NBC12429, NBC12429A
http://onsemi.com
10
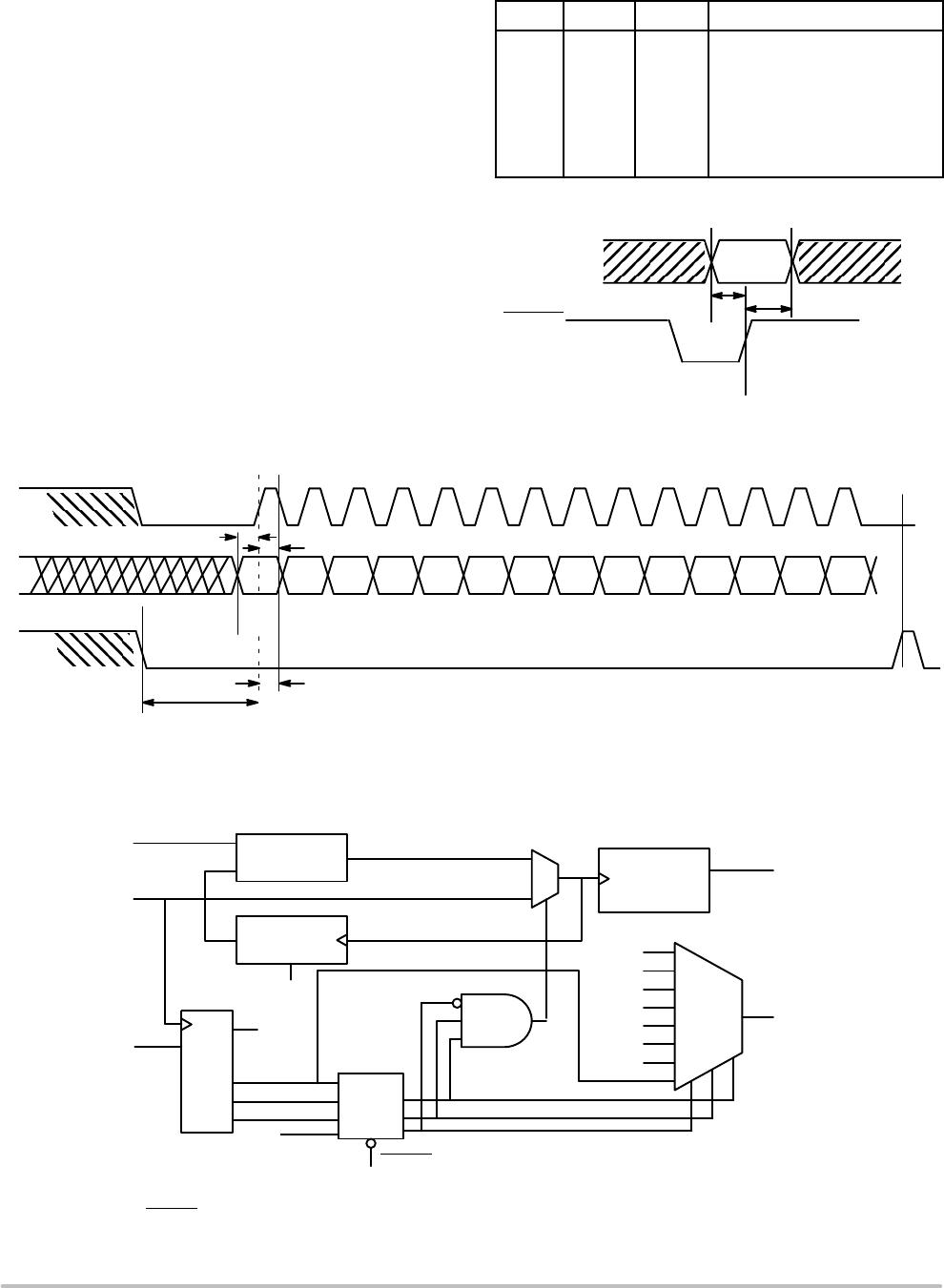
S_CLOCK signal samples the information on the S_DATA
line and loads it into a 14 bit shift register. Note that the
P_LOAD
signal must be HIGH for the serial load operation
to function. The Test register is loaded with the first three
bits, the N register with the next two, and the M register with
the final nine bits of the data stream on the S_DATA input.
For each register, the most significant bit is loaded first (T2,
N1, and M8). A pulse on the S_LOAD pin after the shift
register is fully loaded will transfer the divide values into the
counters. The HIGH to LOW transition on the S_LOAD
input will latch the new divide values into the counters.
Figures 5 and 6 illustrate the timing diagram for both a
parallel and a serial load of the device synthesizer.
M[8:0] and N[1:0] are normally specified once at
powerup through the parallel interface, and then possibly
again through the serial interface. This approach allows the
application to come up at one frequency and then change or
fine−tune the clock as the ability to control the serial
interface becomes available.
The TEST output provides visibility for one of the several
internal nodes as determined by the T[2:0] bits in the serial
configuration stream. It is not configurable through the
parallel interface. The T2, T1, and T0 control bits are preset
to ‘000’ when P_LOAD
is LOW so that the PECL F
OUT
outputs are as jitter−free as possible. Any active signal on the
TEST output pin will have detrimental affects on the jitter
of the PECL output pair. In normal operations, jitter
specifications are only guaranteed if the TEST output is
static. The serial configuration port can be used to select one
of the alternate functions for this pin.