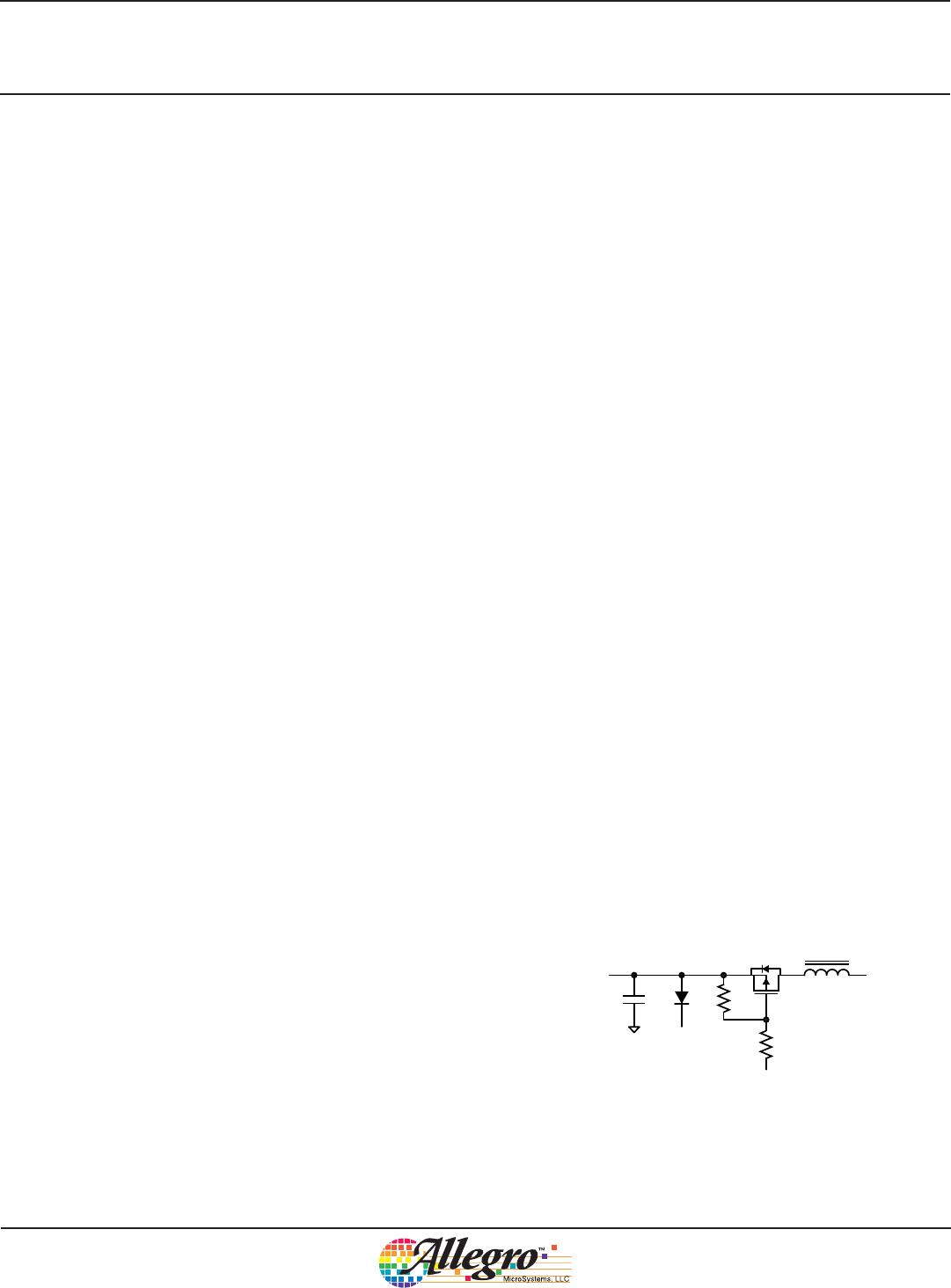
Automotive High Current LED Controller
A6265
10
Allegro MicroSystems, LLC
115 Northeast Cutoff
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 U.S.A.
1.508.853.5000; www.allegromicro.com
Diagnostics
The circuit includes several diagnostic and safety functions to
assist in ensuring safe operation of the LEDs, the A6265, and the
external components. When any fault is detected, one or both of
the fault flag outputs, FF1 and FF2, will be inactive (high imped-
ance, open drain) until the fault is removed. The action taken by
the A6265 when a fault occurs is defined in table 1. To be able to
monitor the state of FF1 and FF2, add a suitable external pull-up
resistor.
The A6265 will continue to drive the LEDs under most fault con-
ditions and will only disable the drive to the LEDs when a high
voltage hazard is present or the external components are likely to
be over-stressed. For output short circuits or open LED condi-
tions, the fault status is latched until EN is taken low or a power
cycle occurs. For output short circuits or a shorted LED string,
the fault status is latched until either EN is taken low for a period
greater than the disable time, or a power cycle occurs.
At start-up, a Fault Blank period, t
FB ,
occurs before the fault
detection circuitry becomes active. This period allows steady
state conditions to be established before fault monitoring takes
place.
Note that no fault blanking is applied to open LED faults. This
is generally not an issue because the charging of the output filter
capacitor provides a degree of filtering. In addition, extremely
high voltages are prevented from causing potential device break-
down, for example in the external switching MOSFET.
VREG Undervoltage If the voltage at VREG, V
REG
, drops
below the specified turnoff voltage, V
REGUV
, the gate drive
output, SG, will be driven low and both fault flags, FF1 and
FF2, will be high impedance. V
REG
must rise above the turn-on
threshold, V
REGUV
+ V
REGUV
, before the output circuits are
activated. This ensures that the external FET is operating in its
fully enhanced state and avoids permanent damage to the FET,
caused by overheating.
LED Undercurrent Under some circuit conditions, particularly
during a low input voltage condition, it is possible that there
could be insufficient drive to maintain the current to the LEDs
at the required level. If the voltage across the LED current sense
resistor, R
SS
, falls below the target sense voltage, V
IDL
, by an
amount that is more than the LED undercurrent voltage differ-
ence, V
UCL
, the A6265 will indicate an LED undercurrent condi-
tion by setting FF2 to high impedance. However, the A6265 will
continue to drive the output. When the output again reaches the
required current level, FF2 will go low.
Overtemperature Warning If the chip temperature exceeds
the overtemperature threshold, T
JF
, fault flag FF2 will be high
impedance. No action will be taken by the A6265 to limit the
chip temperature. An external control circuit must take action
to avoid permanent damage to the A6265 and/or the LEDs. The
temperature will continue to be monitored and the fault flags will
be deactivated when the temperature drops below the recovery
threshold provided by the hysteresis, T
Jhys
.
LED Diagnostics The status of the LEDs in the load can be
determined by monitoring the voltage with respect to ground at
the three pins LP, LF, and LA, namely V
LP
, V
LF
, and V
LA
. These
voltages provide two differential voltage measurements:
• the voltage across a single reference LED:
V
LED
= V
LF
– V
LP
(5)
• the ratio of the voltage across all LEDs in a single string:
V
STR
= V
LA
– V
LP
(6)
The voltage, V
STR
, is derived from the voltage across all LEDs in
the string, by an external resistor divider with a ratio equal to the
quantity of LEDs in the string. To minimize the effects of the bias
currents introducing an offset voltage, it is recommended that the
resistor between LP and LA should be approximately 560 .
So for example, if eight LEDs were used, the ratio required
would be an eighth, therefore the resistor connected between LA
and the anode end of the LED string would be 3.9 k;
560 / [560 + 3900] = 1/8 .
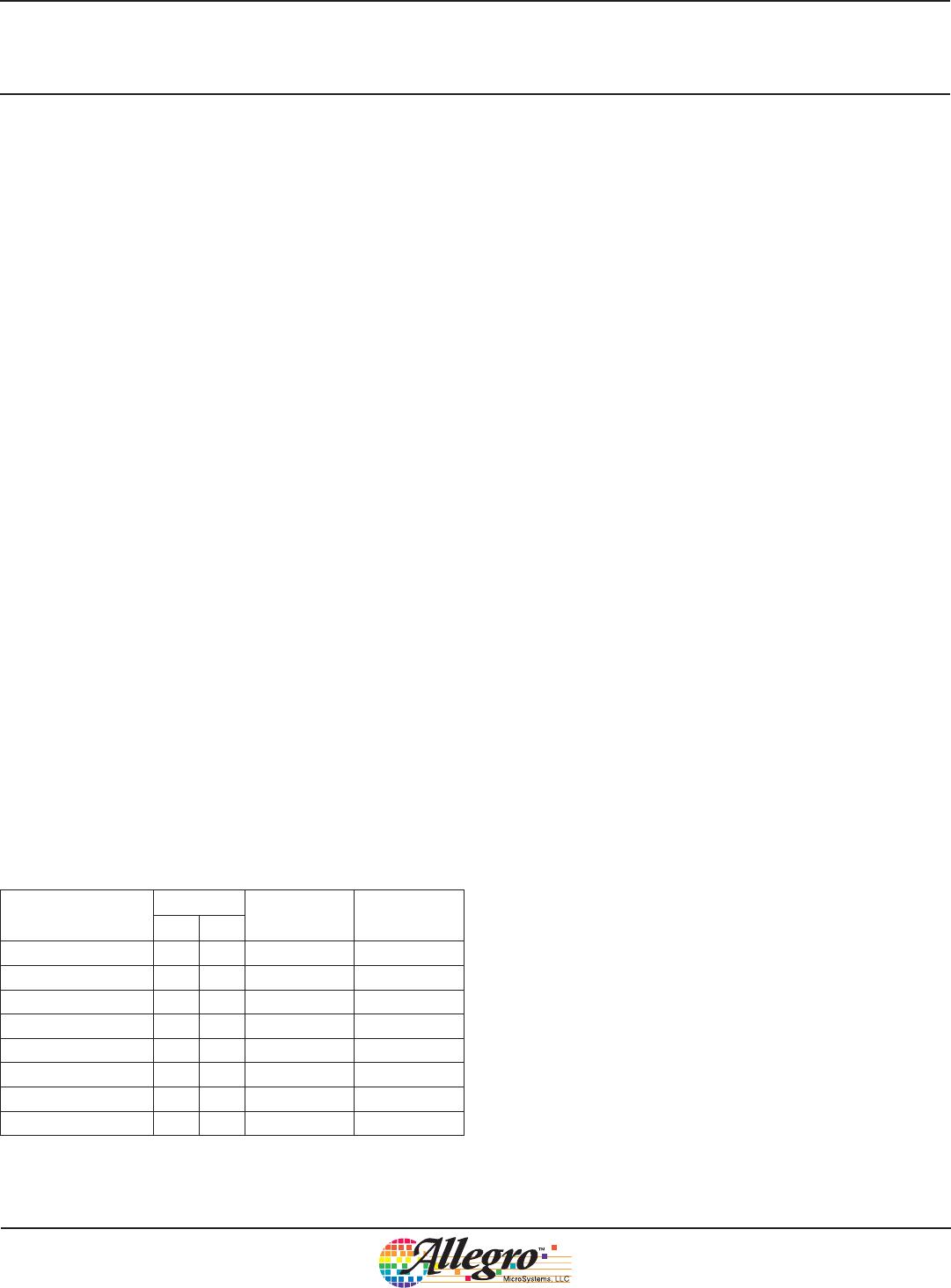
Table 1. Fault Table
Fault
Pin
Action Latched
FF1 FF2
No Fault L L No Action –
VREG Undervoltage Z Z Disable* No
Output Short Z L Disable* Yes
LED Undercurrent L Z No Action No
Overtemperature L Z No Action No
Open LED L Z Disable* Yes
Shorted LED L Z No Action No
Shorted LED String Z L Disable* Yes
* SG low, MOSFET off
L = active pull-down, Z = inactive, open drain