LT3480
9
3480fe
For more information www.linear.com/LT3480
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
OPERATION
FB Resistor Network
The output voltage is programmed with a resistor divider
between the output and the FB pin. Choose the 1% resis-
tors according to:
R1=R2
V
OUT
0.79V
−1
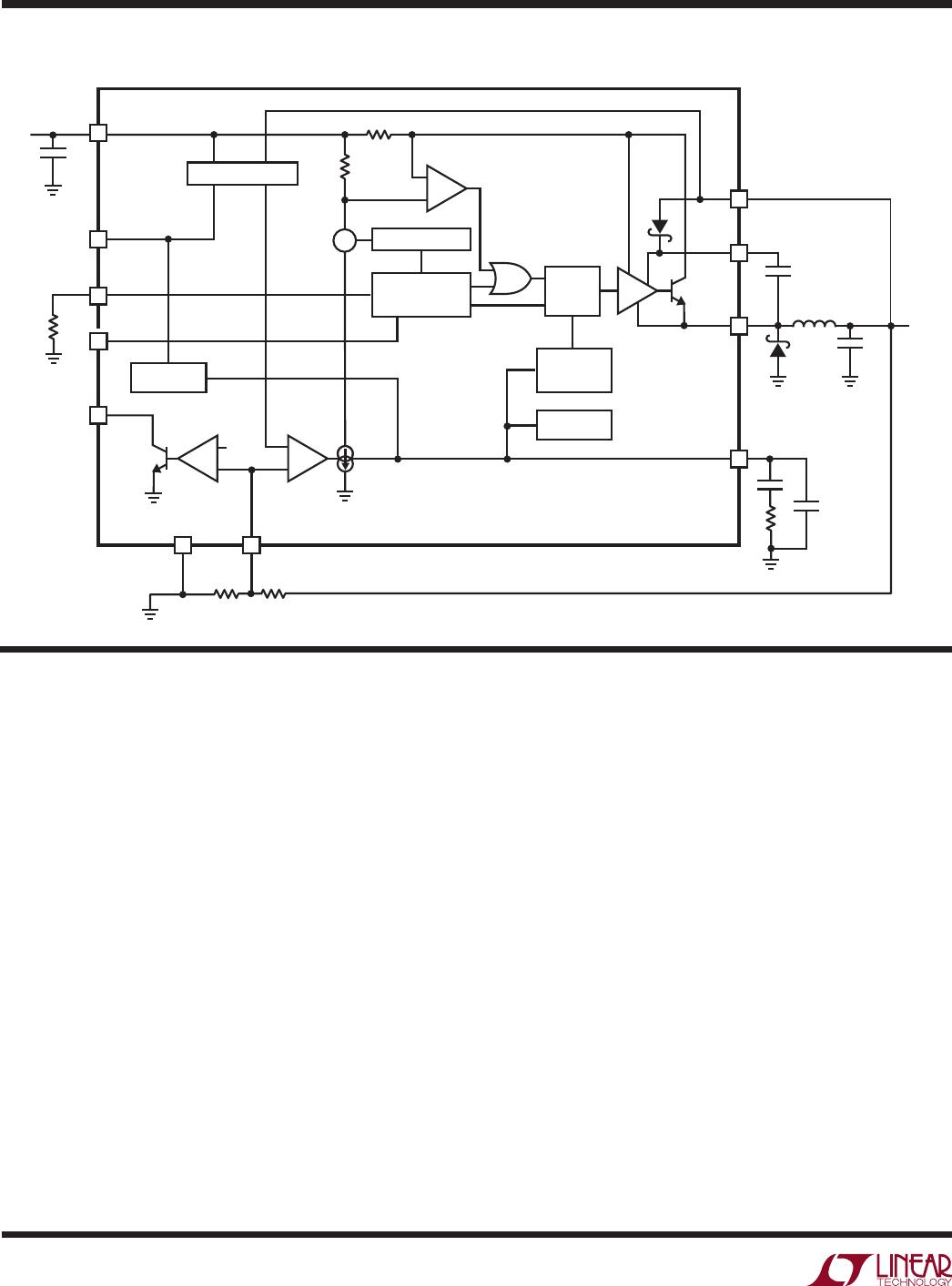
Reference designators refer to the Block Diagram.
Setting the Switching Frequency
The LT3480 uses a constant frequency PWM architecture
that can be programmed to switch from 200kHz to 2.4MHz
by using a resistor tied from the RT pin to ground. A table
showing the necessary R
T
value for a desired switching
frequency is in Figure 1.
SWITCHING FREQUENCY (MHz)
R
T
VALUE (kΩ)
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.0
2.2
2.4
187
121
88.7
68.1
56.2
46.4
40.2
34
29.4
23.7
19.1
16.2
13.3
11.5
9.76
8.66
Figure 1. Switching Frequency vs. R
T
Value
Operating Frequency Tradeoffs
Selection of the operating frequency is a tradeoff between
efficiency, component size, minimum dropout voltage, and
maximum input voltage. The advantage of high frequency
operation is that smaller inductor and capacitor values may
be used. The disadvantages are lower efficiency, lower
maximum input voltage, and higher dropout voltage. The
highest acceptable switching frequency (f
SW(MAX)
) for a
given application can be calculated as follows:
f
SW(MAX)
=
D
OUT
t
ON(MIN)
V
D
+ V
IN
– V
SW
(
where V
IN
is the typical input voltage, V
OUT
is the output
voltage, V
D
is the catch diode drop (~0.5V) and V
SW
is the
internal switch drop (~0.5V at max load). This equation
shows that slower switching frequency is necessary to
safely accommodate high V
IN
/V
OUT
ratio. Also, as shown
in the next section, lower frequency allows a lower dropout
voltage. The reason input voltage range depends on the
switching frequency is because the LT3480 switch has finite
minimum on and off times. The switch can turn on for a
minimum of ~150ns and turn off for a minimum of ~150ns.
Typical minimum on time at 25°C is 80ns. This means that
the minimum and maximum duty cycles are:
MIN
SW
ON(MIN)
DC
MAX
= 1– f
SW
t
OFF(MIN
where f
SW
is the switching frequency, the t
ON(MIN)
is the
minimum switch on time (~150ns), and the t
OFF(MIN)
is
the minimum switch off time (~150ns). These equations
show that duty cycle range increases when switching
frequency is decreased.
The LT3480 contains a power good comparator which trips
when the FB pin is at 86% of its regulated value. The PG
output is an open-collector transistor that is off when the
output is in regulation, allowing an external resistor to pull
the PG pin high. Power good is valid when the LT3480 is
enabled and V
IN
is above 3.6V.
The LT3480 has an overvoltage protection feature which
disables switching action when the V
IN
goes above 38V
typical (36V minimum). When switching is disabled, the
LT3480 can safely sustain input voltages up to 60V.