NCP1075A/B, NCP1076A/B, NCP1077A/B, NCP1079A/B
www.onsemi.com
22
V
BO(OFF)
V
BO(ON)
V
CC
O/AC_OVP
Drain
current
V
CC(MIN)
V
CC(ON)
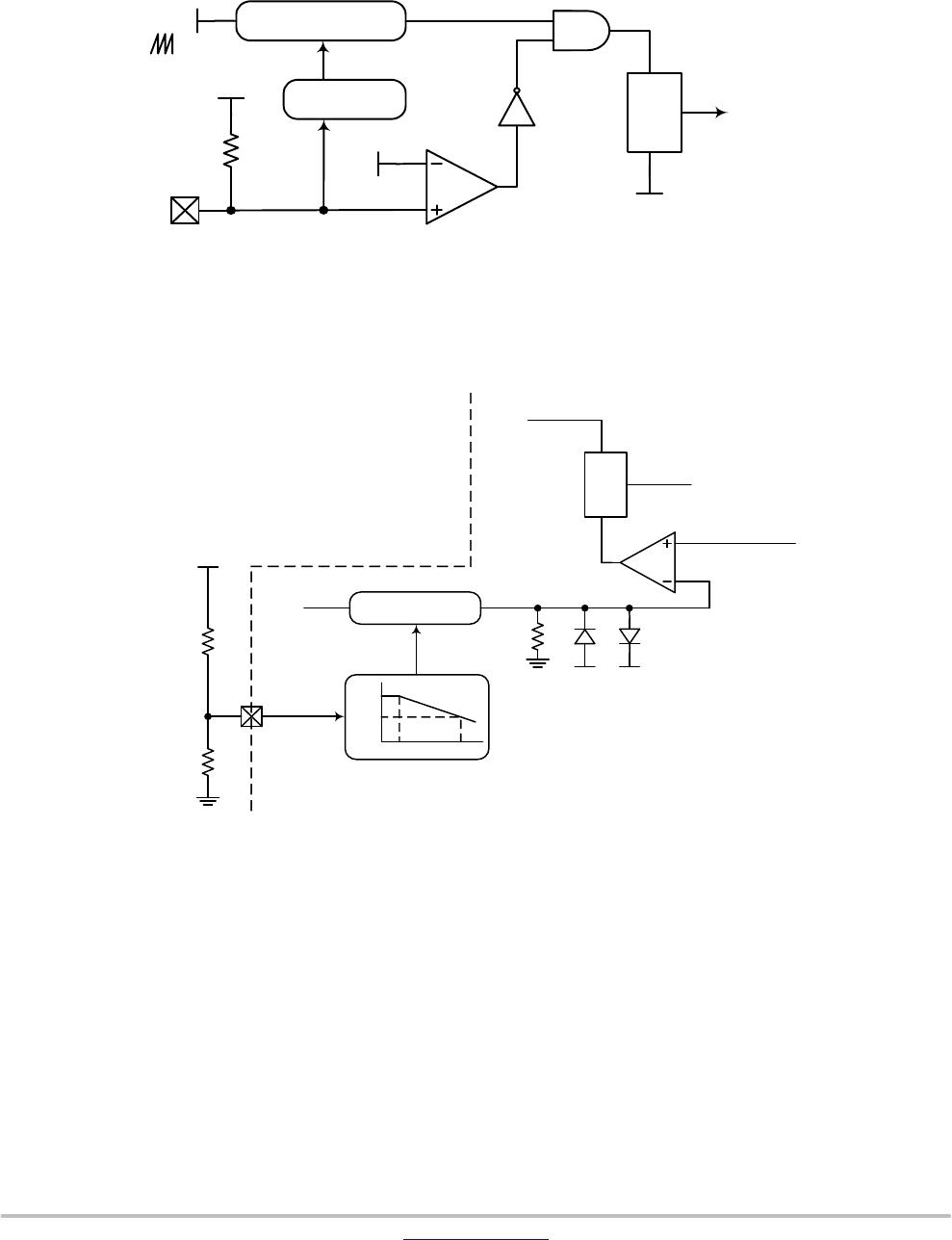
Timer
50 ms
Soft−start Soft−start
Figure 43. Brown−out Functionality in Soft−start
If voltage on VCC pin is higher than V
CC(ON)
and voltage
on BO/AC_OVP pin is higher than V
BO(ON)
then IC starts
pulsing, drain current is increasing for 10 ms (Soft−start).
Brown−out is inhibited during Soft−start, when Soft−start
ended, Brown−out checked if is voltage on BO/AC_OVP
pin higher than V
BO(OFF)
. If the voltage is lower, timer count
50 ms and if the voltage don’t increase over V
BO(OFF)
then
IC stops switching as one can see on Figure 43.
Frequency Foldback
The reduction of no−load standby power associated with
the need for improving the efficiency, requires to change the
traditional fixed−frequency type of operation. This device
implements a switching frequency folback when the
feedback current passes above a certain level, I
FBfold
, set
around 68 mA. At this point, the oscillator enters frequency
foldback and reduces its switching frequency.
The internal peak current set−point is following the
feedback current information until its level reaches the
minimal freezing level point of I
freeze
. Below this value, the
peak current set−point is frozen to 30% of the I
PK(0)
. The
only way to further reduce the transmitted power is to
diminish the operating frequency down to f
MIN
(27 kHz
typically). This value is reached at a feedback current level
of I
FBfold(END)
(100 mA typically). Below this point, if the
output power continues to decrease, the part enters skip
cycle for the best noise−free performance in no−load
conditions. Figures 44 and 45 depict the adopted scheme for
the part.