT2 RPT1 Alarm setting
11111Once per second
11110Once per minute
11100Once per hour
11000Once per day
10000Once per month
00000Once per year
AI03664
IRQ/FT/OUT
ACTIVE FLAG
0Fh0Eh 10h
HIGH-Z