By CJ 247
S8550 is a general-purpose PNP transistor. It is a commonly used amplifier and switch and can be widely used in signal amplification, current, voltage control, etc. The S8550 transistor has some current amplification characteristics and is suitable for use in medium and small power applications. As a component widely used in electronic equipment, the transistor S550 can make the circuit more stable and efficient.
Transistor S8550 is a PNP type transistor. Its shape is similar to a small silicon chip and consists of three areas. The middle area is called the base area, and the areas on both sides are called the emitter area and the collector area respectively. When current passes through the base region, the current in the emitter region and collector region is controlled, thereby realizing various functions of the electronic device. Transistor S8550 is a very important electronic component. It can help us realize various functions of electronic equipment and improve the stability and efficiency of the circuit.

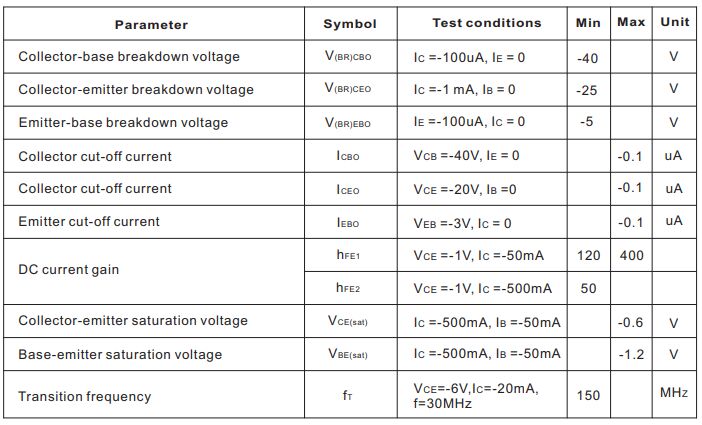
Ⅰ.Main parameters of S8550
•Transistor type: PNP
•Current-Collector (Ic) (maximum): 500 mA
•Voltage- ollector-emitter breakdown (max): 25 V
•Vce saturation voltage drop (maximum value) at different Ib and Ic: 600mV @ 50mA, 500mA
•Current-collector cutoff (max): 100nA
•DC current gain (hFE) (minimum value) at different Ic, Vce: 120 @ 50mA, 1V
•Power-Maximum: 300 mW
•Operating temperature: 150°C (TJ)
•Characteristic frequency fT: 150MHz
•Package/casing: SOT-23-3(SC-59,TO-236-3)
Ⅱ.The function of S8550
S8550 can amplify signals. When the input signal is relatively weak, the transistor S8550 can amplify it enough to drive other components, thereby making the circuit more sensitive and efficient. The transistor S8550 is also able to control the current, thereby improving the stability of electronic equipment. Especially in DC power supplies, the transistor S8550 can help us control the size of the current to avoid circuit damage or failure.
1.Amplify signals: Amplifiers can be used in various applications, such as audio amplifiers, wireless communication systems, and other electronic devices that need to amplify weak signals. However, in order for the transistor to work properly and achieve effective signal amplification, the design of its peripheral circuits needs to be carefully considered, including power supply, input and output impedance, feedback, etc. Although the S8550 is a common transistor, in actual applications, different types of transistors may need to be selected based on specific needs and conditions. For example, for high-frequency or wide-bandwidth amplification applications, other types of transistors or field-effect transistors may need to be selected.
2.Constant current source: S8550 can be used as a constant current source. With appropriate circuit configuration, it can provide stable current output for various applications, such as LED drivers.
3.Switching function: S8550 can be used as an electronic switch. When the input signal voltage is less than the cut-off value, it can control the current path between the collector and emitter by controlling its base current, thereby realizing the switching state of the circuit. This feature is used very extensively in digital logic circuits and digital control applications.
4.Voltage reversal protection: S8550 is a switching device used for voltage reversal protection in circuits. It prevents current from flowing back and damaging other electronic components.
5.Modulator: In some applications, S8550 can be used to modulate signals, such as PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) control, to achieve precise control in circuits.
6.Oscillator: The S8550 can be used as part of an oscillator to generate a signal of a specific frequency, such as in a clock circuit.
Ⅲ. Working principle of S8550
A triode is a type of semiconductor device consisting of three semiconductor regions: emitter region, base region and collector region. These three regions form two junctions: the emitter junction and the collector junction. When the voltage applied to the emitter junction is greater than its maximum voltage, the emitter junction is forward biased. At this time, the majority carriers (usually electrons) in the emitter region will cross the emitter junction and enter its region driven by the electric field force. These electrons are called the emitter current (le).
In the base region, some electrons will collide with atoms in the base region to generate new electron and hole pairs. These new pairs of electrons and holes continue to move, driven by electric field forces. Among them, some electrons will flow to the collector area to form the collector current (IC), while the empty electrons will flow to the emitter area to form the base return current (lb).
In this way, the triode can control the current flowing through different areas, thereby achieving signal amplification, switching and other operations. This is also the reason why transistors are widely used in electronic circuits.
Ⅳ.The XIMUM RATINGS and ELCTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS of S8550
1.MAXIMUM RATINGS(Ta=25℃ unless otherwise noted)

2.ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS(TA = 25°C unless otherwise noted)
Ⅴ.S8550 Equivalents
1.MPSA92: MPSA92 is a high current PNP transistor, suitable for some applications that require higher current amplification.
2.2N3906: 2N3906 is another common PNP transistor that is often used as a replacement for S8550. It usually has similar current and voltage ratings.
3.2SA733: 2SA733 is another PNP type transistor that can be used in amplification and switching applications.
4.BC557: BC557 is another PNP type transistor usually used in low to medium power applications. Its parameters are also similar to the S8550.
5.KSP2907: KSP2907 is also a PNP transistor and is often used as one of the alternatives to S8550.
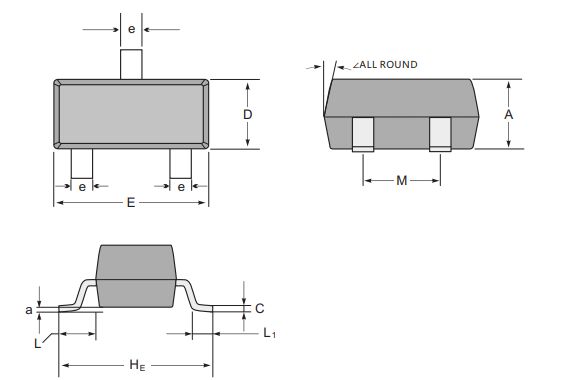
Ⅵ.S8550 packaging
1.TO-92: TO-92 package is one of the most common package types of S8550. It is a small plastic package that usually has three pins that connect the emitter, base, and collector. The S8550 in TO-92 package is suitable for general low-power applications.
2.SOT-23: The SOT-23 package is a surface mount (SMT) package that is generally smaller and suitable for applications on high-density circuit boards. The S8550 is also available in SOT-23 package.

Ⅶ.Definition of S8550
As an audio amplifier, S8550 is used in electronic products such as radio cassette players and electric toys. The triode S8550 is a commonly used ordinary triode. It is a low-voltage, high-current, small-signal PNP silicon triode. Its function is to amplify weak signals. It can be used as an electrical signal with a large amplitude and can also be used as a non-contact switch.
After electrons enter the base region, they first become dense near the emitter junction, gradually forming an electron concentration difference. Under the action of the concentration difference, the electron flow is prompted to diffuse in the base region toward the collector junction, and is pulled into the collector by the electric field of the collector junction. The collector current lc is formed in the base area, and a small part of the electrons recombine with the holes in the base area. The ratio of the diffuse electron flow and the complex electron flow determines the amplification ability of the three tubes.
Ⅷ.The difference between S8550 and S8050
The S8550 and S8050 are two different bipolar (bipolar) transistors, their main differences are:
1.Current amplification factor (hFE):
The S8550 generally has a higher current amplification factor (hFE) and is suitable for applications requiring higher current amplification.
S8050 usually has a lower current amplification factor (hFE) and is suitable for some low-power applications.
2.Polarity:
S8550 is a PNP transistor. In the S8550, the current mainly flows from the Emitter to the Base, and then from the Base to the Collector.
S8050 is an NPN transistor. In the S8050, the current mainly flows from the emitter to the base, and then flows from the base to the collector.
3.Use:
Due to the difference in polarity, the S8550 is mainly used in PNP type circuits such as load switches and certain amplification applications.
S8050 is mainly used in NPN type circuits, such as signal amplification and digital logic applications.
4.Pin configuration:
The pin configurations of the S8550 and S8050 are similar, with emitter, base, and collector, but the pin layout may be a little different in the specific model, so you need to check the data sheet of the specific model to ensure correct connections.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.How to use S8550 transistor correctly in the circuit?
Make sure you select the correct polarity type. S8550 is a PNP transistor, so the current mainly flows from the emitter to the base, and then from the base to the collector. When connecting to other PNP or NPN transistors, make sure the polarity matches. Check the S8550's datasheet for its maximum current and voltage ratings. Be sure not to exceed these ratings in your circuit to prevent transistor damage. Control the base current to control the working state of the transistor. Increasing base current will cause the transistor to turn on, decreasing base current will cause the transistor to turn off. Use appropriate resistors or other control components to limit and control base current.
2.What is an example of S8550?
The s8550 is an example of a PNP transistor'' used in various digital electronics applications. It's also used to execute simple electronic projects involving AC Circuits or DC Electric Circuits. Some widely used cases are audio amplifier circuits and driving loads below 700mA.
3.What is the function of S8050?
Overview of the S8050 Transistor: The S8050 is a small-signal NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) that belongs to the S8000 series. This transistor is designed for general-purpose amplification and switching applications, offering consistent performance and excellent thermal stability.