By ON Semiconductor / Fairchild 205
Ⅰ.Introduction to 1N4148
1N4148 is a small high-speed switching diode, which switches quickly. It is widely used for one-way conduction isolation in circuits with high signal frequency, communications, computer boards, TV circuits and industrial control circuits. The 1N4148 is a fast recovery diode commonly used in rectification, protection and switching applications in electronic circuits. This type of diode is made of silicon material and has a fast reverse recovery time, usually in the nanosecond range.
1N4148 diodes are readily available in smaller sizes at lower cost. Therefore, this diode can be selected based on its highest reverse recovery time and power dissipation from 80 milliwatts to 1 kilowatt.
.jpg)
Ⅱ.Introduction to 1N4007
1N4007 is a plastic packaged general-purpose silicon material rectifier diode with a DO-41 package. It is widely used in various AC to DC rectifier circuits. Also used in bridge rectifier circuits. 1N4007 uses the unidirectional conductivity of the diode to convert alternating current in alternating directions into pulsed direct current in a single direction.
The 1N4007 is a rectifier diode commonly used in electronic circuits for rectification, protection and power supply applications. It is a member of the 1N400x series, which includes a variety of rectifier diodes, of which 1N4007 is one of the most common and widely used models in the series.
1N4007 can also be used in any general application that requires a general purpose diode. It is designed for high voltage operation and can easily handle voltages below 1000V. 1000mA average forward current, 3W power consumption and small size and cost penalty also make it an ideal choice for various applications. Ideal for any application.
It should be noted that IN4007 is a diode with polarity. You need to pay attention to its positive and negative polarity. Correct wiring should be performed when using it to avoid component damage caused by misoperation.

Ⅲ.Specification parameters of 1N4148 and 1N4007
1.1N4148
•Product:General Purpose Diodes
•Package/Box:DO-35
•Peak reverse voltage:100 V
•Maximum surge current:4A
•If-Forward current: 300mA
•Configuration:Single
•Recovery time:4 ns
•Vf-Forward voltage:1V
•Ir-reverse current:5 uA
•Minimum operating temperature:-55℃
•Maximum operating temperature:+175℃
•Height:1.91 mm
•Length: 4.56 mm
•Subcategories: Diodes & Rectifiers
•Type:Small Signal Switching Diode
•Vr-Reverse voltage: 100 V
2.1N4007
•Package/Box:DO-41
•Vr-reverse voltage:1 kV
•If-Forward current: 1A
•Configuration:Single
•Vf-Forward voltage:1.1 V
•Maximum surge current:27 A
•Ir-reverse current:5 uA
•Recovery time:1.5 us
•Minimum operating temperature:-55℃
•Maximum operating temperature:+175℃
•Series:1N400X
•Subcategories:Diodes & Rectifiers
IV.Differences in working modes between 1N4148 and 1N4007
1.1N4148
•Diodes work like signaling diodes, allowing current to flow in a single direction, i.e. from anode to cathode. Depending on how it is connected across the voltage source, the 1N4148 diode has two modes of operation: forward biased and reverse biased.
•Forward biased mode: In forward biased mode, it works like a closed switch and allows current to flow through it.
•Reverse bias mode: In reverse bias mode, it operates as an open switch and does not allow current to flow.
•Below a specified voltage (cutoff voltage), the diode shows high resistance, above that specific voltage, it shows low resistance.
2.1N4007
(1)Forward conduction (forward work):
•Once the forward voltage reaches or exceeds the forward breakdown voltage of the 1N4007 (usually 0.7 volts), current can flow through the diode.
•When a forward voltage (also called forward bias) is applied across the 1N4007, it starts conducting. The direction of the forward voltage is in the same direction as the arrow on the diode, which is the polarity of the diode.
•In the forward conduction state, 1N4007 behaves as a very low resistance, allowing current to pass freely.
(2)Reverse cutoff (reverse work):
•The reverse breakdown voltage of the 1N4007 is typically around 1000 volts, which means that below this voltage, almost no current flows through the diode. This provides protection against reverse voltage.
•When a reverse voltage (also called reverse bias) is applied to the 1N4007, it is in a reverse-blocking state.
Ⅴ.Electrical characteristics of 1N4148 and 1N4007
•1N4148(Values are at TA = 25°C unless otherwise noted) (Note 2)
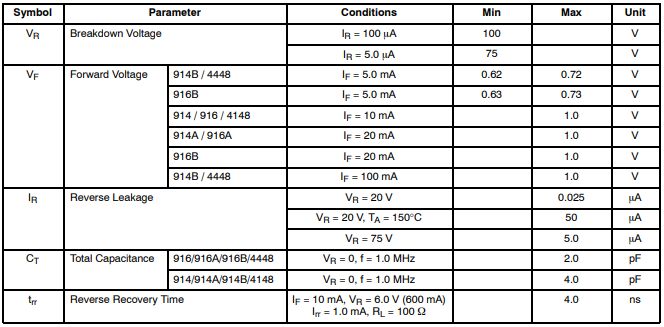
•1N4007
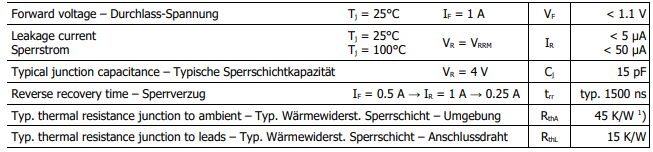
Ⅵ.The difference in reverse breakdown voltage between 1N4148 and 1N4007
1.1N4148
•1N4148 is a fast recovery diode.
•Reverse breakdown voltage is usually around 100 volts.
•This low reverse breakdown voltage makes the 1N4148 suitable for some low voltage applications, but not suitable for high voltage environments.
2.1N4007
•1N4007 is a general-purpose rectifier diode commonly used to rectify alternating current into direct current.
•The reverse breakdown voltage is 1000 volts, which is 1 kilovolt.
•This higher reverse breakdown voltage makes the 1N4007 suitable for use in high voltage environments such as power supplies and high voltage rectifier circuits.
Ⅶ.Main applications of 1N4148 and 1N4007
1.1N4148
•Rectifier: 1N4148 can be used to rectify AC signals into DC signals. This is very common in various power supplies and electronic circuits to ensure that devices receive stable DC power.
•Fast recovery diode application: 1N4148 is often used as a fast recovery diode in other circuits to reduce reverse recovery time and improve performance.
•High-frequency applications: Due to its faster switching speed, 1N4148 is also used in high-frequency RF circuits, such as modems, RF amplifiers and wireless communication equipment.
•Signal clipping and protection: 1N4148 can be used in clipping circuits to remove negative pulses in signals, and can also be used to protect electronic components to prevent reverse voltage or current from damaging other components.
•Fast switching applications: Due to its fast reverse recovery time, 1N4148 is ideally suited for high frequency switching circuits such as switching power supplies, inverters and pulse modulation circuits.
2.1N4007
•Power supply: 1N4007 is used to rectify AC signals into DC signals, which is a key component of the power supply for many electronic devices.
•Switching power supply: 1N4007 can be used for rectification in switching power supplies to provide stable DC power supply.
•Rectifier circuits: This type of diode is commonly found in rectifier circuits such as bridge rectifiers to ensure that the power extracted from the power supply is in the form of DC.
•Charger: It can be used in charger circuits to convert AC power into DC power required by the battery.
•Power Inverter: The inverter converts DC power into AC power and 1N4007 can be used in the rectification stage to ensure that the output of the inverter is DC power.
•Motor Control: In motor control circuits, 1N4007 is usually used for rectification to provide the DC power required by the motor.
•Power supply filtering: 1N4007 can be used in power supply filtering circuits to remove high-frequency noise components of AC signals.
•Battery charging: In some battery charging applications, 1N4007 can be used to prevent reverse battery discharge.
Ⅷ.The difference between 1N4148 and 1N4007
1.Type
•1N4148 is a fast recovery diode commonly used in high frequency electronic circuits.
•1N4007 is a rectifier diode usually used to rectify alternating current into direct current.
2.Current rating
•The 1N4148 usually has a lower current rating, usually around 200 milliamps.
•The 1N4007 usually has a higher current rating, typically 1 Ampere (A).
3.Reverse breakdown voltage
•The reverse breakdown voltage of 1N4148 is usually around 100 volts, which is relatively low.
•The reverse breakdown voltage of 1N4007 is 1000 volts (1 kilovolt), which is relatively high.
4.Reverse recovery time
•1N4148 has fast reverse recovery time, typically in the nanosecond range.
•The reverse recovery time of 1N4007 is relatively slow, usually in the microsecond level.
Ⅸ.Common points between 1N4148 and 1N4007
1.Basic characteristics of diodes: Whether it is 1N4148 or 1N4007, they are all diodes with some common diode characteristics, such as forward conduction and reverse blocking.
2.Package type: Generally, both 1N4148 and 1N4007 are available in similar small packages, such as DO-35 or DO-204AL.
3.Uses: Both are used in electronic circuits for different types of rectification, protection and switching applications, although they are more commonly used in different fields.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.What is the difference between the temperature characteristics of 1N4148 and 1N4007?
1N4148 generally has relatively good temperature characteristics. It can still maintain relatively stable performance at higher temperatures, which makes it suitable for certain high-temperature environments. 1N4007 is generally suitable for applications within the standard temperature range. It is not designed for high frequency applications like fast recovery diodes, so its temperature characteristics focus primarily on performance under temperature conditions common in general industrial and electronic equipment.
2.What is the performance of 1N4148 and 1N4007 in high frequency circuits?
1N4148 generally provides lower reverse recovery loss in high-frequency circuits, thereby helping to reduce signal distortion. Using 1N4007 in high-frequency circuits may result in larger reverse recovery losses and may cause signal distortion.
3.Are there any other similar diode replacements suitable for the 1N4148?
1N914,1N5817,1N4448,BAT41
4.Are there any other similar diode replacements suitable for the 1N4007?
1N4001 to 1N4006 series,UF4007,1N5400 series, 1N5820 to 1N5822 series