© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21073K-page 9
24AA65/24LC65/24C65
5.0 READ OPERATION
Read operations are initiated in the same way as write
operations with the exception that the R/W
bit of the
slave address is set to one. There are three basic types
of read operations: current address read, random read
and sequential read.
5.1 Current Address Read
The 24XX65 contains an address counter that main-
tains the address of the last word accessed, internally
incremented by one. Therefore, if the previous access
(either a read or write operation) was to address n (n is
any legal address), the next current address read
operation would access data from address n + 1. Upon
receipt of the slave address with R/W
bit set to one, the
24XX65 issues an acknowledge and transmits the
eight-bit data word. The master will not acknowledge
the transfer but does generate a Stop condition and the
24XX65 discontinues transmission (Figure 4-3).
5.2 Random Read
Random read operations allow the master to access
any memory location in a random manner. To perform
this type of read operation, first the word address must
be set. This is done by sending the word address to the
24XX65 as part of a write operation (R/W
bit set to ‘0’).
After the word address is sent, the master generates a
Start condition following the acknowledge. This
terminates the write operation, but not before the
internal Address Pointer is set. Then the master issues
the control byte again, but with the R/W
bit set to a one.
The 24XX65 will then issue an acknowledge and
transmit the eight-bit data word. The master will not
acknowledge the transfer, but does generate a Stop
condition which causes the 24XX65 to discontinue
transmission (Figure 4-4).
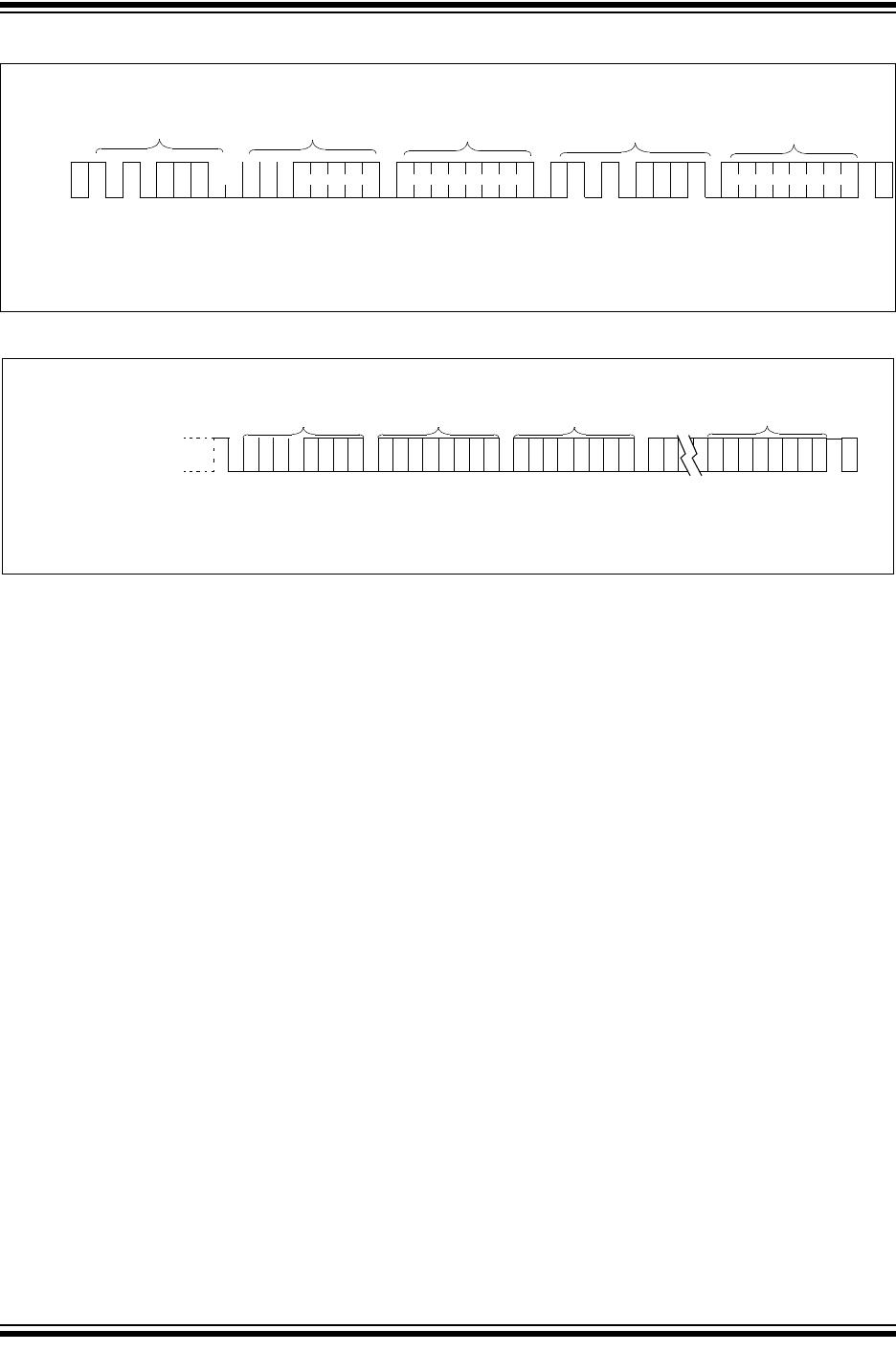
5.3 Sequential Read
Sequential reads are initiated in the same way as a
random read except that after the 24XX65 transmits the
first data byte, the master issues an acknowledge as
opposed to the Stop condition used in a random read.
This acknowledge directs the 24XX65 to transmit the
next sequentially addressed 8-bit word (Figure 4-5).
Following the final byte transmitted to the master, the
master will NOT generate an acknowledge, but will
generate a Stop condition.
To provide sequential reads the 24XX65 contains an
internal Address Pointer which is incremented by one
at the completion of each operation. This Address
Pointer allows the entire memory contents to be serially
read during one operation.
5.4 Contiguous Addressing Across
Multiple Devices
The device select bits A2, A1, A0 can be used to
expand the contiguous address space for up to 512K
bits by adding up to eight 24XX65's on the same bus.
In this case, software can use A0 of the control byte
as
address bit A13, A1 as address bit A14 and A2 as
address bit A15.
5.5 Noise Protection
The SCL and SDA inputs have filter circuits which
suppress noise spikes to assure proper device
operation even on a noisy bus. All I/O lines incorporate
Schmitt Triggers for 400 kHz (Fast mode) compatibility.
5.6 High Endurance Block
The location of the high endurance block within the
memory map is programmed by setting the leading bit
7 (S/HE) of the configuration byte to ‘0’. The upper bits
of the address loaded in this command will determine
which 4K block within the memory map will be set to
high endurance. This block will be capable of
10,000,000 erase/write cycles typical (Figure 8-1).
The high endurance block will retain its value as the
high endurance block even if it resides within the
security block range. The high endurance setting
always takes precedence to the security setting.
Note: The high endurance block cannot be
changed after the security option has been
set with a length greater than zero. If the
H.E. block is not programmed by the user,
the default location is the highest block of
memory which starts at location 0x1E00
and ends at 0x1FFF.