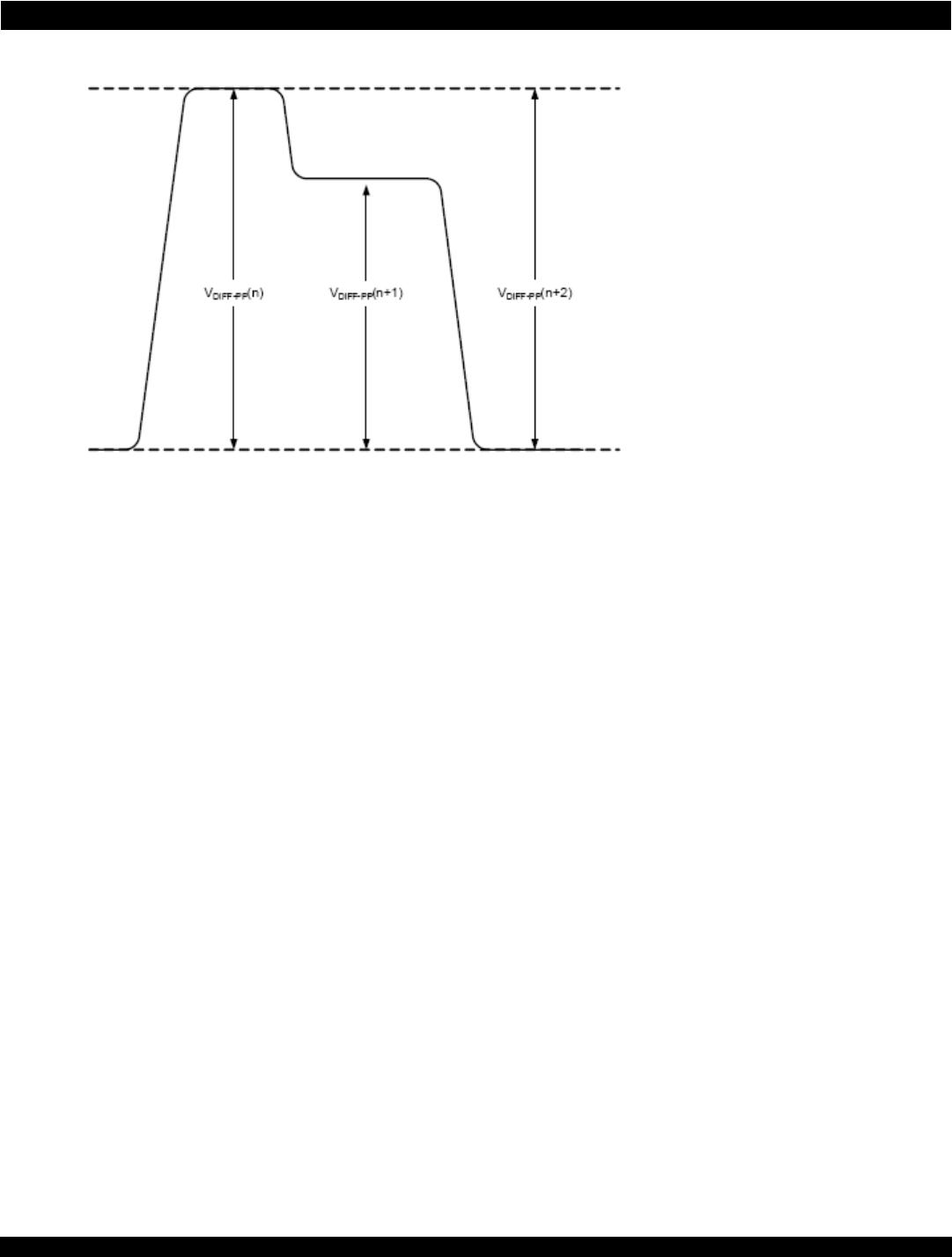
Tsi721 Datasheet 41 April 4, 2016
Integrated Device Technology
3.7.3.3 1.25 Gbps, 2.5 Gbps, and 3.125 Gbps LP-Serial Links
This section explains the requirements for Level I RapidIO LP-Serial short and long run electrical interfaces of nominal baud
rates of 1.25, 2.5, and 3.125 Gbps using NRZ coding (thus, 1 bit per symbol at the electrical level). The Tsi721’s SerDes meet
all of the requirements listed below. The electrical interface is based on a high speed, low voltage logic with a nominal
differential impedance of 100 Ohm. Connections are point-to-point balanced differential pair and signaling is unidirectional.
The level of links defined in this section are identical to those defined in the RapidIO Interconnect Specification (Revision 2.1),
1x/4x LP-Serial Electrical Specification.
3.7.3.4 Equalization
With the use of high speed serial links, the interconnect media will cause degradation of the signal at the receiver. Effects such
as Inter-Symbol Interference (ISI) or data dependent jitter are produced. This loss can be large enough to degrade the eye
opening at the receiver beyond what is allowed in the specification. To negate a portion of these effects, equalization can be
used in the transmitter and/or receiver, but it is not required at baud rates less than 3.125 Gbps.
3.7.3.5 Explanatory Note on Level I Transmitter and Receiver Specifications
AC electrical specifications are provided for the transmitter and receiver. Long run and short run interfaces at three baud rates
are described.
The parameters for the AC electrical specifications are guided by the XAUI electrical interface specified in Clause 47 of IEEE
802.3ae-2002.[1] The goal of this standard is that electrical designs for Level I electrical designs can reuse XAUI, suitably
modified for applications at the baud intervals and runs described herein.
3.7.3.6 Level I Electrical Specification
3.7.3.6.1 Level I Transmitter Characteristics
Level I LP-Serial transmitter electrical and timing specifications are stated in the text and tables of this section. The differential
return loss, S11, of the transmitter in each case must be better than:
• -10 dB for (Baud Frequency) / 10 < Freq(f) < 625 MHz, and
• -10 dB + 10log(f/625 MHz) dB for 625 MHz <= Freq(f) <= Baud Frequency
The reference impedance for the differential return loss measurements is 100 Ohm resistive. Differential return loss includes
contributions from on-chip circuitry, chip packaging and any off-chip components related to the driver. The output impedance
requirement applies to all valid output levels.
The Tsi721 satisfies the specification requirement that the 20%-80% rise/fall time of the transmitter, as measured at the
transmitter output, in each case has a minimum value 60 ps.
Similarly, the timing skew at the output of an LP-Serial transmitter between the two signals that comprise a differential pair
does not exceed 25 ps at 1.25 Gbps, 20 ps at 2.5 Gbps, and 15 ps at 3.125 Gbps.