PCA9555 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP Semiconductors N.V. 2017. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet Rev. 10 — 8 November 2017 28 of 34
NXP Semiconductors
PCA9555
16-bit I
2
C-bus and SMBus I/O port with interrupt
• Process issues, such as application of adhesive and flux, clinching of leads, board
transport, the solder wave parameters, and the time during which components are
exposed to the wave
• Solder bath specifications, including temperature and impurities
15.4 Reflow soldering
Key characteristics in reflow soldering are:
• Lead-free versus SnPb soldering; note that a lead-free reflow process usually leads to
higher minimum peak temperatures (see Figure 30
) than a SnPb process, thus
reducing the process window
• Solder paste printing issues including smearing, release, and adjusting the process
window for a mix of large and small components on one board
• Reflow temperature profile; this profile includes preheat, reflow (in which the board is
heated to the peak temperature) and cooling down. It is imperative that the peak
temperature is high enough for the solder to make reliable solder joints (a solder paste
characteristic). In addition, the peak temperature must be low enough that the
packages and/or boards are not damaged. The peak temperature of the package
depends on package thickness and volume and is classified in accordance with
Table 16
and 17
Moisture sensitivity precautions, as indicated on the packing, must be respected at all
times.
Studies have shown that small packages reach higher temperatures during reflow
soldering, see Figure 30
.
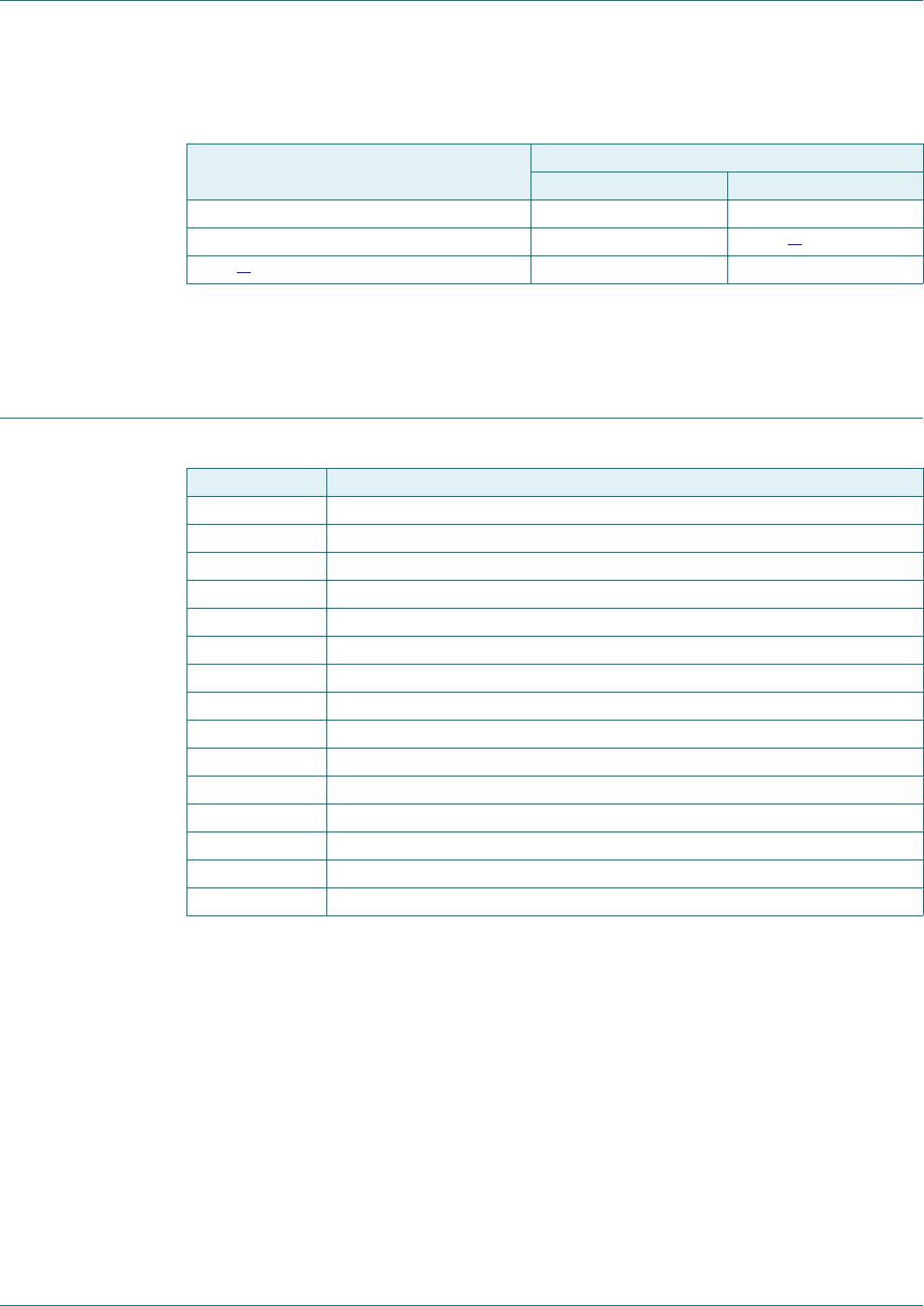
Table 16. SnPb eutectic process (from J-STD-020C)
Package thickness (mm) Package reflow temperature (C)
Volume (mm
3
)
< 350 350
< 2.5 235 220
2.5 220 220
Table 17. Lead-free process (from J-STD-020C)
Package thickness (mm) Package reflow temperature (C)
Volume (mm
3
)
< 350 350 to 2000 > 2000
< 1.6 260 260 260
1.6 to 2.5 260 250 245
> 2.5 250 245 245