By Belden Wire 237
Paired cable is a type of cable commonly used in telecommunications communications and data transmission that consists of two insulated wires (usually copper wires) that are tightly twisted together to form a pair. These two conductors are often referred to as a "twisted pair" and they run parallel throughout the length of the cable.
The main feature of paired cables is their twisted wire construction, which helps reduce electromagnetic interference and crosstalk (interference between two wires). This makes paired cables ideal for transmitting data signals, especially in network communications.

Paired cable consists of two insulated wires (usually copper) that are tightly twisted together to form a pair. These two wires are often called the "positive" and "negative" wires, or the "transmitting wire" and the "receiving wire".
The paired cable adopts the balanced transmission method. This means that when transmitting data signals, positive and negative charges are simultaneously transmitted in the paired wires. This balanced transmission characteristic makes the cable more resistant to electromagnetic interference from the outside, because interference from the outside affects both conductors at the same time, and the cable receiving end can identify and eliminate these interferences.
Paired cables carry differential signals. The transmitter sends positive current on one wire and negative current on the other wire. This differential signaling method helps improve signal quality because it reduces the effects of common-mode interference (interference that also affects both wires).
On the receiving end, the receiving device compares the signals on the two wires and uses the differences between them to restore the original data signal. This process helps eliminate the influence of external interference and crosstalk on the data, thus ensuring reliable data transmission.
The twisted construction of the twisted pairs helps reduce crosstalk. Crosstalk means that when multiple pairs of cables are arranged side by side, the signal in one pair of cables may interfere with the signal in the adjacent cable. Because the two wires in a twisted pair are tightly twisted together, the electromagnetic field effects between them cancel each other out, reducing crosstalk.
Ⅰ. The difference between paired cables and single-pair cables
1. Structure
Paired Cable: A paired cable consists of two insulated wires, often referred to as the "positive wire" and the "negative wire," or the "transmitting wire" and the "receiving wire." The two wires are tightly twisted together to form a pair, hence the name "paired" cable. The purpose of the twisted wires is to reduce electromagnetic interference and crosstalk, making data transmission more reliable.
Single-Pair Cable: A single-pair cable generally refers to a single insulated conductor without a paired partner conductor. This type of cable consists of a single conductor and usually has no twisted structure, so it does not have the noise immunity characteristics of a paired cable.
2. Purpose
Paired cables:
Telephone system: Paired cables are also used to transmit telephone signals, including traditional telephone lines and VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) telephone systems. Telephone lines usually use paired cables to transmit voice signals.
Data Communications and Networking: Paired cables are a type of cable widely used in data communications and network connections, especially in LANs and WANs. They are used to connect computers, routers, switches and other network devices for data transfer and internet connection. Common paired cable standards include Cat 5e, Cat 6, Cat 6a, Cat 7, etc., which support different data transfer rates, from Gigabit Ethernet to Ten Gigabit Ethernet, etc.
Home Network: Paired cables are often used in home networks to connect devices such as computers, smartphones, TVs, game consoles, etc. in order to share Internet connections and resources.
Industrial Automation: In industrial control and automation systems, paired cables are used to transmit control signals, sensor data, and monitoring information.
Single pair cable:
Short-distance data transmission: Due to its relatively low performance, single-pair cable is generally not used for high-speed data transmission and long-distance communications. However, in some specific applications they may be used for short distance data transmission needs.
Specialized Applications: Single-pair cable may be used in some specific applications, but these applications are relatively rare because in many cases, paired cables provide better resistance to electromagnetic interference and performance.
Audio transmission: Single-pair cable is usually used for low-frequency signal transmission, such as audio signals. They are commonly found in sound systems, speaker cables, and connections between audio equipment.
3.Performance
Paired cables: Paired cables are generally capable of supporting higher transmission speeds, depending on their type and size. Common paired cable types include Cat 5e, Cat 6, Cat 6a, Cat 7, etc., which can support different transmission rates from Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps) to Ten Gigabit Ethernet (10 Gbps). Paired cables generally have higher bandwidth and can transmit larger amounts of data. Higher bandwidth helps support multimedia, high-definition video and large-capacity data transmission. Because the paired cables adopt a twisted structure, they have strong resistance to electromagnetic interference and crosstalk. This means that in complex electromagnetic environments, paired cables can generally provide more reliable signal transmission, reducing data loss and bit error rates. Paired cables are suitable for a wide range of applications, including network communications, telephone systems, home networks, and industrial automation, and perform particularly well in scenarios requiring high-speed data transmission.
Single-pair cable: Single-pair cable generally does not support as high transmission speeds as paired cable. They are usually used for low-frequency signal transmission, such as audio transmission, and therefore have poor performance in high-speed data transmission. The relatively low bandwidth limits the data transmission capabilities of single-pair cables and is generally not suitable for applications requiring large bandwidths. Single-pair cables have weak anti-interference capabilities and are easily affected by electromagnetic interference. This means that in noisy environments, data transmission may not be stable enough. Single-pair cables are mainly used for audio transmission and some low-frequency signal transmission applications, such as audio systems, speaker cables, etc. When it comes to high-speed data communications, single-pair cables are usually not the preferred option.
Ⅱ. Transmission performance of paired cables
The signal attenuation of a pair of cables is proportional to the length of the cable. The longer the cable, the greater the attenuation. This is the physical law of cables. The length of the cable is generally marked in feet or meters. The audio and video signal passing through a long-distance cable will cause signal attenuation. The difference has also become the basis for comparing cable quality (different attenuation of cables per unit length for transmitting the same signal).
The capacitive reactance of the cable and the material of the wire determine the frequency range of the transmitted signal. Within a suitable transmission distance, if the image is blurred, most of the cables do not meet the requirements of high-frequency transmission, resulting in the loss of high-frequency signal.
The transmission distance of a paired cable refers to the maximum distance over which the signal can be transmitted stably. Transmission distance is affected by a variety of factors, including cable type, transmission speed, and signal quality. Generally speaking, as the transmission speed increases, the transmission distance may decrease, so relay equipment may be needed to extend the distance.
The cable is also a huge antenna that absorbs electromagnetic waves existing in space. If the cable is not shielded or is poorly shielded, any type of electromagnetic interference will directly act on the useful signal, reducing the signal-to-noise ratio of the signal.
Paired cables feature a twisted wire construction, which helps reduce the effects of electromagnetic interference and crosstalk. Therefore, they usually have better anti-interference ability, can provide stable signal transmission in noisy electromagnetic environment, and reduce data loss and bit error rate.
The paired cable design and twisted wire construction help maintain signal quality and ensure reliable data transmission. Signal quality is usually measured by Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), with high SNR indicating better signal quality.
Paired cables are usually required to meet specific standard specifications, such as the TIA/EIA-568 standard (for network cables) or the TIA/EIA-568-C standard. These standards ensure cable performance and interoperability.
Paired cables introduce a certain amount of delay when transmitting signals, which is the time it takes for the signal to travel. Latency may be a consideration in certain applications, such as real-time audio and video transmission and high-frequency trading.
The slope describes the time difference of different lengths of the twisted pair for signal transmission. It depends on the twisting process and twisting type of the twisted pair. When a large time delay error occurs, the slope compensation of the cable is required.
Impedance is one of the important parameters describing the technical specifications of a cable, establishing a baseline for the correct flow of signals. The flow of this signal maintains the power conversion of the entire system. Imagine water flowing through a large-diameter water pipe. As long as the diameter of the water pipe remains constant, the structure and flow of the water flow will not change. When this water flow is introduced into a water pipe with a small mouth, the situation has changed: due to the existence of the bottleneck, the structure of the water flow is disrupted, and all the water flow cannot pass through the bottleneck at the same time, causing part of the water flow to flow in the opposite direction, and finally it is still blocked. The main stream reintroduces the flow of water.
Ⅲ. Advantages and disadvantages of paired cables
1.Advantages
Cost-Effectiveness: Paired cable is one of the relatively inexpensive communication mediums and therefore is generally cost-effective in setting up and maintaining network infrastructure. This makes it a preferred choice for many homes, businesses, and organizations.
Flexibility: Paired cables are suitable for a variety of applications including data communications, phone systems, home networking, industrial automation, and more. They can be used to transmit different types of signals, from data to audio, and have good versatility.
Ease of Installation: Paired cables are relatively simple to install and can be easily routed inside buildings for a variety of environments, including homes, offices, and industrial locations. Plus, it's easy to connect and plug in.
Anti-interference ability: The paired cables adopt a twisted wire structure to help reduce electromagnetic interference and crosstalk. This gives them excellent anti-interference capabilities in noisy electromagnetic environments and can provide stable signal transmission.
Wide support: paired cables are widely supported and widely used, and there are many standards and specifications to ensure the interoperability of paired cables produced by different manufacturers.
Upgradeability: The performance of paired cables can be improved by upgrading the cable type and gauge. This means that when higher speeds or greater bandwidth are required, upgrades can be made relatively easily without having to replace the entire cable system.
Safety: Because paired cables typically do not emit significant amounts of electromagnetic radiation during transmission, they are more suitable for sensitive equipment and environments with high safety requirements.
Variety of specifications and performance options: There are a variety of paired cable specifications to meet the performance needs of different applications, from basic Cat 5e to high-performance Cat 6a and Cat 7, etc.
2. Disadvantages
Limited transmission distance: The transmission distance of paired cables is subject to certain limitations, especially in the case of high-speed data transmission. As the transmission rate increases, the transmission distance may decrease, so relay equipment may be required in long-distance communications.
Factors that limit performance: Cable performance is affected by many factors, including cable quality, connection quality, installation method, and environmental conditions. Improper installation or low-quality cabling and connections can cause performance degradation.
Bandwidth limitations: Although paired cables can provide relatively high bandwidth, in some high-bandwidth applications, such as ultra-high-definition video or high-capacity data transmission, it may be necessary to choose other transmission media, such as optical fiber.
Not suitable for all applications: Although paired cables perform well in many applications, for some special applications, such as high-speed long-distance data transmission or very low latency requirements, it may be necessary to choose another transmission medium.
Signal attenuation: Signals may be attenuated when transmitted over long distances, resulting in reduced signal quality. This can be mitigated by using signal amplifiers or better cable specifications, but is still a challenge.
Maintenance Required: Paired cables require regular maintenance to ensure their performance. Maintenance includes checking connections, replacing damaged cable sections and upgrading systems to meet new performance needs.
Electromagnetic interference: Although paired cables have certain anti-interference ability, they may still be affected by electromagnetic interference in an extremely noisy electromagnetic environment, thereby affecting the signal quality.
Weight and Volume: Paired cables can be heavier and take up more space than some other transmission media, such as wireless communications or fiber optics. This may limit its application in some special environments.
Ⅳ. Types of paired cables
Cat 5e (Category 5e) cable
Cat 5e cable is a common type of paired cable used to support Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps) data transmission. Cat 5e cable is designed to support Gigabit Ethernet, which means it is capable of transmitting data rates up to 1 Gbps. This makes it suitable for network environments that require high-speed data transmission, such as office networks and home networks.
The nominal bandwidth of Cat 5e cable is 100 MHz, which is twice the bandwidth of Cat 5 cable. This means it can transfer more data, support multimedia applications and large-capacity file transfers. Cat 5e cable uses a twisted wire construction to help reduce electromagnetic interference and crosstalk. It has good anti-interference ability and can provide stable signal transmission in general electromagnetic environment.
Cat 5e cable is a general-purpose performance cable suitable for a variety of networking and communications applications, including data communications, phone systems, home networks, and small office networks. Cat 5e cables comply with the TIA/EIA-568 standard, which ensures interoperability between Cat 5e cables and related equipment produced by different manufacturers, making it a universal standard.
Cat 6 (Category 6) cables
Cat 6 cable provides higher performance, supporting Gigabit Ethernet and Ten Gigabit Ethernet (10 Gbps) data transmission. It is typically used in network environments that require higher bandwidth. Cat 6 cable can support data transmission of Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet. This makes it ideal for applications requiring higher bandwidth and speed, such as large enterprise networks and data centers.
The nominal bandwidth of Cat 6 cable is typically 250 MHz, which is much higher than the bandwidth of Cat 5e cable. This means it can transfer larger amounts of data, supporting large-capacity file transfers and multimedia applications. Like Cat 5e cable, Cat 6 cable also adopts a twisted wire structure, which has good anti-interference ability and can provide stable signal transmission in an electromagnetic interference environment. Relative to Cat 5e cable, Cat 6 cable can support longer transmission distances, especially at Gigabit Ethernet speeds, which makes it more advantageous in large buildings or data centers.
Cat 6a (Category 6a) cable
Cat 6a cable is an improved version of Cat 6 that provides higher bandwidth and better performance, capable of supporting 10 Gigabit Ethernet and performing well in high frequency ranges. It is suitable for enterprise-class networks and data centers. The nominal bandwidth of Cat 6a cable is usually 500 MHz, which is twice the bandwidth of Cat 6 cable. This means it can transmit larger data capacity and support high-definition video, large file transfer and multimedia applications.
Like Cat 5e and Cat 6 cables, Cat 6a cables use a twisted wire construction, which has excellent anti-interference performance and can provide reliable signal transmission in electromagnetic interference environments. Cat 6a cable not only provides high-speed transmission capabilities, but also supports longer transmission distances, especially at ten Gigabit Ethernet rates, making it very useful in large buildings and data centers.
Cat 7 (Category 7) cables
Cat 7 cable is a high-performance cable that supports 10 Gigabit Ethernet transmission and provides better immunity to interference. It is suitable for special environments requiring high performance and anti-interference capabilities. Cat 7 cable can support 10 Gigabit Ethernet data transmission, which means it can provide high-speed network connection, suitable for large-capacity data transmission and multimedia applications.
The nominal bandwidth of Cat 7 cable is 600 MHz, which is twice the bandwidth of Cat 6a cable. This enables it to transmit larger amounts of data, supporting HD video, VR, large file transfers and other high-bandwidth applications.
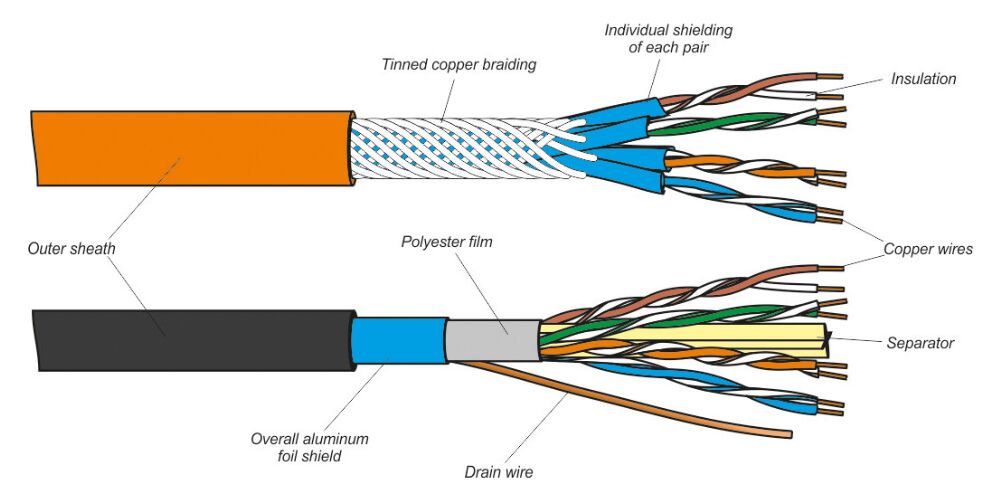
Cat 7 cable uses a double-shield design, which includes a full metal shield and independent shielding for each pair of wires. This shielding structure gives Cat 7 cables extremely high anti-interference capabilities and can provide excellent signal transmission quality in electromagnetic interference environments.
Cat 8 (Category 8) cables
Cat 8 cable is the latest paired cable standard that provides ultra-high bandwidth and supports 25 Gigabit Ethernet and 40 Gigabit Ethernet transmission. It is mainly used in data centers and specific high-performance networks. Cat 8 cable is capable of supporting data transmission of 25 Gigabit Ethernet and 40 Gigabit Ethernet. This means it can provide extremely high-speed network connections, suitable for ultra-high-speed data transfer and high-volume data traffic.
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
Unshielded Twisted Pair UTP cable is a paired cable without shielding. Cable is a common paired cable that is commonly used in applications such as data communications, telephone systems, and home networking. Unlike shielded twisted pair (STP) cable, UTP cable has no additional shielding, but it still reduces EMI and crosstalk by twisting pairs of wires together. UTP cable consists of one or more pairs of twisted wires, each pair includes two insulated conductors. These strands are usually made of copper. It is very simple to install and can be easily wired inside a building. It typically connects to devices and outlets using an RJ-45 connector, which is also common and easy to plug and unplug.
The twisted wire structure of UTP cable helps reduce electromagnetic interference and crosstalk, especially in low to medium interference environments. But compared with STP cable, its anti-interference performance is lower. UTP cables use standardized connectors and specifications, so there is generally good interoperability between UTP cables and related equipment produced by different manufacturers.
Shielded twisted pair (STP) cable
Shielded twisted pair STP cable has a shield, and the cable is a paired cable that is more resistant to interference and crosstalk than unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables. STP cables are very useful in some special environments, especially where higher electromagnetic interference suppression is required, such as industrial control systems.
Each twisted pair of STP cable is wrapped in a metal shield, usually made of aluminum foil and sometimes includes a metal braid. The function of these shielding layers is to reduce the impact of external electromagnetic interference on the internal signals of the cable and provide better anti-interference performance.
Due to the protection of the shielding layer, STP cables can provide stable signal transmission in environments with severe electromagnetic interference. This makes it particularly suitable for industrial control systems, medical equipment and other applications that are very sensitive to interference. STP cable is also a general-purpose performance cable, suitable for various network and communication applications, including data communication, telephone system, home network, office network, etc. It usually uses the same RJ-45 connector as UTP cable.
Relative to UTP cable, STP cable generally costs more because it contains a shielding layer and a metal braid. This makes it more suitable for use in special environments that require high anti-interference performance.
coaxial cable
Coaxial cable is a communication cable that consists of a center conductor, insulation layer, shielding layer and outer insulation layer. Coaxial cables are usually used to transmit high-frequency signals, especially widely used in TV signal transmission, broadband Internet, cable TV and some special communication applications. Although coaxial cable is not a typical paired cable, it also contains two conductors (a center conductor and an outer conductor) and is commonly used for television signal transmission, broadband Internet and some special communication applications.
Coaxial cables are widely used for television signal transmission, cable television systems, satellite television, broadcast signal transmission and broadband Internet connections. It is also used in some special communications applications such as radar systems and aeronautical communications. Due to its shielding layer, coaxial cable has excellent anti-interference capabilities and can provide stable signal transmission in environments with heavy electromagnetic interference.
The transmission distance of coaxial cable can vary according to different specifications and applications. Coaxial cable can support longer transmission distances, making it suitable for connecting long-distance devices.
Ⅴ.Application fields of paired cables and how to choose paired cables suitable for specific applications
1. Field of application
Telephone Systems: Paired cables are widely used in traditional telephone systems. They are used to connect telephone equipment, including landlines, fax machines, modems, etc., for voice communications and data transmission.
Computer Networks: Paired cables are a key component in building a computer network and are used to connect devices such as computers, servers, routers, and switches. They are used to transmit data, voice and video signals and support various network applications, including Internet access, LAN and WAN, etc.
Cable and Satellite Television: Paired cables are used to transmit cable television signals and satellite television signals. These signals include various television channels and interactive services.
Data Center: Paired cables are used in data centers to connect servers, storage devices, network equipment and data transmission. High-performance paired cables such as Cat 6a, Cat 7 and Cat 8 are commonly used to support high-speed data transmission and data center applications.
Home Network: Paired cables are used to establish a LAN in a home environment to connect various devices such as computers, smartphones, smart TVs, and streaming media devices. This facilitates file sharing, internet access and entertainment streaming within the home.
Industrial Automation: In industrial environments, paired cables are used to connect sensors, controllers, and automation equipment to support industrial automation and monitoring.
Security Systems: Paired cables are used to connect security cameras, surveillance equipment and access control systems to support video surveillance and security management.
Sound Systems: Paired cables are also used to connect audio equipment such as speakers, microphones and sound systems for audio transmission and music performances.
2. How to choose the right paired cable for a specific application
Determine bandwidth needs: First, determine how much bandwidth your network or application requires. Bandwidth requirements are often a key factor in selecting cable specifications. If high bandwidth is required, such as supporting high-definition video streaming or large file transfers, then you need to choose higher performance cable specifications, such as Cat 6a, Cat 7, Cat 8, etc.
Consider the transmission distance: Determine the transmission distance that needs to be covered. Different cable specifications support different transmission distances. Generally speaking, higher performance cables can support longer transmission distances. Therefore, consider network layout and device location when selecting cables.
Understanding Environmental Factors: Consider the network deployment environment. Some environments may be more susceptible to electromagnetic interference, such as industrial areas or near medical equipment. If your network operates in a high-interference environment, you may want to choose cables with good interference immunity, such as STP cables or Cat 7/Cat 8 cables.
Evaluate the cost: Different specifications and performance levels of cable pairs will affect the price. Determine your budget constraints and weigh performance needs against cost. Sometimes it may be more cost-effective to choose lower performance cables, but make sure you don't sacrifice network performance.
Comply with standards: Make sure the cable you select complies with applicable industry standards, such as TIA/EIA-568. Standard-compliant cables generally provide better interoperability and reliability.
Choose the appropriate performance class: Paired cables are available in different performance classes such as Cat 5e, Cat 6, Cat 6a, Cat 7, Cat 8, etc. Choosing the appropriate performance level will directly impact network performance and scalability.

Ⅵ. Precautions for installation and maintenance of paired cables
1.Installation
Select the appropriate cable size: Before you begin the installation, make sure you have selected the appropriate cable size for your network needs. This includes factors such as bandwidth requirements, transmission distance and application environment.
Avoid crossing cables with power cords: Paired cables should be kept a certain distance from power cords to reduce electromagnetic interference. It is better to cross cables and power lines vertically or horizontally rather than cross them.
Keep cables tidy: When installing, make sure cables are neatly arranged and avoid kinks and excessive bends. This helps reduce signal loss and interference.
Use the correct connector: Use the correct type of connector, such as an RJ-45 connector, to ensure a reliable connection.
Avoid pulling on cables: Avoid pulling on cables excessively during installation and maintenance to prevent wire breakage or connector damage.
Mark cables: Mark cables for identification and maintenance. Use appropriate labeling or identification methods to differentiate between different cable connections.
2. Maintenance
Check connections regularly: Check cable connections regularly to make sure the connectors are tight and not loose or damaged. Loose connections can cause signal interruptions.
Avoid physical damage: Avoid rolling over, tripping over, or inflicting physical damage on the cable to maintain its integrity.
Check cable integrity: Check whether the outer insulation layer of the cable is intact to ensure that the inner insulation of the cable is not damaged.
Keep it clean: Keep cable channels and connectors clean. Dust and dirt may affect signal transmission.
Avoid electromagnetic interference: Ensure that cables are not subject to electromagnetic interference during maintenance and avoid arranging cables near potential sources of interference.
Backup and Logging: Back up network configurations and log cabling connections for troubleshooting and maintenance when needed.
Regular testing: Perform regular cable testing to ensure signal quality meets expected performance standards. Testing can detect problems in the cable and help make timely repairs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the role and importance of paired cables in network communications?
Paired cables are designed to provide reliable data transmission. They reduce the effects of electromagnetic interference and crosstalk by winding data lines together in pairs, ensuring data integrity and accuracy. This is critical to ensure the reliability of network communications. Different sizes and performance levels of cable pairs support different bandwidth and speed requirements. Higher performance cables provide faster data transfer speeds, which are critical to supporting mission-critical applications such as high-bandwidth applications, high-volume data transfers and streaming media. Paired cables support network expansion and enhancement. By upgrading to higher performance cable specifications, networks can meet growing bandwidth demands without completely replacing the infrastructure.
2. What are the differences in the application of paired cables in home networks and industrial networks?
Typical home networks don't usually require very high bandwidth, as they are primarily used for standard applications such as basic internet access, email, social media, and streaming. Therefore, Cat 5e or Cat 6 cables are usually sufficient for the needs. Industrial networks generally require higher bandwidth because they may need to transmit large amounts of data, such as sensor data, surveillance video, and industrial automation control signals. Therefore, Cat 6a, Cat 7 or Cat 8 cables are usually used for high bandwidth needs.
3.How reliable are twisted pair cables?
The most widely used twisted pair cable is UTP (unshielded twisted pair) - like for Ethernet. It is lightweight, thin and flexible, reliable under 100 meters, and inexpensive. But over 100 meters, data loss can occur due to signal degradation and propagation delay