By STMicroelectronics 323
TYN616 is a three-terminal thyristor (TRIAC) integrated circuit. TRIAC is a bidirectional triggered thyristor used in switching and control applications in AC circuits. It is mainly used to control AC loads such as lights, electric heaters, power tools and other electrical equipment.
TYN616 uses clip assembly technology, they provide excellent performance in terms of surge current capability. TYN616 is a low-power SCR that can control the current value at 16 amps and can handle 600 volts. SCRs are latching switches, instructing them to continue operating until a specific value of current passes, called the holding current.
The working mechanism of TYN616 is that the latch current is the current that allows the device to enter the locked state when sufficient voltage is not applied to trigger the SCR (one-way silicon controlled rectifier). In this state, the SCR will not conduct, even if sufficient voltage is applied to it. When the latch current is lower than the applied current, the SCR is triggered and conducts. When in the off state, the applied current reaches the blocking current again, thus turning off the SCR.
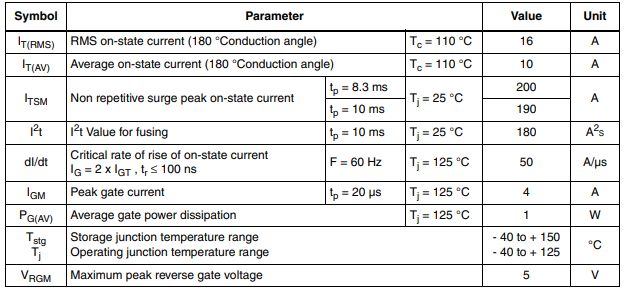
Ⅰ.Main parameters of TYN616
•Rated repetitive off-state voltage VDRM:600V
•Off-state leakage current (at VDRM IDRM):10 uA
•Vf-forward voltage:1.6 V
•Gate trigger voltage-Vgt:1.5 V
•Gate trigger current-Igt:25 mA
•Minimum operating temperature:-40°C
•Maximum operating temperature:+125°C
•Current rating:10 A
•Maximum holding current Ih:40 mA
•Non-repetitive on-state current:167A
•Type:SCRs
•Voltage-off state:600 V
•Current - Off state (maximum):5 µA
•Current - non-repetitive surge 50, 60Hz (Itsm):160A, 167A
•Package type:TO-220 or TO-220AB
•ECCN Code:EAR99
•Leakage Current (Max):2mA
•Non-Repetitive Pk On-state Cur:200 A
•Number of Terminations:3
•Terminal Position:SINGLE
Ⅱ.Main uses of TYN616
1.Power tools: TYN616 can be used in power tools to control the speed and power of the motor to achieve precise control. A thyristor is a semiconductor device whose conduction state can be changed by controlling the voltage applied to its gate (control electrode). By changing the gate voltage, the current through the thyristor can be controlled, thereby controlling the speed and power of the motor. The main advantage of using thyristors in power tools is that they can achieve stepless speed regulation, that is, they can be adjusted arbitrarily within the entire speed range. This is more convenient and more precise than adjusting the speed by changing the motor's magnetic field. In addition, the switching speed of the thyristor is also very fast, which can realize quick start, stop and braking, thereby improving the operating efficiency and precision of the power tool.
2.Lighting control: TYN616 is often used in lighting systems, such as dimming applications, to control the brightness of lights. This is useful for situations such as home lighting, commercial lighting, and stage lighting. This not only helps people adjust lighting appropriately in different environments and situations, but also saves energy and extends the service life of lamps. In home lighting, the dimming function of TYN616 thyristor can make it easier for people to adapt to different lighting environments, such as requiring darker lights when reading or watching TV and brighter lights when cooking or cleaning. In addition, it can be integrated with smart home systems to enable higher levels of lighting control, such as automatically adjusting light brightness based on the time of day or room usage. In commercial lighting, TYN616 thyristor can help achieve efficient use of energy. For example, when there are no people in certain areas of a shopping mall or office, the dimming function can automatically turn off or dim the lights, thereby saving energy. At the same time, its dimming function can also make the lighting in the space softer and more comfortable, thereby improving people's work efficiency. In stage lighting, TYN616 thyristor can be used to achieve complex lighting effects. By controlling the speed, brightness and color of lights, you can help create more realistic and engaging performances.
3.Electric heater control: It can be used to control the heating power of the electric heater to achieve temperature control or constant temperature functions. This is common in household appliances such as electric kettles, electric blankets, and ovens.
4.Household appliances: In some household appliances, such as rice cookers, electric stoves, induction cookers, etc., TYN616 can be used to control the power of the heating element in order to adjust the cooking temperature or power.
Ⅲ.Characteristics of TYN616
•Absolute ratings (limiting values)
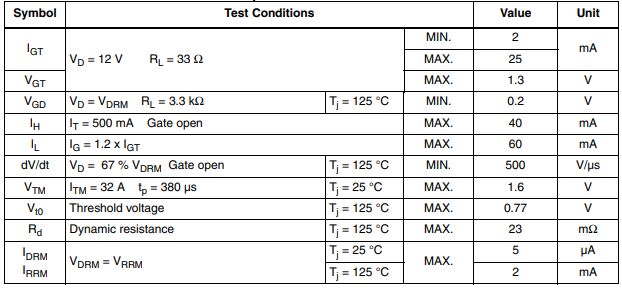
•Electrical characteristics (Tj= 25 °C, unless otherwise specified)
•Thermal resistance

Ⅳ.The working principle of TYN616
1.Structure: TYN616 has three main pins, usually labeled MT1 (Main Terminal 1), MT2 (Main Terminal 2) and G (Gate). MT1 and MT2 are the main current paths, while G is the control pin.
2.Trigger: In order for the TYN616 to conduct current, sufficient trigger current (usually a positive pulse) must be applied to the G pin to activate the device. Triggering the current causes the TRIAC to enter a conductive state, allowing current to flow through MT1 and MT2.
3.Bidirectional conduction: TRIAC is a bidirectional thyristor, which means that it can conduct both directions of alternating current. Its main purpose is to control when the current conducts by controlling the trigger current on the G pin.
4.Shutdown: Once TYN616 is triggered to conduct, it will continue to conduct until the AC current passes zero voltage, and then it will automatically shut down. This is one of the characteristics of TRIAC that makes it suitable for controlling alternating current.
5.Zero crossing control: In order to avoid the desynchronization of voltage and current, TYN616 usually triggers when the AC voltage passes through zero. This helps reduce current and voltage discontinuities, thereby reducing interference and noise.
6.Current control: By controlling the timing and amplitude of the trigger current, the conduction angle of TYN616 can be controlled, thereby controlling the average power of the load connected to it. This allows the load to be dimmed or controlled.
Ⅴ.Trigger mode and control mode of TYN616
1.Trigger method
•Voltage triggering: In some specific applications, voltage triggering can be used. This is done by applying a certain voltage to the G pin to trigger the TYN616. The magnitude and timing of the voltage determines the triggering angle.
•Positive pulse trigger: This is the most common triggering method, which triggers the TYN616 by applying a positive pulse current to the G (Gate) pin. The timing and amplitude of the trigger pulse can be used to control the conduction angle, thereby adjusting the power of the load.
•Negative pulse trigger: Similar to positive pulse trigger, but uses negative pulse current trigger. This can also be used to control the conduction angle, but in a different way.
•Zero-crossing triggering: This triggering method triggers the TRIAC when the voltage crosses the zero point to reduce voltage and current discontinuities. This is great for reducing electromagnetic interference and noise.
2.Control method
•Phase control: Phase control controls the conduction time by changing the firing angle to adjust the average power of the load. This is typically used in dimming applications.
•Unidirectional control: In unidirectional control, the TRIAC can conduct only one direction of current. This works for single phase loads such as most household lighting.
•Bidirectional control: Bidirectional control allows the TRIAC to conduct current in both directions. This applies to two-phase loads such as electric heaters and some motor controls.
•Pulse Width Modulation (PWM): Using PWM control method, the current can be controlled with different pulse widths during the conduction period. This is suitable for applications requiring precise control, such as motor speed control.
Ⅵ.Use TYN616 to control the load
1.Connect the circuit
Connect the MT1 and MT2 pins of the TYN616 to the AC power lines of the power circuit so that current flows through the TYN616. Connect the G (Gate) pin of TYN616 to the control circuit to trigger the TYN616 to turn on.
2.Select triggering method
Select the appropriate trigger method, such as positive pulse trigger or zero crossing trigger, according to specific application requirements. Use a trigger circuit to generate the required trigger signal to trigger the TYN616 to turn on.
3.Control method
Select the control method, such as one-way control or two-way control, according to the load type. If you need to dim the light or control the power of the load, you can use phase control or PWM control.
4.Trigger angle control
Control the trigger angle to adjust the conduction time of TYN616, thereby controlling the average power of the load. An earlier trigger angle will cause more current to pass through, and a later trigger angle will result in less current flow.
5.Protection and security
Include necessary overcurrent protection and overtemperature protection in the circuit to ensure the safe operation of TYN616 and the load. Follow electrical safety standards and recommendations to avoid shock and fire hazards.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.What are the temperature range and environmental characteristics of TYN616?
The TYN616 typically operates over the -40°C to +125°C range. The storage temperature range is generally wider and TYN616 can be stored from -40°C to +150°C. TYN616 is usually affected by electrical noise and EMC, so measures may need to be taken to reduce electromagnetic interference and improve electrical compatibility when designing the circuit.
2.What are the alternative models of TYN616?
NTMFD4C66N,BT137,BT139,MAC97A6
3.What are the pins of TYN616?
MT1 is one of the main current pins of TYN616. It is used to connect the AC power line to the TRIAC so that current can flow through the device. MT2 is the other main current pin of TYN616. It is used to return current to the power supply, forming a complete current path. The G pin is the control pin of TYN616. By applying a trigger signal.