MT89L86 Data Sheet
12
Zarlink Semiconductor Inc.
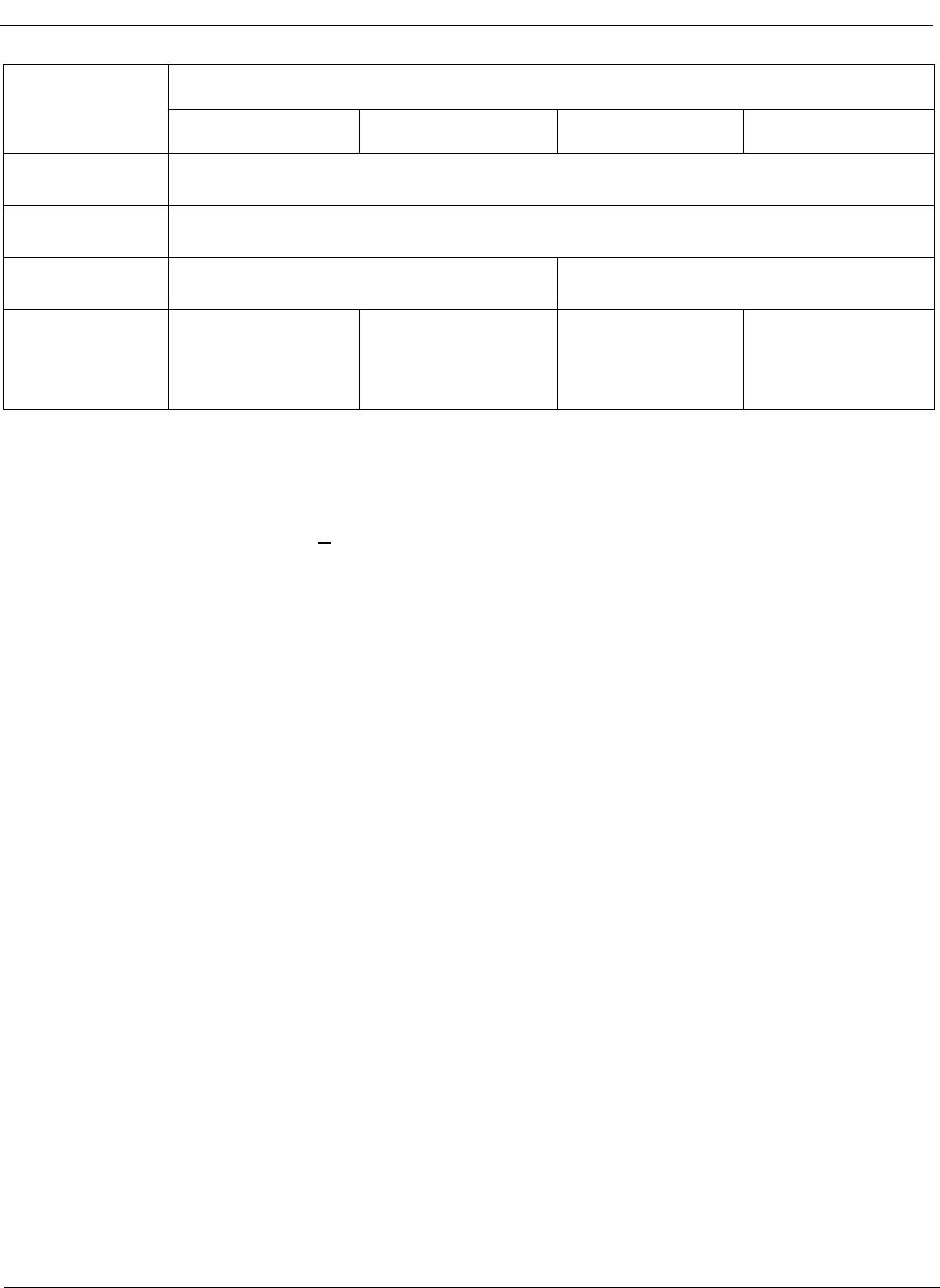
Table 4 - Constant Throughput Delay Values
Microprocessor Port
The non-multiplexed bus interface provided by the MT89L86 is identical to that provided in the MT8986 Digital
Switch device. In addition to the non-multiplexed bus, this 3.3 V MT89L86 device provides an enhanced
microprocessor interface with multiplexed bus structure compatible to both Motorola and Intel buses. The
multiplexed bus structure is selected by the CPU Interface Mode (IM) input pin.
If the IM input pin is connected to ground, the MT89L86’s parallel port assumes its default Motorola non-multiplexed
bus mode identical to that of MT8986. If the IM input is connected HIGH, the internal parallel microprocessor port
provides compatibility to MOTEL (MOtorola and InTEL compatible bus) interface allowing direct connection to Intel,
National and Motorola CPUs.
The on-chip MOTEL circuit automatically identifies the type of CPU Bus connected to the device. This circuit uses
the level of the DS/RD
input pin at the rising edge of the AS/ALE to identify the appropriate bus timing connected to
the MT89L86. If DS/RD
is LOW at the rising edge of AS/ALE then the Motorola bus timing is selected. If DS/RD is
HIGH at the rising edge of AS/ALE, the Intel bus timing is selected.
When the parallel port of this device is operating in Motorola, National or Intel multiplexed bus interfaces, the
signals available for controlling the device are: AD0-AD7 (Data and Address), ALE/AS (Address Latch
Enable/Address Strobe), DS/RD
(Data Strobe/Read), R/W\WR (Read/Write\Write), CS (Chip Select) and DTA (Data
Acknowledgment). In the Motorola non-multiplexed bus mode, the interface control signals are: data bus (AD0-
AD7), six address input lines (A0-A5) and four control lines (CS
, DS, R/W and DTA). See Figures 25 to 27 for each
CPU interface timing.
The parallel microprocessor port provides the access to the IMS, Control registers, the Connection Memory High,
the Connection Memory Low and the Data Memory. All locations can be read or written except for the data memory
which can be read only.
Software Control
The address bus on the microprocessor interface selects the internal registers and memories of the MT89L86. If
the A5 address input is LOW, the Internal Control, Interface Mode, Stream Pair Selection and Frame Input Offset
registers are addressed by the A4 to A0 bits according to Table 5. If the A5 input is HIGH, the remaining address
input lines are used to select memory subsections of up to 128 locations corresponding to the maximum number of
channels per input or output stream. The address input lines and the Stream Address bits (STA) of the Control
register give the user the capability of accessing all sections of the MT89L86’s Data and Connect memories.
The Control and Interface Mode Selection registers together control all the major functions of the device. The
Interface Mode Select register should be set up during system power-up to establish the desired switching
configuration as explained in the Serial Interface and Switching Configurations sections.
Data Rate Throughput Delay (d)
2.048 Mb/s d=[32 + (32 - IN) + (OUT - 1)]; (expressed in # time-slots)
2.048 Mb/s time-slot: 3.9s
IN: input time-slot (from 1 to 32)
OUT: output time-slot (from 1 to 32)
4.096 Mb/s d=[64 + (64 - IN) + (OUT - 1)]; (expressed in # time-slots)
4.096 Mb/s time-slot: 1.95 s
IN: input time-slot (from 1 to 64)
OUT: output time-slot (from 1 to 64)
8.192 Mb/s d=[128 + (128 - IN) + (OUT - 1)]; (expressed in # time-slots)
8.192 Mb/s time-slot: 0.975 s
IN: input time-slot (from 1 to 128)
OUT: output time-slot (from 1 to 128)