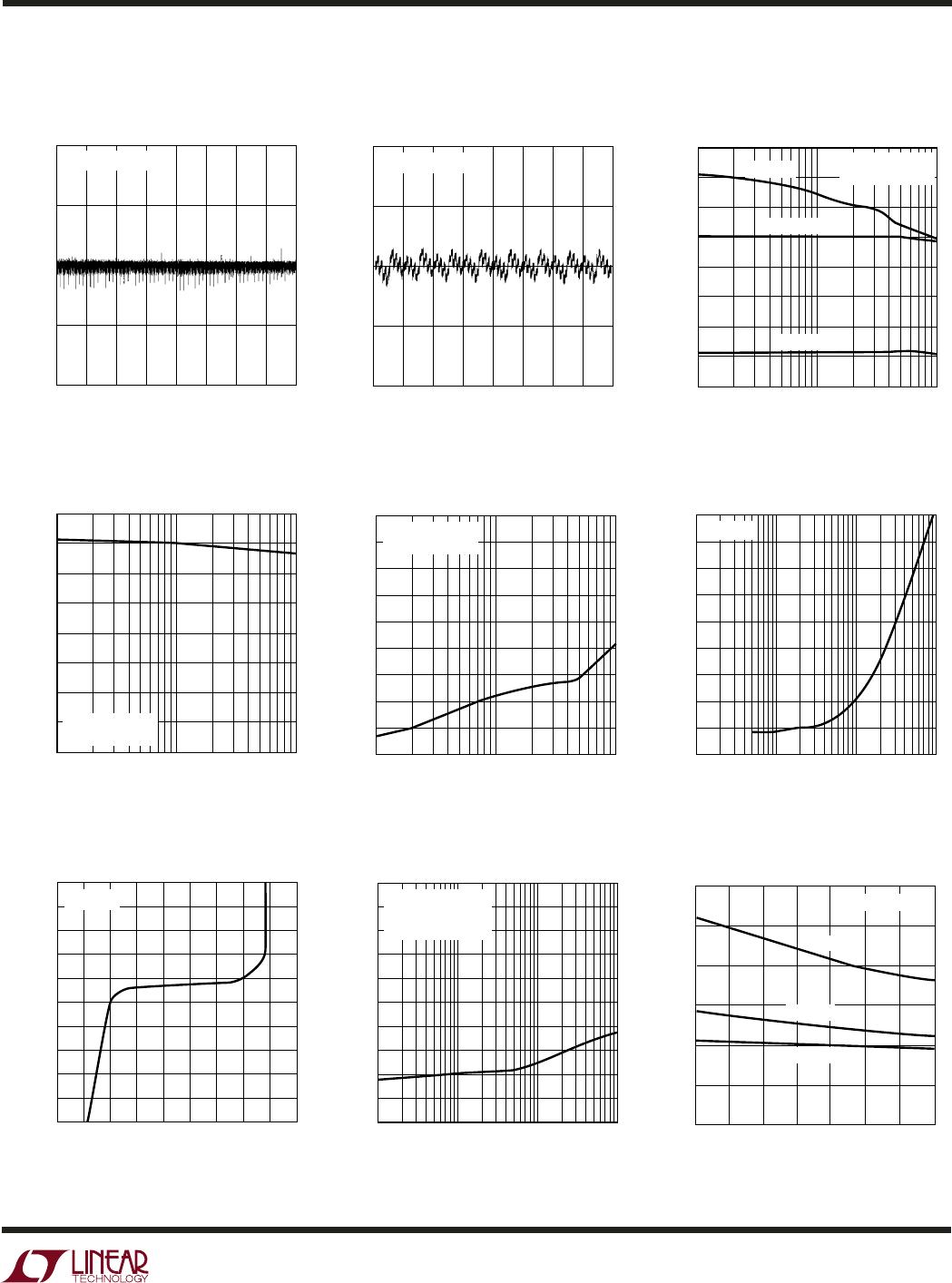
4
LTC1401
1401fa
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
f
SAMPLE(MAX)
Maximum Sampling Frequency ● 200 kHz
t
CONV
Conversion Time f
CLK
= 3.2MHz ● 4.1 µs
t
ACQ
Acquisition Time 315 ns
f
CLK
CLK Frequency ● 0.1 3.2 MHz
t
CLK
CLK Pulse Width (Notes 5 and 8) ● 60 ns
t
WK(NAP)
Time to Wake Up from Nap Mode 350 ns
t
1
CLK Pulse Width to Return to Active Mode ● 60 ns
t
2
CONV↑ to CLK↑ Setup Time ● 100 ns
t
3
CONV↑ After Leading CLK↑ ● 0ns
t
4
CONV Pulse Width (Note 7) ● 50 ns
t
5
Time from CLK↑ to Sample Mode 80 ns
t
6
Aperture Delay of Sample-and-Hold Jitter < 50ps 45 ns
t
7
Minimum Delay Between Conversion (Note 5) ● 350 550 ns
t
8
Delay Time, CLK↑ to D
OUT
Valid C
LOAD
= 20pF ● 60 120 ns
t
9
Delay Time, CLK↑ to D
OUT
Hi-Z C
LOAD
= 20pF ● 60 120 ns
t
10
Time from Previous Data Remains Valid After CLK↑ C
LOAD
= 20pF ● 15 50 ns
t
11
Minimum Time Between Nap/Sleep Request to Wake Up Request (Notes 5 and 8) ● 50 ns
TI I G CHARACTERISTICS
W
U
Note 1: Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. Exposure to any Absolute
Maximum Rating condition for extended periods may affect device
reliability and lifetime.
Note 2: All voltage values are with respect to GND.
Note 3: When these pin voltages are taken below GND or above V
CC
, they
will be clamped by internal diodes. This product can handle input currents
greater than 40mA without latch-up if the pin is driven below GND or
above V
CC
.
Note 4: When these pin voltages are taken below GND, they will be clamped
by internal diodes. This product can handle input currents greater than 40mA
without latch-up if the pin is driven below GND. These pins are not clamped
to V
CC
.
Note 5: Guaranteed by design, not subject to test.
Note 6: Integral nonlinearity is defined as the deviation of a code from a
straight line passing through the actual endpoints of the transfer curve.
The deviation is measured from the center of the quantization band.
Note 7: The rising edge of CONV starts a conversion. If CONV returns low
at a bit decision point during the conversion, it can create small errors. For
best performance, ensure that CONV returns low either within 120ns after
the conversion starts (i.e., before the first bit decision) or after the 14
clock cycles. (Figure 13 Timing Diagram).
Note 8: If this timing specification is not met, the device may not respond
to a request for a conversion. To recover from this condition a NAP
request is required.
The ● denotes specifications which apply over the full operating temperature range,
unless otherwise noted specifications are at T
A
= 25°C. V
CC
= 3V, f
SAMPLE
= 200kHz, t
r
= t
f
= 5ns, unless otherwise specified.