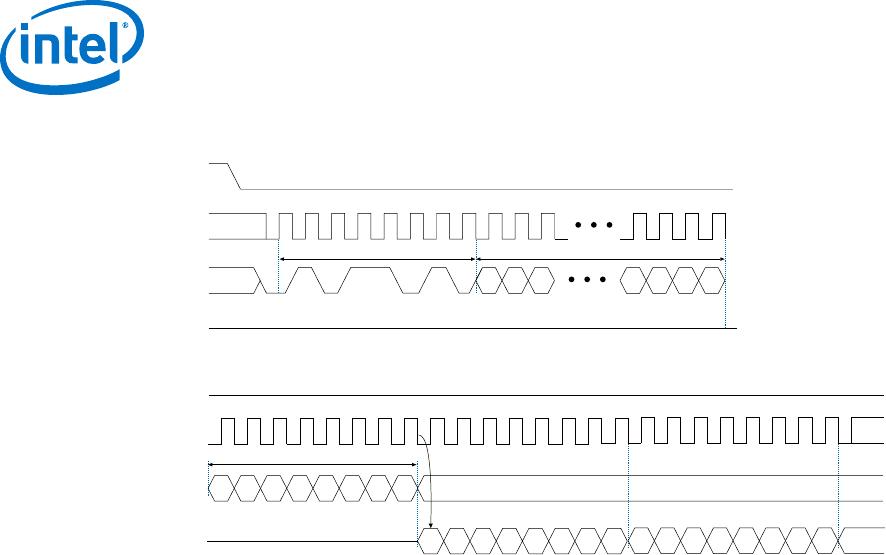
Figure 16. Erase Bulk Operation Timing Diagram
Operation Code (C7h)
DATA0
nCS
DCLK
0 1
2
3 4
5
6 7
The device initiates a self-timed erase bulk cycle immediately after the nCS signal is
driven high. For details about the self-timed erase bulk cycle time, refer to t
EB
in the
related information below.
You must account for this delay before accessing the memory contents. Alternatively,
you can check the write in progress bit in the status register by executing the read
status operation while the self-timed erase cycle is in progress. The write in progress
bit is set to 1 during the self-timed erase cycle and 0 when it is complete. The write
enable latch bit in the status register is reset to 0 before the erase cycle is complete.
1.9.12. Erase Sector Operation (D8h)
The erase sector operation allows you to erase a certain sector in the EPCQ-A device
by setting all the bits inside the sector to 1 or 0xFF. This operation is useful if you
want to access the unused sectors as a general purpose memory in your applications.
You must execute the write enable operation before the erase sector operation.
When you execute the erase sector operation, you must first shift in the erase sector
operation code, followed by the 3-byte address (A[23..0]) of the chosen sector on
the DATA0 pin. The 3-byte address for the erase sector operation can be any address
inside the specified sector. Drive the nCS signal high after the eighth bit of the erase
sector operation code has been latched in.
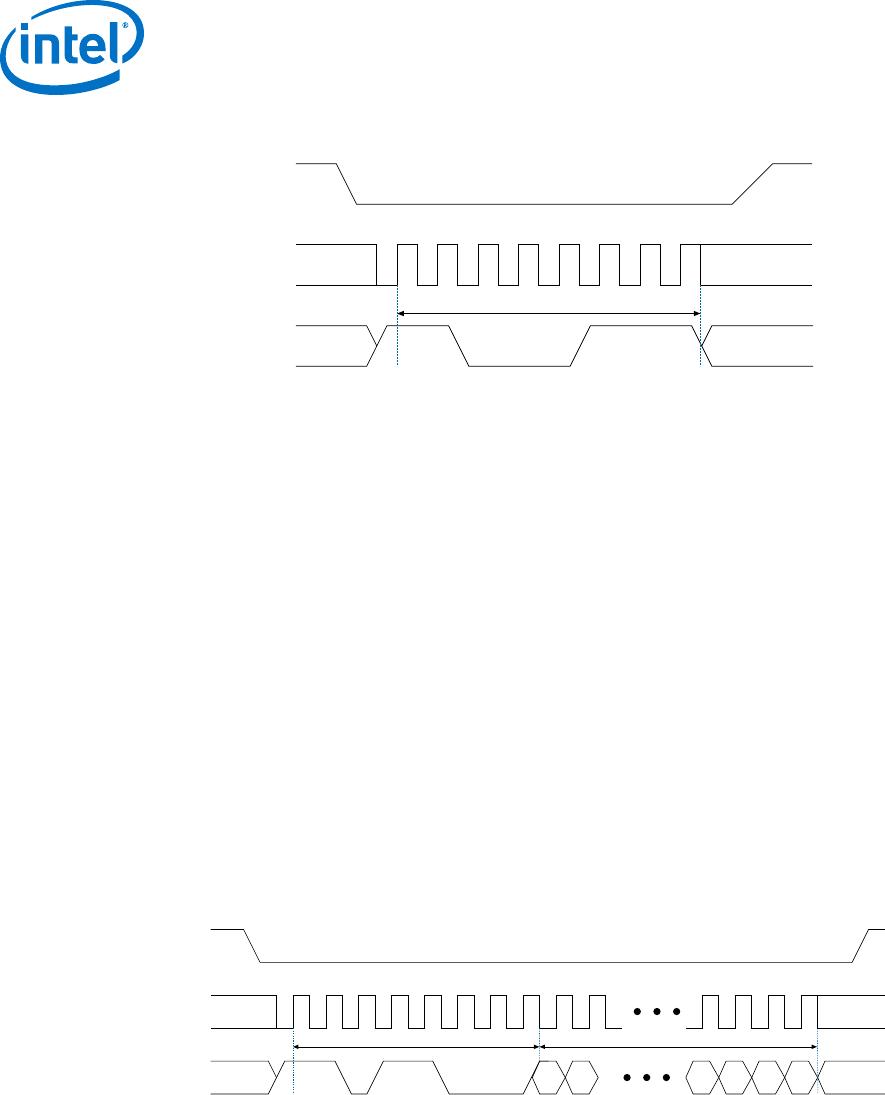
Figure 17. Erase Sector Operation Timing Diagram
DATA0
Operation Code (D8h) 24-Bit Address
nCS
DCLK
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 28 29 30 31
3 2
1 023 22
MSB
The device initiates a self-timed erase sector cycle immediately after the nCS signal is
driven high. For details about the self-timed erase sector cycle time, refer to t
ES
in the
related information below. You must account for this amount of delay before another
page of memory is written. Alternatively, you can check the write in progress bit in the
status register by executing the read status operation while the self-timed erase cycle
is in progress. The write in progress bit is set to 1 during the self-timed erase cycle
and 0 when it is complete. The write enable latch bit in the status register is set to 0
before the self-timed erase cycle is complete.
1. EPCQ-A Serial Configuration Device Datasheet
CF52014 | 2018.04.11
EPCQ-A Serial Configuration Device Datasheet
28