LTC4219
12
4219fd
For more information www.linear.com/LTC4219
applicaTions inFormaTion
If V
DD
drops below 2.65V for greater than 5µs or INTV
CC
drops below 2.5V for greater than 1µs, a fast shutdown
of the switch is initiated. The GATE is pulled down with a
140mA current to the OUT pin.
Overcurrent Fault
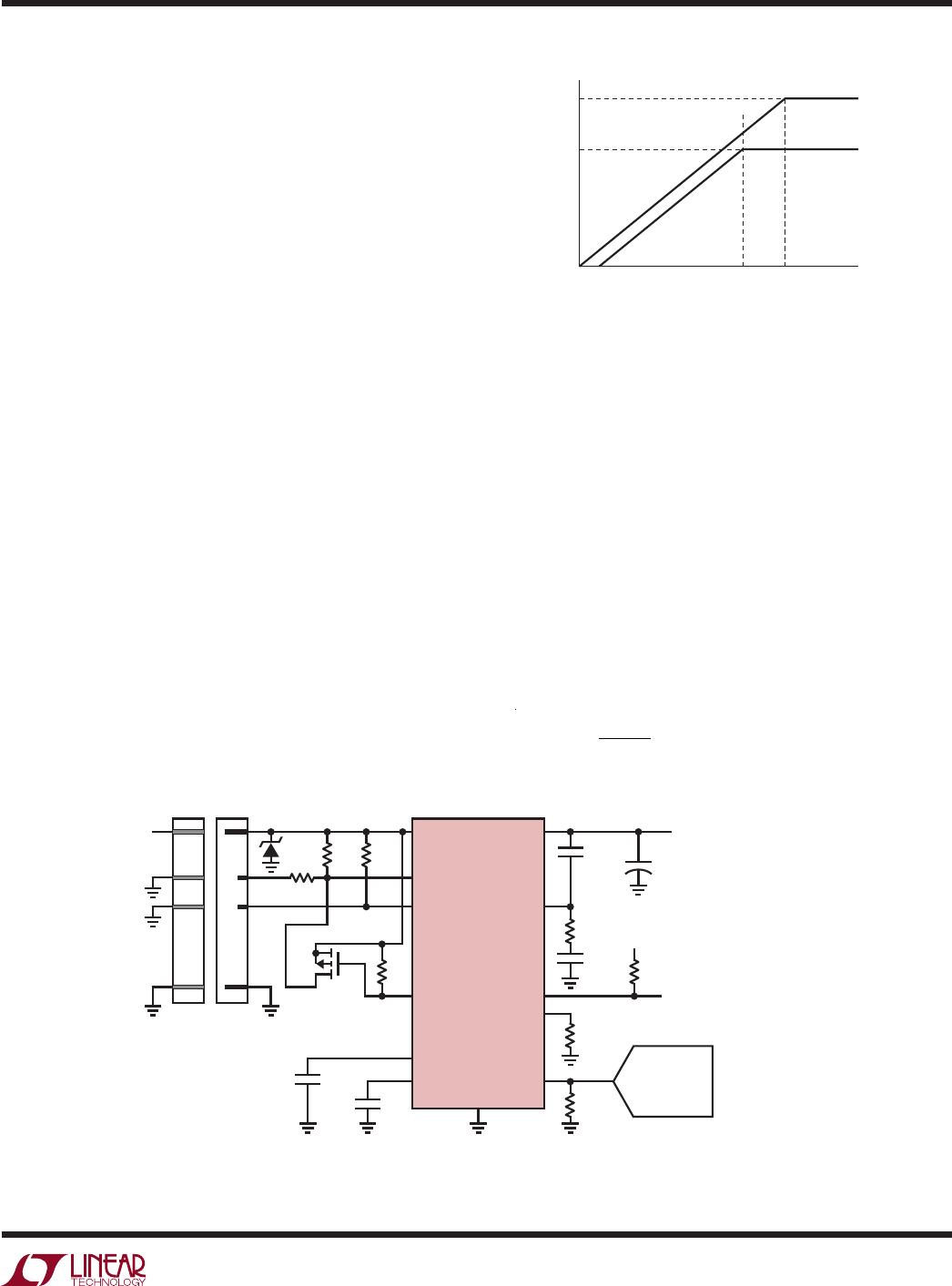
The LTC4219 features an adjustable current limit with
foldback that protects against short circuits and excessive
load current. To prevent excessive power dissipation in the
switch during active current limit, the available current is
reduced as a function of the output voltage sensed by the
FB pin. A graph in the Typical Performance Characteristics
curves shows the current limit versus FB voltage.
An overcurrent fault occurs when the current limit circuitry
has been engaged for longer than the time-out delay set
by the TIMER. Current limiting begins when the MOSFET
current reaches 1.5A to 5.6A (depending on the foldback).
The GATE pin is then brought down with a 140mA GATE-
to-OUT current. The voltage on the GATE is regulated in
order to limit the current to less than 5.6A. At this point,
a circuit breaker time delay starts by charging the external
timing capacitor with a 100µA pull-up current from the
TIMER pin. If the TIMER pin reaches its 1.235V threshold,
the internal switch turns off (with a 250µA current from
GATE to ground). Included in the Typical Performance
Characteristics curves is a graph of the Safe Operating
Area for the MOSFET. From this graph one can determine
the MOSFET’s maximum time in current limit for a given
output power.
Tying the TIMER pin to INTV
CC
will force the part to use
the internally generated (circuit breaker) delay of 2ms.
In either case the F LT pin is pulled low to indicate an
overcurrent fault has turned off the pass MOSFET. For a
given circuit breaker time delay, the equation for setting
the timing capacitor’s value is as follows:
C
T
= t
CB
• 0.083[µF/ms]
After the switch is turned off, the TIMER pin begins
discharging the timing capacitor with a 2µA pull-down
current. When the TIMER pin reaches its 0.21V threshold,
an internal 100ms timer is started. After the 100ms delay,
the switch is allowed to turn on again if the overcurrent
fault latch has been cleared. Bringing the EN1 pin above
When the GATE voltage reaches the MOSFET threshold
voltage, the switch begins to turn on and the OUT volt
-
age follows the GATE voltage as it increases. Once OUT
reaches V
DD
, the GATE will ramp up until clamped by the
6.15V Zener between GATE and OUT.
As the OUT voltage rises, so will the FB pin which is moni
-
toring it. Once the FB pin crosses its 1.235V threshold and
the GATE to OUT voltage exceeds 4.2V, the PG pin pulls
low indicating that the power is good.
Parasitic MOSFET Oscillation
When the N-channel MOSFET ramps up the output dur
-
ing power-up it operates as a source follower. The source
follower configuration may self-oscillate in the range of
25
kHz to
300kHz when the load capacitance is less than
10µF, especially if the wiring inductance from the supply
to the V
DD
pin is greater than 3µH. The possibility of oscil-
lation will increase as the load current (during power-up)
increases.
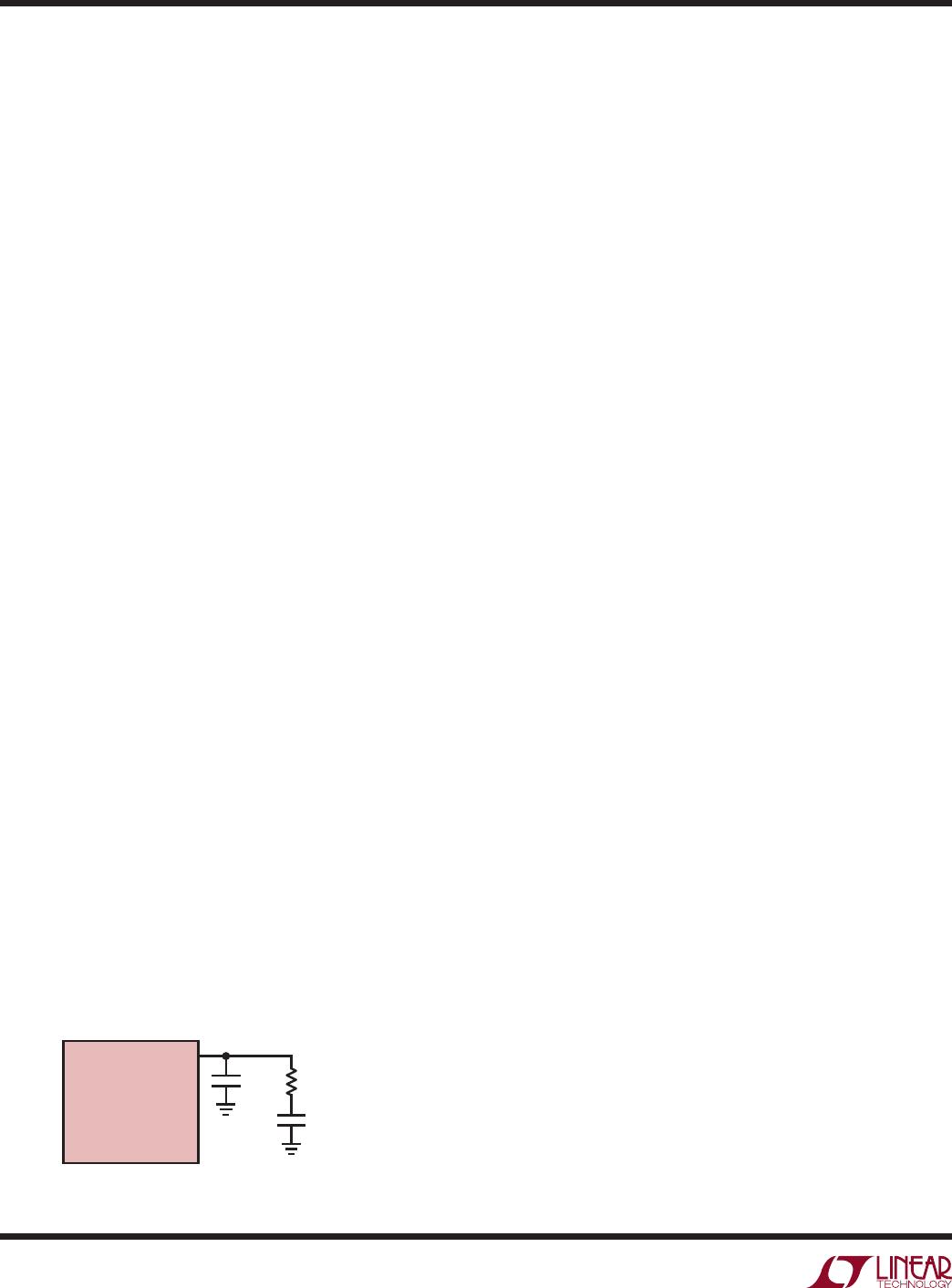
There are two ways to prevent this type of
oscillation. The simplest way is to avoid load capacitances
below 10µF. For wiring inductance larger than 20µH, the
minimum load capacitance may extend to 100µF. A second
choice is to connect an external gate capacitor C
P
>1.5nF
as shown in Figure 3.
Turn-Off Sequence
The switch can be turned off by a variety of conditions. A
normal turn-off is initiated by either the EN1 or EN2 pins
going above their 1.235V threshold. Additionally, several
fault conditions will turn off the switch. These include over
-
current circuit breaker (SENSE pin) or overtemperature.
Normally the switch is turned off with a 250µ
A current
pulling down the GATE pin to ground. With the switch
turned off, the OUT voltage drops which pulls the FB pin
below its threshold. PG then goes high to indicate output
power is no longer good.
Figure 3. Compensation for Small C
LOAD
4219 F03
LTC4219
OPTIONAL
RC TO LOWER
INRUSH CURRENT
GATE
C
P
2.2nF